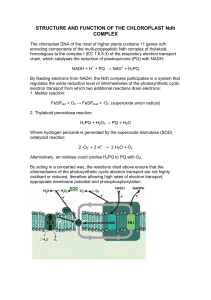
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CHLOROPLAST Ndh
... intermediaries of the photosynthetic cyclic electron transport are not highly oxidised or reduced, therefore allowing high rates of electron transport, appropriate membrane potential and photophosphorylation. ...
... intermediaries of the photosynthetic cyclic electron transport are not highly oxidised or reduced, therefore allowing high rates of electron transport, appropriate membrane potential and photophosphorylation. ...
REVIEW FOR TEST 3: ENERGETICS
... a. know the balanced equation b. know the stages and the location of where they take place c. for glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate and citric acid cycle: 1. list the reactants and products of each stage 2. identify it as an aerobic or anaerobic process ...
... a. know the balanced equation b. know the stages and the location of where they take place c. for glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate and citric acid cycle: 1. list the reactants and products of each stage 2. identify it as an aerobic or anaerobic process ...
Protein Folding and Membrane Structure
... implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
... implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
Puzzle - UBC Blogs
... 1 membranous structure within chloroplast 5 pigment found in chloroplast that can be part of the antennal complex of a photosystem 7 ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate 9 organelle in which photosynthesis occurs 13 source of energy and reducing power 15 Crassulacean acid metabolism 16 spectrum of light waves ...
... 1 membranous structure within chloroplast 5 pigment found in chloroplast that can be part of the antennal complex of a photosystem 7 ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate 9 organelle in which photosynthesis occurs 13 source of energy and reducing power 15 Crassulacean acid metabolism 16 spectrum of light waves ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... Step I: Light Dependent Reactions Photosystem II • The Electron Transport Chain is located within the thylakoid membrane • H+ diffuses thru ATP synthase and this combines ADP + P to make _________ . Photosystem I • Another photon hits chlorophyll releasing energy • This energy (e-) and the H+ from ...
... Step I: Light Dependent Reactions Photosystem II • The Electron Transport Chain is located within the thylakoid membrane • H+ diffuses thru ATP synthase and this combines ADP + P to make _________ . Photosystem I • Another photon hits chlorophyll releasing energy • This energy (e-) and the H+ from ...
Chapter 7 Reading Guide
... Use the information in Chapter 7 (p.125-139) as well as the Bozeman podcasts on the Cell Membrane and Transport Across Cell Membranes to complete the reading guide. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why thes ...
... Use the information in Chapter 7 (p.125-139) as well as the Bozeman podcasts on the Cell Membrane and Transport Across Cell Membranes to complete the reading guide. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why thes ...
2. a) Protein channels help to move material across the cell
... 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways throughout the membrane. That means the membrane is not solid, but more like a 'fluid'. The membrane is depicted as mosaic because like a mosaic that is made up of many di ...
... 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways throughout the membrane. That means the membrane is not solid, but more like a 'fluid'. The membrane is depicted as mosaic because like a mosaic that is made up of many di ...
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
... Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by complex envelope layers that differ in composition among the major groups. These structures protect the organisms from hostile environments, such as extreme osmolarity, harsh chemicals, and even antibiotics. ...
... Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by complex envelope layers that differ in composition among the major groups. These structures protect the organisms from hostile environments, such as extreme osmolarity, harsh chemicals, and even antibiotics. ...
bioch8 - Otterville R
... Because of photorespiration, plants have special adaptations to limit the effect of photorespiration: 1. C4 plants 2. CAM plants ...
... Because of photorespiration, plants have special adaptations to limit the effect of photorespiration: 1. C4 plants 2. CAM plants ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... potential energy of the hydrogen concentration is used in the ATP synthase molecule to form ATP. Very similar to the ETC in cellular respiration. 5. What happens in Photosystem I? Pigments in the antenna complex absorb photons and pass the energy to the photosystem I reaction center. Electrons are e ...
... potential energy of the hydrogen concentration is used in the ATP synthase molecule to form ATP. Very similar to the ETC in cellular respiration. 5. What happens in Photosystem I? Pigments in the antenna complex absorb photons and pass the energy to the photosystem I reaction center. Electrons are e ...
chapter 7 membranes
... across a membrane, ex. Na-K pump which exchanges 3 Na+ for 2 K+ is major electrogenic pump of animal cells. Proton pump is main electrogenic pump of plants, bacteria, and fungi which actively transports H+ out of cell. By generating voltage across membranes, electrogenic pumps store energy that can ...
