Nervous System
... of the brain’s ventricles) Protects the fragile nervous tissue from blows/trauma continually moving (thru sc, subarachnoid, cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla) Forms and drains at a constant rate to maintain normal pressure and volume (solutes include glucose, proteins, NaCl ...
... of the brain’s ventricles) Protects the fragile nervous tissue from blows/trauma continually moving (thru sc, subarachnoid, cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla) Forms and drains at a constant rate to maintain normal pressure and volume (solutes include glucose, proteins, NaCl ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
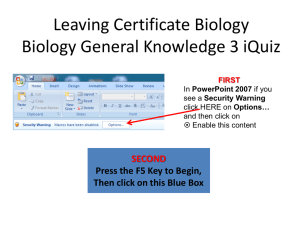
Biology General Knowledge 3 iQuiz
... pollen tube can gain access to the embryo sac to deliver its nuclei and effect fertilisation and through which water enters seeds is called the .. Micropyle ...
... pollen tube can gain access to the embryo sac to deliver its nuclei and effect fertilisation and through which water enters seeds is called the .. Micropyle ...
Posterior Pituitary
... The posterior pituitary is significantly different in structure and function from the anterior pituitary. As its name implies, the posterior pituitary is behind the anterior pituitary (toward the back). It contains mostly axons of secretory neurons and neuroglia cells; the cell bodies of these neuro ...
... The posterior pituitary is significantly different in structure and function from the anterior pituitary. As its name implies, the posterior pituitary is behind the anterior pituitary (toward the back). It contains mostly axons of secretory neurons and neuroglia cells; the cell bodies of these neuro ...
Levels of Biological Organization
... Bones are rigid organs that form part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They help to move, support and protect the body as well as producing red and white blood cells. ...
... Bones are rigid organs that form part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They help to move, support and protect the body as well as producing red and white blood cells. ...
Levels of Biological Organization
... Bones are rigid organs that form part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They help to move, support and protect the body as well as producing red and white blood cells. ...
... Bones are rigid organs that form part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They help to move, support and protect the body as well as producing red and white blood cells. ...
Document
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... and the role that sensory experience has in shaping cortical circuits. In a new line of research, further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres ver ...
... and the role that sensory experience has in shaping cortical circuits. In a new line of research, further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres ver ...
Powerpoint
... membrane that covers parts of brain and forms inner lining that encloses spaces within brain and spinal cord (CNS) ...
... membrane that covers parts of brain and forms inner lining that encloses spaces within brain and spinal cord (CNS) ...
Ch. 21.1 Nervous Lecture
... C. Motor neurons receive impulses from the interneurons and cause the tissues of the body to respond. 1. Ex: Muscles contract, glands release hormones, etc ...
... C. Motor neurons receive impulses from the interneurons and cause the tissues of the body to respond. 1. Ex: Muscles contract, glands release hormones, etc ...
Endocrine and nervous system - Glasgow Independent Schools
... the body that helps prepare for and deal with stress. -Also regulates kidney function. ...
... the body that helps prepare for and deal with stress. -Also regulates kidney function. ...
Ch. 35.3
... between the brain stem and cerebrum Thalamus receives messages from the sense organs Hypothalamus controls recognition of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temp ...
... between the brain stem and cerebrum Thalamus receives messages from the sense organs Hypothalamus controls recognition of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temp ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Slide
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... Form barrier between capillaries and neurons Control chemical environment of brain ...
... Form barrier between capillaries and neurons Control chemical environment of brain ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
Brain Anatomy
... physical growth of connections between neurons. • Improve connections with ‘linking,’ emotion, repetition and practice ...
... physical growth of connections between neurons. • Improve connections with ‘linking,’ emotion, repetition and practice ...
Physiology 1B
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to ...
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • 1. I can describe the functions of the nervous system • 2. I can describe the parts of a neuron cell and identify how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and ...
... • 1. I can describe the functions of the nervous system • 2. I can describe the parts of a neuron cell and identify how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and ...