Renaissance Unit Vocabulary List Word Definition or Associated
... Trade route between Europe & China “Renaissance Person who is wellMan” (440) rounded (good at a lot of things) Patrons Person who supported artists Perspective Drawing in 3D Vernacular Marco Polo ...
... Trade route between Europe & China “Renaissance Person who is wellMan” (440) rounded (good at a lot of things) Patrons Person who supported artists Perspective Drawing in 3D Vernacular Marco Polo ...
Note Taking Studyguidechapter13section1answers
... 2. Italy’s location on the Mediterranean Sea also encouraged trade with the Muslim world. 3. Trade routes carried new ideas that were important in shaping the Renaissance. B. Italy’s Vibrant City States 1. Italy was divided into many small city-states 2. The Medici Family, from Florence, were amongs ...
... 2. Italy’s location on the Mediterranean Sea also encouraged trade with the Muslim world. 3. Trade routes carried new ideas that were important in shaping the Renaissance. B. Italy’s Vibrant City States 1. Italy was divided into many small city-states 2. The Medici Family, from Florence, were amongs ...
Chapter 10 Study Guide The Renaissance i
... 51. Which eighteen foot statue is a perfect example of Renaissance harmony, symmetry, and proportion? 52. Who was commissioned to paint the Vatican’s Sistine Chapel? Italy’s Political Decline: The French Invasions 53. Which treaty included Venice despite the anger of the Papal States? 54. Which cou ...
... 51. Which eighteen foot statue is a perfect example of Renaissance harmony, symmetry, and proportion? 52. Who was commissioned to paint the Vatican’s Sistine Chapel? Italy’s Political Decline: The French Invasions 53. Which treaty included Venice despite the anger of the Papal States? 54. Which cou ...
Slide 1
... •More people began to read (The Bible was a popular book) •After reading the Bible, people formed new ideas about Christianity (these ideas were different from official Church teachings ...
... •More people began to read (The Bible was a popular book) •After reading the Bible, people formed new ideas about Christianity (these ideas were different from official Church teachings ...
Chapter 11, Lesson 2 New Ideas and Art
... • Geoffrey Chaucer wrote The Canterbury Tales in English • Stories about people making a religious journey • Includes people from all classes of society • Modern English comes from vernacular form used by Chaucer ...
... • Geoffrey Chaucer wrote The Canterbury Tales in English • Stories about people making a religious journey • Includes people from all classes of society • Modern English comes from vernacular form used by Chaucer ...
Chapter 13 Lesson 2: The Italian Renaissance
... to gain and hold power. – Famous for “It’s better to be feared than loved” ...
... to gain and hold power. – Famous for “It’s better to be feared than loved” ...
The Renaissance
... • When Constantinople fell to the Muslim Turks in 1453, Byzantine Christians fled to the West • These refugees brought with them classical scholarship that had originally been lost to the West • Medieval artists who originally strove to suggest strong spiritual characters started exploring ways to s ...
... • When Constantinople fell to the Muslim Turks in 1453, Byzantine Christians fled to the West • These refugees brought with them classical scholarship that had originally been lost to the West • Medieval artists who originally strove to suggest strong spiritual characters started exploring ways to s ...
5 Themes of the Renaissance
... Our destiny is not determined by anything outside of us. God has bestowed upon us a unique distinction: the liberty to determine the form and value our lives shall acquire….man is the master of his own destiny! ...
... Our destiny is not determined by anything outside of us. God has bestowed upon us a unique distinction: the liberty to determine the form and value our lives shall acquire….man is the master of his own destiny! ...
The Renaissance
... • Location: Italy, where the Renaissance began was literally littered with the remnants of ancient Rome: buildings, aqueducts that still work, sculptures, and monuments. ...
... • Location: Italy, where the Renaissance began was literally littered with the remnants of ancient Rome: buildings, aqueducts that still work, sculptures, and monuments. ...
Music: An Appreciation by Roger Kamien
... The interval of a tritone (3 whole steps) This interval was banned by the church in the end of the Middle Ages. ...
... The interval of a tritone (3 whole steps) This interval was banned by the church in the end of the Middle Ages. ...
No Slide Title
... language like English, Spanish, German, etc… Printing in vernacular allowed more people to read and understand books. ...
... language like English, Spanish, German, etc… Printing in vernacular allowed more people to read and understand books. ...
Renaissance Art
... Renaissance writers produced works that reflected their time. Some wrote in the vernacular. In addition, Renaissance writers wrote either for self-expression or to portray the individuality of their subjects. ...
... Renaissance writers produced works that reflected their time. Some wrote in the vernacular. In addition, Renaissance writers wrote either for self-expression or to portray the individuality of their subjects. ...
Renaissance
... • •More wealth=more influence • •Promoted education and understanding of the world ...
... • •More wealth=more influence • •Promoted education and understanding of the world ...
1. new interest in the classics = politics, art
... “For a man who, in all respects, will carry out only his professions of good, will be apt to be ruined amongst so many who are evil. A prince therefore who desires to maintain himself must learn to be not always good, but to be so or not as necessity may require. It is much more safe to be feared t ...