... across a membrane, ex. Na-K pump which exchanges 3 Na+ for 2 K+ is major electrogenic pump of animal cells. Proton pump is main electrogenic pump of plants, bacteria, and fungi which actively transports H+ out of cell. By generating voltage across membranes, electrogenic pumps store energy that can ...
051607
... – Lateral diffusion is easy (in general) – Transverse diffusion (flip-flop) is slow (sans catalysis) – Integral/peripheral membrane proteins – Membrane asymmetry/modification of fluidity • Inner/outer leaflets different lipids • Lipid rafts: keep multiprotein complexes together • Intracellular ‘anch ...
... – Lateral diffusion is easy (in general) – Transverse diffusion (flip-flop) is slow (sans catalysis) – Integral/peripheral membrane proteins – Membrane asymmetry/modification of fluidity • Inner/outer leaflets different lipids • Lipid rafts: keep multiprotein complexes together • Intracellular ‘anch ...
Study Guide for Membranes and Transport
... give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids compare and contrast the function of carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
... give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids compare and contrast the function of carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
Waiting for the sun to come out: How photosynthesis adapts to
... responsible for converting carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. During photosynthesis in green plants, NADPH is synthesized by the enzyme FNR (Ferredoxin-NADP(H)-Oxidoreductase) in the socalled stroma, the central compartment of the chloroplast. In their publication the scientists show that, by intera ...
... responsible for converting carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. During photosynthesis in green plants, NADPH is synthesized by the enzyme FNR (Ferredoxin-NADP(H)-Oxidoreductase) in the socalled stroma, the central compartment of the chloroplast. In their publication the scientists show that, by intera ...
Organelle Membrane Bound Description/Function Plant/ Animal
... Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Double membranes with thylakoids; takes energy from the sun and makes food (photosynthesis) Membrane bound and used for storage of wastes, food, organic molecules and water (esp. in plants) Membranes full of enzymes; used to digest orga ...
... Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Double membranes with thylakoids; takes energy from the sun and makes food (photosynthesis) Membrane bound and used for storage of wastes, food, organic molecules and water (esp. in plants) Membranes full of enzymes; used to digest orga ...
Introduction to Photosynthesis
... • Fermentation produces organic compounds (alcohol and lactic acid) and occurs in the absence of oxygen ...
... • Fermentation produces organic compounds (alcohol and lactic acid) and occurs in the absence of oxygen ...
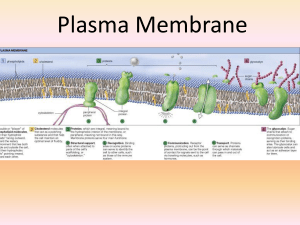
Plasma Membrane
... 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
... 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
Handout
... Only PS I is involved: the reaction center is P700. Electrons travels in a cyclic manner: electrons travel back to PS I. Only ATP is produced without NADPH and oxygen. This system is predominant in bacteria. ...
... Only PS I is involved: the reaction center is P700. Electrons travels in a cyclic manner: electrons travel back to PS I. Only ATP is produced without NADPH and oxygen. This system is predominant in bacteria. ...
Organelles and specialized structures
... energy and use it to make glucose. (T/F) 7. Basal bodies are used wherever a flagella or cilia attaches to the cell membrane. (T/F) 8. The nucleolus of the cell is where nuclear protein synthesis is occurring. (T/F) 9. Proteins and RNA must pass through a nuclear pore when entering or leaving the nu ...
... energy and use it to make glucose. (T/F) 7. Basal bodies are used wherever a flagella or cilia attaches to the cell membrane. (T/F) 8. The nucleolus of the cell is where nuclear protein synthesis is occurring. (T/F) 9. Proteins and RNA must pass through a nuclear pore when entering or leaving the nu ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... cytoplasmic or luminal membrane faces. The extent of exposure on each side of the membrane may vary substantially from one protein to another. Peripheral membrane proteins (b and c) may interact with the exposed portions of integral membrane proteins and are associated with the membrane only by virt ...
... cytoplasmic or luminal membrane faces. The extent of exposure on each side of the membrane may vary substantially from one protein to another. Peripheral membrane proteins (b and c) may interact with the exposed portions of integral membrane proteins and are associated with the membrane only by virt ...
Photosynthesis- is the process that converts light energy into
... Chloroplasts have 3 membranes. The outer 2 are smooth and the inner one makes stacks of thylakoids which is a granum. The chlorophyll and other pigments are found inside the thylakoid membrane. They have the ability to convert light energy into chemical energy. A stack of thylakoids is called a gra ...
... Chloroplasts have 3 membranes. The outer 2 are smooth and the inner one makes stacks of thylakoids which is a granum. The chlorophyll and other pigments are found inside the thylakoid membrane. They have the ability to convert light energy into chemical energy. A stack of thylakoids is called a gra ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.