Major Parts of the Brain:
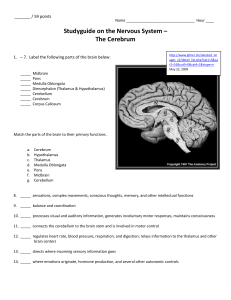
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...
Neuroscience 14b – Organisation of the Cerebral Cortex
... resolution in comparison with MRI. An evoked potential is the electrical response recorded on the EEG to a stimulus. They are often very low in amplitude so in order to distinguish them from things such as background noise, signal averaging is required. This is time locked for the stimulus, and the ...
... resolution in comparison with MRI. An evoked potential is the electrical response recorded on the EEG to a stimulus. They are often very low in amplitude so in order to distinguish them from things such as background noise, signal averaging is required. This is time locked for the stimulus, and the ...
in search of memory traces
... and memory and determine the memory traces involved. In order to do this it is first necessary to find where in the brain the memories are stored, the classical problem of localization. Because learning involves changes in behavior as a result of exposure to stimuli that do not change, there must be ...
... and memory and determine the memory traces involved. In order to do this it is first necessary to find where in the brain the memories are stored, the classical problem of localization. Because learning involves changes in behavior as a result of exposure to stimuli that do not change, there must be ...
Module 5.1 Classical Conditioning
... A. Pavlov accidentally discovered that dogs would salivate to particular sounds in his laboratory, which led him to identify classical conditioning (Figure 5.1) II. Principles of Classical Conditioning (Concept Chart 5.1) A. Pavlov harnessed a dog and placed food (US) on the dog’s tongue and dog sal ...
... A. Pavlov accidentally discovered that dogs would salivate to particular sounds in his laboratory, which led him to identify classical conditioning (Figure 5.1) II. Principles of Classical Conditioning (Concept Chart 5.1) A. Pavlov harnessed a dog and placed food (US) on the dog’s tongue and dog sal ...
classical conditioning
... Discrimination • Producing different responses to two stimuli • The subject learns that one stimuli predicts the UCS and the other does not. ...
... Discrimination • Producing different responses to two stimuli • The subject learns that one stimuli predicts the UCS and the other does not. ...
Neuro 04 Brainstem Student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
Laboratory 9: Pons to Midbrain MCB 163 Fall 2005 Slide #108 1
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
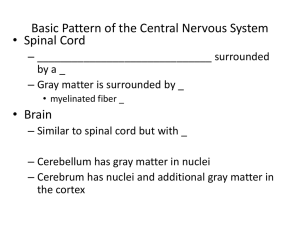
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
... • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
Topic4-Learning
... A NS that has been paired with a UCS to bring about a response formerly caused only by the UCS ...
... A NS that has been paired with a UCS to bring about a response formerly caused only by the UCS ...
Learning - s3.amazonaws.com
... make connections between 2 or more events in the world respond to the effects of personal experiences observation of other people’s experiences ...
... make connections between 2 or more events in the world respond to the effects of personal experiences observation of other people’s experiences ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... primary sensory cortical areas; or to the other set of subnuclei (2), the higher order nuclei, which function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be ...
... primary sensory cortical areas; or to the other set of subnuclei (2), the higher order nuclei, which function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch07use
... The stimulus can become predictable. Desensitization where the effect of the stimulus is dulled by over conditioning. This happens when the S-CR is presented several times. The S-CR is gradual for slightly intense to very intense. ...
... The stimulus can become predictable. Desensitization where the effect of the stimulus is dulled by over conditioning. This happens when the S-CR is presented several times. The S-CR is gradual for slightly intense to very intense. ...
Chapter 6
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
Chapter Outline
... present during the original learning 5. Stimulus discrimination--the ability to distinguish between similar stimuli and to respond only to the one that results in the reinforcer 6. Discriminative stimulus is a signal whether a response will pay off; it is said to exert stimulus control over the resp ...
... present during the original learning 5. Stimulus discrimination--the ability to distinguish between similar stimuli and to respond only to the one that results in the reinforcer 6. Discriminative stimulus is a signal whether a response will pay off; it is said to exert stimulus control over the resp ...
