Electron Transport Chain (1)
... Free-energy change during electron transport: - Loses 2 electrons from breaking down NADH -> NAD+ (oxidizing) - The protein complex includes the pump and a protein that breaks NADH - The electrons travel through the protein - Though, as the electrons travel through, it loses energy, so it is swapped ...
... Free-energy change during electron transport: - Loses 2 electrons from breaking down NADH -> NAD+ (oxidizing) - The protein complex includes the pump and a protein that breaks NADH - The electrons travel through the protein - Though, as the electrons travel through, it loses energy, so it is swapped ...
Ribosomes (20-30nm)
... Ribosomes (20-30nm) Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into p ...
... Ribosomes (20-30nm) Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into p ...
SBI 3C- The Cell: Part Two -use this note as a guide to fill in board
... Chloroplast: found ONLY in plant cells, chloroplasts are where photosynthesis takes place Structure: A. Chloroplasts are surrounded by two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space. B. Each chloroplast also contains a sy ...
... Chloroplast: found ONLY in plant cells, chloroplasts are where photosynthesis takes place Structure: A. Chloroplasts are surrounded by two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space. B. Each chloroplast also contains a sy ...
File
... nuclear membrane; no membrane-bound organelles; bacteria and blue-green bacteria. ● Eukaryote - contain a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles; plants, animals, fungi, and protists. ● Unicellular - single-celled organism; an organism that consists of o ...
... nuclear membrane; no membrane-bound organelles; bacteria and blue-green bacteria. ● Eukaryote - contain a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles; plants, animals, fungi, and protists. ● Unicellular - single-celled organism; an organism that consists of o ...
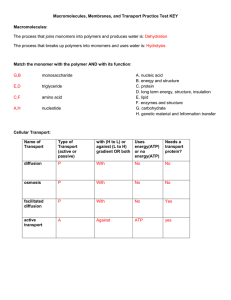
CLASS COPY Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
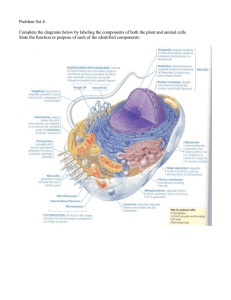
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
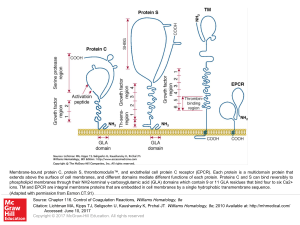
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... Do you understand the basic parts of the cell membrane? Can you model it? Objective: Become familiar with the structure and function of the cell membrane. Use modeling clay to construct a 3D model of cell membrane structures. Use color and labels to distinguish key elements (20 pts. – 10 for model a ...
... Do you understand the basic parts of the cell membrane? Can you model it? Objective: Become familiar with the structure and function of the cell membrane. Use modeling clay to construct a 3D model of cell membrane structures. Use color and labels to distinguish key elements (20 pts. – 10 for model a ...
042407
... • Lipids and proteins – Flip-flop diffusion • Uncommon unless catalyzed (flippase) • Flippases are very specific – Membrane lipids synthesis and transport – Bacterial plasma membrane phospholipids ...
... • Lipids and proteins – Flip-flop diffusion • Uncommon unless catalyzed (flippase) • Flippases are very specific – Membrane lipids synthesis and transport – Bacterial plasma membrane phospholipids ...
4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail
... membranes that aid in converting ADP to ATP by transferring electrons. • ATP synthase – Enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that adds a high-energy phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. • Calvin Cycle – Process by which a photosynthetic organism uses energy to synthesize simple sugars from CO2. ...
... membranes that aid in converting ADP to ATP by transferring electrons. • ATP synthase – Enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that adds a high-energy phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. • Calvin Cycle – Process by which a photosynthetic organism uses energy to synthesize simple sugars from CO2. ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... chemical energy to “power” photosynthesis 1. each pigment has a unique chemical structure sensitive to specific wavelengths of light ...
... chemical energy to “power” photosynthesis 1. each pigment has a unique chemical structure sensitive to specific wavelengths of light ...
Chloroplast Biology - University of Texas at Austin
... sulfur and nitrogen assimilation 2. own genetic system* * Indicates that pathway involves a chloroplast encoded gene in at least some organisms ...
... sulfur and nitrogen assimilation 2. own genetic system* * Indicates that pathway involves a chloroplast encoded gene in at least some organisms ...
4. Photosynthetic Organisms
... The layer in the middle is the mesophyll layer: palisade mesophyll are long rectangular cells and spongy mesophyll are various shaped cells with more air spaces between them ...
... The layer in the middle is the mesophyll layer: palisade mesophyll are long rectangular cells and spongy mesophyll are various shaped cells with more air spaces between them ...
Cell energy
... Electron transport chain • A series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane • Each protein passes energized electrons along from protein to protein • At each step the electron loses energy ...
... Electron transport chain • A series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane • Each protein passes energized electrons along from protein to protein • At each step the electron loses energy ...
11/6/11 10:49 PM Metabolism Poster Questions: Answer the
... a photon is a packet of energy, a particle of light 31. After an electron is removed from the chlorophyll a molecule in the photosystem, how is it replaced in photosystem I and in photosystem II? Photosystem II: Oxygen evolving complex steals an electron from water, replenishing the electron and cre ...
... a photon is a packet of energy, a particle of light 31. After an electron is removed from the chlorophyll a molecule in the photosystem, how is it replaced in photosystem I and in photosystem II? Photosystem II: Oxygen evolving complex steals an electron from water, replenishing the electron and cre ...
1.3 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...
4.2 Overview of Photosynthesis
... Photosynthetic organisms are producers. • Producers make their own source of chemical energy. • Plants, algae, some bacteria and protists • Photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to make sugars. ...
... Photosynthetic organisms are producers. • Producers make their own source of chemical energy. • Plants, algae, some bacteria and protists • Photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to make sugars. ...
KEY WORDS/
... F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around with in the cell membrane Mosaic: membrane made up of lots of different parts ...
... F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around with in the cell membrane Mosaic: membrane made up of lots of different parts ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review
... 15. Is the phosphorylation reaction in the Krebs cycle substrate level or oxidative? 16. How is FADH2 similar to the NADH produced during glycolysis? 17. How is the structure of the mitochondrion suited to its function? 18. As electrons are passed along the ETC they lose energy. Where does this ener ...
... 15. Is the phosphorylation reaction in the Krebs cycle substrate level or oxidative? 16. How is FADH2 similar to the NADH produced during glycolysis? 17. How is the structure of the mitochondrion suited to its function? 18. As electrons are passed along the ETC they lose energy. Where does this ener ...
L2 Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes
... Primary Endosymbiosis (plastids with two membranes) 99% of the time, objects absorbed my phagocytosis become dissolved There may have been a mutation in the cyanobacteria cell wall that made it unrecognisable as food Over time, the cyanobacteria became a plastid ► Lost its autonomy ‐ c ...
... Primary Endosymbiosis (plastids with two membranes) 99% of the time, objects absorbed my phagocytosis become dissolved There may have been a mutation in the cyanobacteria cell wall that made it unrecognisable as food Over time, the cyanobacteria became a plastid ► Lost its autonomy ‐ c ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.