* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis Notes
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Chloroplast wikipedia , lookup
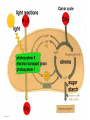
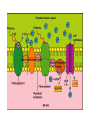
Chapter 9 Energy in the Cell ATP • • • • Adenosine triphosphate Quick source of energy Does not last long The energy is stored in the bonds between the phosphates Structure of the Chloroplast Chloroplast • Contains pigments – Molecules that absorb light of a specific wavelength – Chlorophyll – most common – absorbs most wavelengths EXCEPT green – Carotenoid – red, orange, yellow • Carotenes • Xanthophylls Photosynthesis • Process that captures the sun’s energy and transforms it into simple sugars • 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Occurs in the chloroplast • Two phases: – Light dependent – occurs in the membrane of the thylakoid – makes ATP – Light independent – occurs in the stoma of the chloroplast - makes simple sugars Light Dependent Reactions • Requires sunlight • E from the light is transferred to e• These excited e- enter the e- transport chain of photosystem II – Photosystem – a series of proteins embedded in the membrane of the thylakoid Photosystem II and I • P II – e- is passed down the e- transport chain – makes ATP or pumps H+ into the center of the thylakoid disc at each step • P I – re-energized e- is passed down a second e- transport chain – @ the end, the e- is transferred to NADP – Forms NADPH which is used in the lightindependent reactions – NADP is a carrier – it just transports the e- (like a taxi) The e- Taken From the Chlorophyll Must be Replaced! • In PII water is split: photolysis – Creates oxygen, H+, and e– Oxygen – released – H+ - pumped into the thylakoid to create a concentration gradient – e- returned to the chlorophyll What happens to the H+? • An enzyme ATP synthetase allows the H to move down the concentration gradient and makes ATP Light-Independent Reactions • Calvin Cycle (C3) • Make sugar from CO2 – Carbon fixation • Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast C4 and CAM • Used by plants in dry climates. • In dry climates, the stomata (pores) in the leaves need to stay closed to prevent water loss. This causes the CO2 levels to drop. • If not enough CO2 is available C3 plants will begin grabbing O2 and burning sugars instead of making them (photorespiration) • The protein in the light-independent rxn is more efficient at grabbing CO2