Photosynthesis - Streetsboro City Schools
... photosynthetic organisms; captures light energy Photosynthesis- process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as glucose NADP+ - one of the carrier molecules that transfers high-energy electrons fr ...
... photosynthetic organisms; captures light energy Photosynthesis- process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as glucose NADP+ - one of the carrier molecules that transfers high-energy electrons fr ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
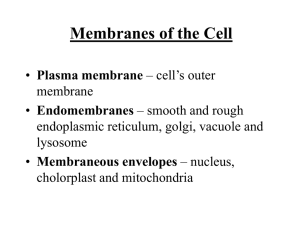
... • Plasma membrane – cell’s outer membrane • Endomembranes – smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
... • Plasma membrane – cell’s outer membrane • Endomembranes – smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
Photosynthesis
... • Powers ATP synthesis • Takes place across the thylakoid membrane • Uses ETC and ATP synthase (enzyme) • H+ move down their concentration gradient through channels of ATP synthase forming ATP from ADP ...
... • Powers ATP synthesis • Takes place across the thylakoid membrane • Uses ETC and ATP synthase (enzyme) • H+ move down their concentration gradient through channels of ATP synthase forming ATP from ADP ...
Biochemical and molecular-genetic methods of the study of
... The crucial components of the photosynthetic apparatus of plants, algae and cyanobacteria are thylakoid membrane embedded pigment-protein complexes, so called photosystems. They capture light energy and mediate its conversion into the energy of chemical bonds. The key component of this intricate mac ...
... The crucial components of the photosynthetic apparatus of plants, algae and cyanobacteria are thylakoid membrane embedded pigment-protein complexes, so called photosystems. They capture light energy and mediate its conversion into the energy of chemical bonds. The key component of this intricate mac ...
Diagrams to Review 1
... increase the SA/Vol ratio The surface area to volume ratio increases with smaller size ...
... increase the SA/Vol ratio The surface area to volume ratio increases with smaller size ...
Slide 1
... electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer compartment between the outer and inner membrane of the mitochond ...
... electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer compartment between the outer and inner membrane of the mitochond ...
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions
... o Reactions of photosynthesis use reactions that function between 0 and 35 degrees Celsius o Higher light intensity= higher rate of photosynthesis There is however, a maximum rate of photosynthesis o Shortage of water can slow photosynthesis and damage plant tissues Some plants in desert areas h ...
... o Reactions of photosynthesis use reactions that function between 0 and 35 degrees Celsius o Higher light intensity= higher rate of photosynthesis There is however, a maximum rate of photosynthesis o Shortage of water can slow photosynthesis and damage plant tissues Some plants in desert areas h ...
Name
... d. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste. _____ 2. Look at Figure 8–1. All of the following are parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT a. structure A. b. structure B. c. structure C. d. structure D. _____ 3. What happens during photosynthesis? a. Heterotrophs consume ATP. b. Heterotrophs produce ATP. ...
... d. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste. _____ 2. Look at Figure 8–1. All of the following are parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT a. structure A. b. structure B. c. structure C. d. structure D. _____ 3. What happens during photosynthesis? a. Heterotrophs consume ATP. b. Heterotrophs produce ATP. ...
Document
... Are about 1µm in diameter and 1-10 µm in length. Are dynamic structure that move, change their shapes and divide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Are about 1µm in diameter and 1-10 µm in length. Are dynamic structure that move, change their shapes and divide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis_student version
... Hot, dry climates plants continue photosynthesis while conserving water ...
... Hot, dry climates plants continue photosynthesis while conserving water ...
3D Visualization of Thylakoid Membrane
... essential for all photosynthetic plant cells. As germinating seedlings are exposed to light, etioplasts in young mesophyll cells become chloroplasts in the developing seedling. The chloroplast thylakoids develop from a paracrystalline tubular structure that is transformed when illuminated into a ser ...
... essential for all photosynthetic plant cells. As germinating seedlings are exposed to light, etioplasts in young mesophyll cells become chloroplasts in the developing seedling. The chloroplast thylakoids develop from a paracrystalline tubular structure that is transformed when illuminated into a ser ...