LCog read ch 3
... configural learning: refers to the school of thought which believes multiple stimuli are seen by organisms as a single, complex stimulus. For example, in sensory preconditioning, the two stimuli are presented together before a US is presented. The two stimuli are associated with one another as a s ...
... configural learning: refers to the school of thought which believes multiple stimuli are seen by organisms as a single, complex stimulus. For example, in sensory preconditioning, the two stimuli are presented together before a US is presented. The two stimuli are associated with one another as a s ...
Learning and Classical Conditioning
... radiation or drugs that led to nausea and vomiting (UCR). ...
... radiation or drugs that led to nausea and vomiting (UCR). ...
13 Learning Guided Notes - Appoquinimink High School
... are successively given as the subject gets ___________________to the ultimate behavior goal IE. If the purpose of putting a rat in a _________________ is to teach it to get from Point A to Point B while following a certain ________________ Every time the rat makes a turn towards the ____________ ...
... are successively given as the subject gets ___________________to the ultimate behavior goal IE. If the purpose of putting a rat in a _________________ is to teach it to get from Point A to Point B while following a certain ________________ Every time the rat makes a turn towards the ____________ ...
Visual Brain
... Receptive Fields • Area of receptors that affects firing rate of a given neuron in the circuit • Receptive fields are determined by monitoring single cell responses. • Research example for vision – Stimulus is presented to retina and response of cell is measured by an electrode. ...
... Receptive Fields • Area of receptors that affects firing rate of a given neuron in the circuit • Receptive fields are determined by monitoring single cell responses. • Research example for vision – Stimulus is presented to retina and response of cell is measured by an electrode. ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypothalamus; acts as biological clock o external sues for circadian rhythms, like light; ex: when squirrel is only in light or darkness, their internal clock’s timing is different than normal, so external ...
... o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypothalamus; acts as biological clock o external sues for circadian rhythms, like light; ex: when squirrel is only in light or darkness, their internal clock’s timing is different than normal, so external ...
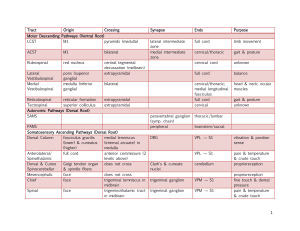
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... cerebellar peduncles: fiber tracts that run through brainstem (trace these) superior: primary output of the cerebellum to red nucleus & thalamus middle: input from the contralateral cerebral cortex via the pons inferior: fibers from ipsilateral spinocerebellar tract (proprioceptive), inferior olives ...
... cerebellar peduncles: fiber tracts that run through brainstem (trace these) superior: primary output of the cerebellum to red nucleus & thalamus middle: input from the contralateral cerebral cortex via the pons inferior: fibers from ipsilateral spinocerebellar tract (proprioceptive), inferior olives ...
AP Psychology
... Describe the adaptive balance between these two phenomena. (see Stimulus Generalization and Discrimination) Describe the role that timing, predictability, and strength of signals play in the speed and strength of conditioned response development. Indicate which type of conditioning produces the stro ...
... Describe the adaptive balance between these two phenomena. (see Stimulus Generalization and Discrimination) Describe the role that timing, predictability, and strength of signals play in the speed and strength of conditioned response development. Indicate which type of conditioning produces the stro ...
Critical terms
... behavior that occurs with no particular goal or purpose other than for the pleasure it provides….and it improves future performance. ...
... behavior that occurs with no particular goal or purpose other than for the pleasure it provides….and it improves future performance. ...
Slide 1
... transduction pathways) of a variety of brain areas associated with arousal (heightened ability to focus), pleasure, and maybe even enhanced learning. GABA (gamma-aminobuteric acid) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and GABA receptors are highly sensitized by ethanol leading to st ...
... transduction pathways) of a variety of brain areas associated with arousal (heightened ability to focus), pleasure, and maybe even enhanced learning. GABA (gamma-aminobuteric acid) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and GABA receptors are highly sensitized by ethanol leading to st ...