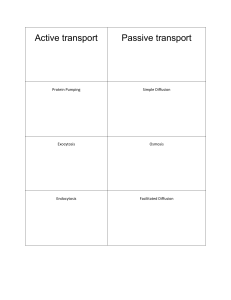
Key Terms:
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
BY 330 Summer 2015Mock Exam 2 Ten molecules of
... completely oxidized. Also allow oxidation of all electron carriers through the electron transport chain. How many protons are pumped from the matrix of the mitochondria to the inner membrane space? How many ATPs are created as a result of only the ETC? How many water molecules are formed? What enzym ...
... completely oxidized. Also allow oxidation of all electron carriers through the electron transport chain. How many protons are pumped from the matrix of the mitochondria to the inner membrane space? How many ATPs are created as a result of only the ETC? How many water molecules are formed? What enzym ...
Facilitated Diffusion vs. Active Transport
... • Particles always move with (down) a concentration gradient. • Uses transport/channel proteins. • Passive transport. • Usually for specific molecules such as glucose. • Facilitated diffusion stops at equilibrium. ...
... • Particles always move with (down) a concentration gradient. • Uses transport/channel proteins. • Passive transport. • Usually for specific molecules such as glucose. • Facilitated diffusion stops at equilibrium. ...
The plasma membrane
... • The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. • It contains two layers of several phospholipids/ lipid molecules with proteins embedded. • A phospholipid is composed of three basic parts ...
... • The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. • It contains two layers of several phospholipids/ lipid molecules with proteins embedded. • A phospholipid is composed of three basic parts ...
Mitochondria
... Fully oxidation of 1 glucose molecule into CO2 • Glycolysis: – Production of 4 ATP but 2 are consumed → 2 ATP ...
... Fully oxidation of 1 glucose molecule into CO2 • Glycolysis: – Production of 4 ATP but 2 are consumed → 2 ATP ...
Printing – LAB Organic Molecule – Lipid
... 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. 5. Receptor proteins transmit signals across a membrane. 6. Transporter and channel proteins form pores through the membrane that ca ...
... 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. 5. Receptor proteins transmit signals across a membrane. 6. Transporter and channel proteins form pores through the membrane that ca ...
EOC Review - Chavis Biology
... G. water. J. sunlight. 15. Which of the following is a reactant in photosynthesis? A. oxygen C. carbon dioxide B. glucose D. ammonia 16. Where in plant cells are the energy-absorbing molecules for photosynthesis located? F. stroma H. thylakoids G. ATP synthase J. mitochondria 17. What happens to the ...
... G. water. J. sunlight. 15. Which of the following is a reactant in photosynthesis? A. oxygen C. carbon dioxide B. glucose D. ammonia 16. Where in plant cells are the energy-absorbing molecules for photosynthesis located? F. stroma H. thylakoids G. ATP synthase J. mitochondria 17. What happens to the ...
Chapter 6: Cells 2
... b. Peroxisomes- contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen. An intermediate product of this process is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a poison, but the peroxisome has another enzyme that converts H2O2 to water. •Some peroxisomes break fatty acids down to smaller molecules t ...
... b. Peroxisomes- contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen. An intermediate product of this process is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a poison, but the peroxisome has another enzyme that converts H2O2 to water. •Some peroxisomes break fatty acids down to smaller molecules t ...
Virtual Cell Tour Assignment
... concerned with three main structures: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. 1. The Cell Membrane ...
... concerned with three main structures: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. 1. The Cell Membrane ...
Chem 400 Biochemistry I
... occurs in the mitochondrion. – Electron transport--electrons are transferred to oxygen. This produces H2O and ATP. Occurs in the mito. ...
... occurs in the mitochondrion. – Electron transport--electrons are transferred to oxygen. This produces H2O and ATP. Occurs in the mito. ...
tougher_plants
... observations from the data Figure 4. Changes in the oxygenproducing activity of PSII determined with thylakoid membranes isolated from leaves after exposed to different temperatures 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, or 50°C in the chambers for 4 h, in wild type and transgenic plants. The values are mean + SE of t ...
... observations from the data Figure 4. Changes in the oxygenproducing activity of PSII determined with thylakoid membranes isolated from leaves after exposed to different temperatures 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, or 50°C in the chambers for 4 h, in wild type and transgenic plants. The values are mean + SE of t ...
Aerobic Metabolism ii: electron transport chain
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons are transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons are transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE: Energetics
... Review Questions: Answer these questions on a separate piece of paper. 1) Draw and label the ATP cycle. 2) Write a balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration and for photosynthesis. 3) Sketch and label a mitochondrion. 4) Create a summary chart to describe the events of: glycolysis, oxidati ...
... Review Questions: Answer these questions on a separate piece of paper. 1) Draw and label the ATP cycle. 2) Write a balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration and for photosynthesis. 3) Sketch and label a mitochondrion. 4) Create a summary chart to describe the events of: glycolysis, oxidati ...
Plasma Membrane
... • Thin, flexible boundary between a cell and its environment. Allows nutrients in and allows waste to leave cell • Plasma membranes have Selective permeability: allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. • A cell membrane is called a fluid mosaic because it behaves more like a ...
... • Thin, flexible boundary between a cell and its environment. Allows nutrients in and allows waste to leave cell • Plasma membranes have Selective permeability: allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. • A cell membrane is called a fluid mosaic because it behaves more like a ...
passive active transport word sort
... out of the cell From hypertonic To hypotonic This is why desalination uses so much electricity to remove salt from ...
... out of the cell From hypertonic To hypotonic This is why desalination uses so much electricity to remove salt from ...
Integral membrane proteins and free electron lasers
... and free-interface diffusion, are often used; however, the commercial and in-house crystallization screens used are often different from those used for soluble proteins. Given the importance of the membrane for membrane protein function and stability, dramatic success has been achieved with methods ...
... and free-interface diffusion, are often used; however, the commercial and in-house crystallization screens used are often different from those used for soluble proteins. Given the importance of the membrane for membrane protein function and stability, dramatic success has been achieved with methods ...
Aerobic Metabolism ii: electron transport chain
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons ae transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons ae transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
Aerobic Metabolism ii: electron transport chain
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons ae transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
... As electrons pass through the ETC, protons ae transported from the matrix and released into the inter membrane space As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient (pH) arise across the inner membrane and this elecrochemical proton gradient is often referred as protonmotive force ...
AP Biology Final Exam Study guide Fall 2013
... The difference between fermentation and cellular respiration ...
... The difference between fermentation and cellular respiration ...
Biogenesis and origin of thylakoid membranes
... would restructure into ordered lamellae by the addition of monogalactosyl diacylglycerol [44]. They concluded that the light harvesting complex together with monogalactosyl diacylglycerol is responsible for lamellae organization of the thylakoid membrane. Therefore interaction between thylakoid prot ...
... would restructure into ordered lamellae by the addition of monogalactosyl diacylglycerol [44]. They concluded that the light harvesting complex together with monogalactosyl diacylglycerol is responsible for lamellae organization of the thylakoid membrane. Therefore interaction between thylakoid prot ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.