operant conditioning of feeding behavior in aplysia
... animals underwent surgical and handling procedures that were identical to the other groups, but the Control group did not receive any nerve stimulation. The conditioning was evaluated by counting the number of bites during a 5 min observation period. The observation period either immediately followe ...
... animals underwent surgical and handling procedures that were identical to the other groups, but the Control group did not receive any nerve stimulation. The conditioning was evaluated by counting the number of bites during a 5 min observation period. The observation period either immediately followe ...
Practice Test Questions over Learning Notes
... B. Neutral Stimulus (NS) D. None of the above 3. Which of the following occurs when the conditioned stimulus (CS) no longer produces a response, therefore, it returns to being a neutral stimulus (NS)? A. Acquisition B. Emotion C. Extinction D. Generalization 4. ___________ is when the conditioned st ...
... B. Neutral Stimulus (NS) D. None of the above 3. Which of the following occurs when the conditioned stimulus (CS) no longer produces a response, therefore, it returns to being a neutral stimulus (NS)? A. Acquisition B. Emotion C. Extinction D. Generalization 4. ___________ is when the conditioned st ...
neuro 04 brainstem student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Fall 2015 10-6 Chapter 7 Pt 1
... The diminished (weakened) responding that occurs when the conditioned stimulus no longer signals an upcoming unconditioned stimulus ...
... The diminished (weakened) responding that occurs when the conditioned stimulus no longer signals an upcoming unconditioned stimulus ...
File - Mr. Treska`s Class
... • Repeat trials at 10- to 15-second intervals, with a test trial after every 10 conditioning trials. • After each test trial ask for a show of hands of those who salivated. • When all or most of the students have demonstrated conditioning, begin extinction using the same test-trial procedure (in whi ...
... • Repeat trials at 10- to 15-second intervals, with a test trial after every 10 conditioning trials. • After each test trial ask for a show of hands of those who salivated. • When all or most of the students have demonstrated conditioning, begin extinction using the same test-trial procedure (in whi ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Paired, egg-shaped masses that form the superolateral walls of the third ventricle Connected at the midline by the intermediate mass Contains four groups of nuclei – anterior, ventral, dorsal, and posterior Nuclei project and receive fibers from the cerebral cortex Thalamus Thalamic Function Afferen ...
... Paired, egg-shaped masses that form the superolateral walls of the third ventricle Connected at the midline by the intermediate mass Contains four groups of nuclei – anterior, ventral, dorsal, and posterior Nuclei project and receive fibers from the cerebral cortex Thalamus Thalamic Function Afferen ...
Applications of Classical Conditioning
... The diminished (weakened) responding that occurs when the conditioned stimulus no longer signals an upcoming unconditioned stimulus ...
... The diminished (weakened) responding that occurs when the conditioned stimulus no longer signals an upcoming unconditioned stimulus ...
Classical Conditioning
... species – Only overt behaviors can be reinforced by the environment – Principle of the selection is based in the behavioral discrepancy ...
... species – Only overt behaviors can be reinforced by the environment – Principle of the selection is based in the behavioral discrepancy ...
Learning
... in classical conditioning, the ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal and UCS in operant conditioning, responding differently to stimuli that signal a behavior will be reinforced or will not be reinforced ...
... in classical conditioning, the ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal and UCS in operant conditioning, responding differently to stimuli that signal a behavior will be reinforced or will not be reinforced ...
Learning
... • This is passive learning (automatic…learner does NOT have to think). • Unconditional Stimulus (UCS)- something that elicits a natural, reflexive response. • Unconditional Response (UCR)- response to the UCS. ...
... • This is passive learning (automatic…learner does NOT have to think). • Unconditional Stimulus (UCS)- something that elicits a natural, reflexive response. • Unconditional Response (UCR)- response to the UCS. ...
Neuroscience 14a – Introduction to Consciousness
... number of different nuclei which perform 3 main tasks: o Cholinergic projections excite the individual thalamic relay nuclei which lead to activation of the cerebral cortex. o Cholinergic projections to the intralaminar nuclei, which in turn project to all areas of the cortex . o Cholinergic project ...
... number of different nuclei which perform 3 main tasks: o Cholinergic projections excite the individual thalamic relay nuclei which lead to activation of the cerebral cortex. o Cholinergic projections to the intralaminar nuclei, which in turn project to all areas of the cortex . o Cholinergic project ...
Chapter 5 - Angelfire
... • Ex: Dogs salivate naturally when they are fed • In his study, Pavlov taught dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell that signaled that food was coming • Often involves reflexive behavior( a relatively simple, unlearned behavior governed by the nervous system, that occurs automatically when the app ...
... • Ex: Dogs salivate naturally when they are fed • In his study, Pavlov taught dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell that signaled that food was coming • Often involves reflexive behavior( a relatively simple, unlearned behavior governed by the nervous system, that occurs automatically when the app ...
Rexed`s Lamina
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
... Cerebral aqueduct – Old term: Aqueduct of Sylvius ...
... Cerebral aqueduct – Old term: Aqueduct of Sylvius ...
N.L. Strominger et al. Cerebellum, in Noback`s Human
... layer of origin. Although unipolar brush cells also are excitatory, their axons are restricted to the granular layer, where they increase the excitation upon granule cells. The Golgi, Purkinje, stellate, and basket cells are inhibitory neurons, whose neurotransmitter is GABA. They act as modulators. ...
... layer of origin. Although unipolar brush cells also are excitatory, their axons are restricted to the granular layer, where they increase the excitation upon granule cells. The Golgi, Purkinje, stellate, and basket cells are inhibitory neurons, whose neurotransmitter is GABA. They act as modulators. ...
Learning File - Eastern Mediterranean University Open CourseWares
... Punishment usually allows the quickest way to modify behavior that might be dangerous to an individual if allowed to continue. (e.g. child running towards a busy street) ...
... Punishment usually allows the quickest way to modify behavior that might be dangerous to an individual if allowed to continue. (e.g. child running towards a busy street) ...
Lecture 6
... the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative thinking?). Frontal area important for short term working memory, and plann ...
... the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative thinking?). Frontal area important for short term working memory, and plann ...
Learning Habituation Mere Exposure Effect Behavioral Learning
... Stimuli such as money or tokens, that acquire the Reinforcement programs by which the number of reinforcing power by a learned association with responses required for a reinforcement varies from ...
... Stimuli such as money or tokens, that acquire the Reinforcement programs by which the number of reinforcing power by a learned association with responses required for a reinforcement varies from ...
CHAPTER 6: LEARNING
... Chapter 6 LEARNING Section 1: Classical Conditioning Section 2: Operant Conditioning ...
... Chapter 6 LEARNING Section 1: Classical Conditioning Section 2: Operant Conditioning ...
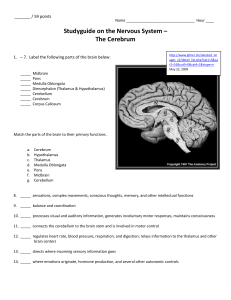
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...