Slide 1
... •contained in the cytosol, a gelatin like fluid containing ions, and organic molecules ...
... •contained in the cytosol, a gelatin like fluid containing ions, and organic molecules ...
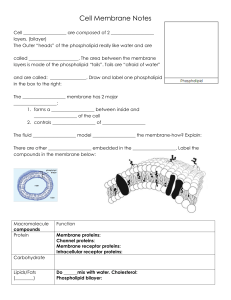
Cell Membrane Notes
... called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ________________. Draw and label one phospholipid in the box to the right: The ___________________ membrane has 2 major ___________________: 1. forms a ...
... called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ________________. Draw and label one phospholipid in the box to the right: The ___________________ membrane has 2 major ___________________: 1. forms a ...
1.17 * Energy Flow and Photosynthesis
... Autotrophs – an organism (such as a plant) that obtains energy directly from light • they make their own food Heterotrophs – an organism (such as an animal) that obtains energy by eating other organisms • they can’t make their own food ...
... Autotrophs – an organism (such as a plant) that obtains energy directly from light • they make their own food Heterotrophs – an organism (such as an animal) that obtains energy by eating other organisms • they can’t make their own food ...
Biozentrum: Research group Martin Spiess
... Membrane transport to the cell surface Proteins are sorted between organelles and transported in membrane vesicles. Our research focuses on the molecules and mechanisms that mediate this. In particular, we study the pathways how proteins are transported to the cell surface and secreted. ...
... Membrane transport to the cell surface Proteins are sorted between organelles and transported in membrane vesicles. Our research focuses on the molecules and mechanisms that mediate this. In particular, we study the pathways how proteins are transported to the cell surface and secreted. ...
CELLS QQ#2 (TOC#4) HW: CELLS Notes (TOC#5)
... blocks of proteins? Why is the rough ER crucial to cell ...
... blocks of proteins? Why is the rough ER crucial to cell ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
8.3 122-125
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
Name
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
The Light-Dependent Reactions: Generating ATP
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
Bio 8.3 HW Process of PS
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
Exam practice answers 5
... Therefore, more energy is available for photosynthesis. (d) They contain a number of different pigments, particularly those that can absorb the wavelengths of light that penetrates to greater depth in the water — that is blue light. Red pigments absorb blue light. A range of pigments including red a ...
... Therefore, more energy is available for photosynthesis. (d) They contain a number of different pigments, particularly those that can absorb the wavelengths of light that penetrates to greater depth in the water — that is blue light. Red pigments absorb blue light. A range of pigments including red a ...
1 Two ATP molecules each give a phosphate group to a glucose
... leave the chlorophyll molecule As a result the chlorophyll molecule becomes ionised – photoionisation Electrons are passed along a number of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions The electrons lose energy at each stage and some of this energy is used to move H+ ions (protons ...
... leave the chlorophyll molecule As a result the chlorophyll molecule becomes ionised – photoionisation Electrons are passed along a number of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions The electrons lose energy at each stage and some of this energy is used to move H+ ions (protons ...
GOLGI APPARATUS
... ON MEMBRANES LYSOSOMES - MEMBRANE-BOUND SAC OF ENZYMES - CELL USES LYS. TO DIGEST MACROMOLECULES - pH OF THE INSIDE IS USUALLY AROUND 5 - LYS. PUMPS H+ IONS FROM THE CYTOSOL INTO THE INSIDE ...
... ON MEMBRANES LYSOSOMES - MEMBRANE-BOUND SAC OF ENZYMES - CELL USES LYS. TO DIGEST MACROMOLECULES - pH OF THE INSIDE IS USUALLY AROUND 5 - LYS. PUMPS H+ IONS FROM THE CYTOSOL INTO THE INSIDE ...
The Cell Membrane 2015
... charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across t ...
... charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across t ...
Active Transport
... Energy is required because molecules are being pumped against their concentration gradient Proteins that work as pumps are called protein pumps. These protein pumps are membrane bound receptors. ...
... Energy is required because molecules are being pumped against their concentration gradient Proteins that work as pumps are called protein pumps. These protein pumps are membrane bound receptors. ...
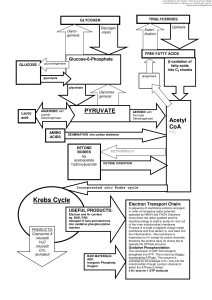
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria containing a single chromosome and no membrane-bound organelles or nuclear envelope. Gram negative bacteria have two membranes – an inner and an outer. ...
... Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria containing a single chromosome and no membrane-bound organelles or nuclear envelope. Gram negative bacteria have two membranes – an inner and an outer. ...
BIO STUDY GUIDE - Biochemistry and Cells
... 29. balance equations (simple … matter can not be created or destroyed but it may be rearranged). 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What tests are used to identify the following: -monosaccharides -polysaccharide – plant starch - proteins – turn yellow -proteins – turn purple -fats 33 ...
... 29. balance equations (simple … matter can not be created or destroyed but it may be rearranged). 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What tests are used to identify the following: -monosaccharides -polysaccharide – plant starch - proteins – turn yellow -proteins – turn purple -fats 33 ...
How Do Molecules Cross the Plasma Membrane? 1. Indicate the
... 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
... 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
Chloroplast
... 1. Amyloplasts are pigment free, store starch grains. Chromoplasts have no chlorophyll, have abundance of carotenoids, colours attract animals. Chloroplasts are specialized organelles for photosynthesis, contain chlorophyll. ...
... 1. Amyloplasts are pigment free, store starch grains. Chromoplasts have no chlorophyll, have abundance of carotenoids, colours attract animals. Chloroplasts are specialized organelles for photosynthesis, contain chlorophyll. ...
Oct_7
... Ions need to lose hydration [ ions associated with a lot of water molecules…it’s hard to transport such a big molecule] [any thing with a high charge in an aqueous environment has reacted with water..we talked about this last class as well] ...
... Ions need to lose hydration [ ions associated with a lot of water molecules…it’s hard to transport such a big molecule] [any thing with a high charge in an aqueous environment has reacted with water..we talked about this last class as well] ...
Structure and Function of Membranes
... What you need to know! • Why membranes are selectively permeable. • The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. ...
... What you need to know! • Why membranes are selectively permeable. • The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.