Quizon ch5-6-7-8new.doc
... e. Both the c and d are correct. 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are called: a. enzymes. b. coenzymes. c. reaction cofactors. d. substrates. e. reactants 3. A final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an early enzyme in the pathway. This is likely to be an exa ...
... e. Both the c and d are correct. 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are called: a. enzymes. b. coenzymes. c. reaction cofactors. d. substrates. e. reactants 3. A final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an early enzyme in the pathway. This is likely to be an exa ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
... chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar (glucose) from carbon dioxide 1i – In the mitochondria and chloroplasts energy from electrons is stored for ATP production (Chemiosmosis) ...
... chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar (glucose) from carbon dioxide 1i – In the mitochondria and chloroplasts energy from electrons is stored for ATP production (Chemiosmosis) ...
DiscBio: C9 Voc Definitions
... 19. metabolic pathway; 20 metabolism; 21 mitochondrion; 22 NADH; 23 NADPH; 24 oxidative phosphorylation; 25 photosynthesis; 26 photosystem; 27 photosystem I; 28 photosystem II; 29 producer; 30 proton gradient; 31 pyruvate; 32 reaction center; 33 rubisco; 34 stoma; 35 stroma; 36 thylakoid 1. oxygen-d ...
... 19. metabolic pathway; 20 metabolism; 21 mitochondrion; 22 NADH; 23 NADPH; 24 oxidative phosphorylation; 25 photosynthesis; 26 photosystem; 27 photosystem I; 28 photosystem II; 29 producer; 30 proton gradient; 31 pyruvate; 32 reaction center; 33 rubisco; 34 stoma; 35 stroma; 36 thylakoid 1. oxygen-d ...
chl - Govt College Aron
... autumn leaves. Chloroplasts: (Chloro= green) Chlorophyll-containing plastids which are the sites of photosynthesis •Found in eukaryotic algae, leaves and other green plant organs •Are lens-shaped and measure about 2µm by 5µm •Are dynamic structures that change shape, move and divide. ...
... autumn leaves. Chloroplasts: (Chloro= green) Chlorophyll-containing plastids which are the sites of photosynthesis •Found in eukaryotic algae, leaves and other green plant organs •Are lens-shaped and measure about 2µm by 5µm •Are dynamic structures that change shape, move and divide. ...
Where does photosynthesis take place?
... chlorophyll pigments are greatly reduced revealing the other pigments • Carotenoids are pigments that are either red, orange, or yellow ...
... chlorophyll pigments are greatly reduced revealing the other pigments • Carotenoids are pigments that are either red, orange, or yellow ...
Investigating the organization, assembly and physical properties of
... Biological cells and some internal structures are surrounded by membranes comprised of lipid bilayers and membrane proteins. Certain specialized biomembranes are stacked into multi-layers, allowing a high content of protein-lipid bilayers in a small volume. Chloroplasts (the photosynthetic organelle ...
... Biological cells and some internal structures are surrounded by membranes comprised of lipid bilayers and membrane proteins. Certain specialized biomembranes are stacked into multi-layers, allowing a high content of protein-lipid bilayers in a small volume. Chloroplasts (the photosynthetic organelle ...
Chapter 10-Photosynthesis
... Substances that absorb visible light Chlorophyll a-most important Accessory pigments chlorophyll b and carotenoids Organized into photosystems ...
... Substances that absorb visible light Chlorophyll a-most important Accessory pigments chlorophyll b and carotenoids Organized into photosystems ...
Photosynthesis Notes
... chain – makes ATP or pumps H+ into the center of the thylakoid disc at each step • P I – re-energized e- is passed down a second e- transport chain – @ the end, the e- is transferred to NADP – Forms NADPH which is used in the lightindependent reactions – NADP is a carrier – it just transports the e- ...
... chain – makes ATP or pumps H+ into the center of the thylakoid disc at each step • P I – re-energized e- is passed down a second e- transport chain – @ the end, the e- is transferred to NADP – Forms NADPH which is used in the lightindependent reactions – NADP is a carrier – it just transports the e- ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.