EXAM 2 Fall2007.doc
... e. entropy has been decreased. 7. The second law of thermodynamics states that for chemical reactions: a. entropy always increases. b. entropy always decreases. c. free energy always increases. d. free energy always decreases. e. anabolic reactions must always be paired with catabolic reactions. 8. ...
... e. entropy has been decreased. 7. The second law of thermodynamics states that for chemical reactions: a. entropy always increases. b. entropy always decreases. c. free energy always increases. d. free energy always decreases. e. anabolic reactions must always be paired with catabolic reactions. 8. ...
cell-transport-questions-2012
... Online Activity 6.2 –Dissect a Cell Membrane Cells and their organelles have unique selectively permeable boundaries, called membranes, which are composed primarily of phospholipids and proteins. Why do the phospholipid molecules arrange themselves in that pattern when they are poured into the beake ...
... Online Activity 6.2 –Dissect a Cell Membrane Cells and their organelles have unique selectively permeable boundaries, called membranes, which are composed primarily of phospholipids and proteins. Why do the phospholipid molecules arrange themselves in that pattern when they are poured into the beake ...
8_3bio
... • Energy from the electrons is used by the molecules in the electron transport chain to transport H+ ions from the stroma into the inner thylakoid space. ...
... • Energy from the electrons is used by the molecules in the electron transport chain to transport H+ ions from the stroma into the inner thylakoid space. ...
Chapter 10- Photosynthesis
... and release energy. - Released energy is trapped by chlorophylls, which act as a sink for energy harvested by all pigments. - The trapped energy is then used to transfer a chlorophyll electron to an acceptor molecule. C. How ATP and NADPH Form in Chloroplasts - Electrons expelled from chlorophyll go ...
... and release energy. - Released energy is trapped by chlorophylls, which act as a sink for energy harvested by all pigments. - The trapped energy is then used to transfer a chlorophyll electron to an acceptor molecule. C. How ATP and NADPH Form in Chloroplasts - Electrons expelled from chlorophyll go ...
By: Zara Bryant And Megan Shultz
... Sausage-shaped, about the size of bacteria Two membranes: a smooth outer, and a smooth folded membrane – with numerous layers Mitochondria provide the energy a cell needs to move, divide, produce secretory products, contract - in short, they are the power centers of the cell. They are about the ...
... Sausage-shaped, about the size of bacteria Two membranes: a smooth outer, and a smooth folded membrane – with numerous layers Mitochondria provide the energy a cell needs to move, divide, produce secretory products, contract - in short, they are the power centers of the cell. They are about the ...
Exam 2 Short Answers Ch 4-8.doc
... from the light dependent reactions to completely reduce carbon dioxide to glucose in the Calvin cycle. 11. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, the synthesis of ______________ is coupled to the diffusion of protons. 12. The _________________ is composed of a light-harvesting compl ...
... from the light dependent reactions to completely reduce carbon dioxide to glucose in the Calvin cycle. 11. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, the synthesis of ______________ is coupled to the diffusion of protons. 12. The _________________ is composed of a light-harvesting compl ...
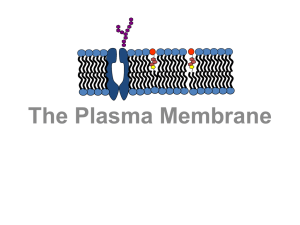
Plasma membrane
... Unlike eukaryotes, bacteria can have a wide variety of fatty acids within their membranes. Along with typical saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, The relative proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temper ...
... Unlike eukaryotes, bacteria can have a wide variety of fatty acids within their membranes. Along with typical saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, The relative proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temper ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Ch 3
... osmosis, isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic, facilitated diffusion, cytoplasm, glycolysis, molecule, ribosome, glucose, proteins, organelles, fructose, chemical reactions, ATP, mRNA, tRNA 1.) Describe passive transport. 2.) Water moves into a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is ____________ ...