... “For a man who, in all respects, will carry out only his professions of good, will be apt to be ruined amongst so many who are evil. A prince therefore who desires to maintain himself must learn to be not always good, but to be so or not as necessity may require. It is much more safe to be feared t ...
Chapter 16: Renaissance and Reformation
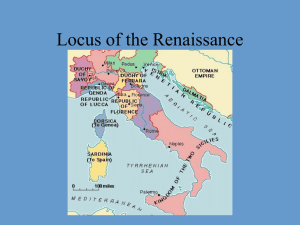
... 3. Where did the Renaissance begin? City-states of Italy 4. What city-state was the birthplace of the Renaissance? Florence Renaissance Art Be able to identify the following artist and their works: 1. Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa. Proportions of the Human Figure, The Last Supper 2. Raphael School of ...
... 3. Where did the Renaissance begin? City-states of Italy 4. What city-state was the birthplace of the Renaissance? Florence Renaissance Art Be able to identify the following artist and their works: 1. Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa. Proportions of the Human Figure, The Last Supper 2. Raphael School of ...
European renaissance and reformation
... During the Middle Ages people showed devotion to God by wearing rough clothing and eating plain foods Renaissance thought people could enjoy life and still serve God Material luxuries such as expensive clothing, good music, and fine foods. Spirit of Renaissance was secular- worldly not spiritu ...
... During the Middle Ages people showed devotion to God by wearing rough clothing and eating plain foods Renaissance thought people could enjoy life and still serve God Material luxuries such as expensive clothing, good music, and fine foods. Spirit of Renaissance was secular- worldly not spiritu ...
Chp 12
... and architects change over the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries? • What is the purpose of applying linear perspective to painting? • What were the differences in the ways painters in Italian cities and those in Flanders achieved depth and dimension in their work? • How did the scholarly interests ...
... and architects change over the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries? • What is the purpose of applying linear perspective to painting? • What were the differences in the ways painters in Italian cities and those in Flanders achieved depth and dimension in their work? • How did the scholarly interests ...
The Renaissance - HISTORY APPRECIATION
... world and that turned inward - lay, as it were, beneath a common veil, dreaming or half awake. The veil was woven of faith, childlike prejudices, and illusion; seen through it, world and history appeared in strange hues; man recognized himself only as a member of a race, a nation, a party, a corpora ...
... world and that turned inward - lay, as it were, beneath a common veil, dreaming or half awake. The veil was woven of faith, childlike prejudices, and illusion; seen through it, world and history appeared in strange hues; man recognized himself only as a member of a race, a nation, a party, a corpora ...
Chapter 1 Section 1
... – Society placed a new emphasis on individual achievement – Renaissance Ideal was a person with a wide variety of talent in different areas ...
... – Society placed a new emphasis on individual achievement – Renaissance Ideal was a person with a wide variety of talent in different areas ...
CHAPTER 5
... second development was the investigation of movement and human anatomy. The realistic portrayal of the individual person, especially the human nude, became one of the chief aims of Italian Renaissance art. (pages 166-167) ...
... second development was the investigation of movement and human anatomy. The realistic portrayal of the individual person, especially the human nude, became one of the chief aims of Italian Renaissance art. (pages 166-167) ...
Renaissance Guided Notes
... Renaissance ideas still influence modern thought Led to the Reformation & creation of new religions Why Italy? City States Begins in Italy and spreads North Urban unlike the rest of Europe Merchants Merchants dominated politics Belief in individual achievement The Medici Ruling family of ___________ ...
... Renaissance ideas still influence modern thought Led to the Reformation & creation of new religions Why Italy? City States Begins in Italy and spreads North Urban unlike the rest of Europe Merchants Merchants dominated politics Belief in individual achievement The Medici Ruling family of ___________ ...
he word "Renaissance" is a French word that means “rebirth
... _________________, or_________________, outlook due to the discovery of the “New World” and new contact with the ancient civilizations further _____________. Renaissance intellectuals, Sir Thomas More and ______________ of Rotterdam had a growing _______________ in individual __________________ ____ ...
... _________________, or_________________, outlook due to the discovery of the “New World” and new contact with the ancient civilizations further _____________. Renaissance intellectuals, Sir Thomas More and ______________ of Rotterdam had a growing _______________ in individual __________________ ____ ...
The Renaissance
... growth of the arts and learning The Renaissance was an age of recovery from the disasters of the 14th century, such as the plague, political instability, and a decline of Church power Recovery went hand-in-hand with a rebirth of interest in ancient culture (e.g., ancient Greece and Rome) A new ...
... growth of the arts and learning The Renaissance was an age of recovery from the disasters of the 14th century, such as the plague, political instability, and a decline of Church power Recovery went hand-in-hand with a rebirth of interest in ancient culture (e.g., ancient Greece and Rome) A new ...
Renaissance
... -angry about the selling of indulgence$ -an indulgence was a way to pay $$ to be released from the punishment due to a sin -nailed his 95 theses to the church door -started Protestant Reformation -encouraged Catholics to reform their own church ...
... -angry about the selling of indulgence$ -an indulgence was a way to pay $$ to be released from the punishment due to a sin -nailed his 95 theses to the church door -started Protestant Reformation -encouraged Catholics to reform their own church ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.