... osmosis, isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic, facilitated diffusion, cytoplasm, glycolysis, molecule, ribosome, glucose, proteins, organelles, fructose, chemical reactions, ATP, mRNA, tRNA 1.) Describe passive transport. 2.) Water moves into a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is ____________ ...
Photosynthesis in nature - Ms. Pass's Biology Web Page
... eating other organisms or their by-products (includes decomposers) ...
... eating other organisms or their by-products (includes decomposers) ...
Photosynthesis review - Warren County Schools
... CIRCLE ALL THAT ARE TRUE about the LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION. A. High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain. B. Pigments in photosystems II and I absorb light. C. ATP synthase helps H+ ions in the thylakoid space to pass through the membrane to the stroma. D. ATP and NADPH are us ...
... CIRCLE ALL THAT ARE TRUE about the LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION. A. High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain. B. Pigments in photosystems II and I absorb light. C. ATP synthase helps H+ ions in the thylakoid space to pass through the membrane to the stroma. D. ATP and NADPH are us ...
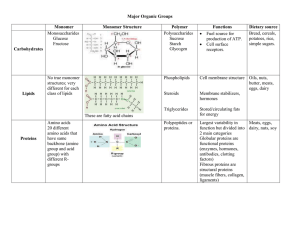
Chemistry of Macromolecules
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
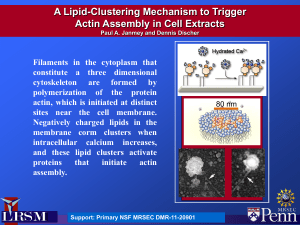
Biochemical screen for potential membrane fission catalysts
... Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune ...
... Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune ...
Answers to exam 1 review #2
... 21. ATP releases energy when the bond undergoes a dehydration reaction T F 22. Delta G is negative when the products have less free energy that the reactants T F 23. In the synthesis of ATP the products have less free energy that the reactants T F 24. When a reaction is spontaneous Delta G is positi ...
... 21. ATP releases energy when the bond undergoes a dehydration reaction T F 22. Delta G is negative when the products have less free energy that the reactants T F 23. In the synthesis of ATP the products have less free energy that the reactants T F 24. When a reaction is spontaneous Delta G is positi ...
Full Content Review
... • When: all the time – there are reactions that require light (day) and reactions that do not require light (night) • How: The light dependents reactions in the thylakoid and the light independent reactions (Calvin cycle) in the stroma ...
... • When: all the time – there are reactions that require light (day) and reactions that do not require light (night) • How: The light dependents reactions in the thylakoid and the light independent reactions (Calvin cycle) in the stroma ...
INTRODUCTION to BIOENERGETICS H.R. Kaback
... membranes represents the bridge between biochemistry and physiology. While ATP is the currency of energy exchange in the cytosol, electrochemical ion gradients across energytransducing membranes are involved in a large number of seemingly unrelated processes such as oxidative phosphorylation, active ...
... membranes represents the bridge between biochemistry and physiology. While ATP is the currency of energy exchange in the cytosol, electrochemical ion gradients across energytransducing membranes are involved in a large number of seemingly unrelated processes such as oxidative phosphorylation, active ...
Induction of membrane hole by pH low
... Peptide-membrane Interactions: Peptide Insertion and Induced Hole Formation Y. Deng & G. H. Wei Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China ...
... Peptide-membrane Interactions: Peptide Insertion and Induced Hole Formation Y. Deng & G. H. Wei Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China ...
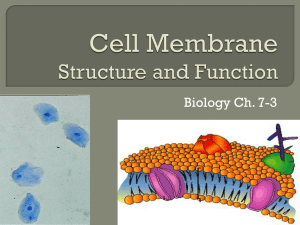
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and
... A biologist ground up some plant leaf cells and then centrifuged the mixture to fractionate the organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, whereas organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most ...
... A biologist ground up some plant leaf cells and then centrifuged the mixture to fractionate the organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, whereas organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.