Synapses - Franklin College
... -Transmit electric impulses (action potentials) from one end to the other (one cell may be more than 3 feet long) ...
... -Transmit electric impulses (action potentials) from one end to the other (one cell may be more than 3 feet long) ...
The Nervous System
... Central Nervous System (CNS) – consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – consists of all nerves and ganglia that lie outside the CNS Central Nervous System (CNS) The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord are complex o ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS) – consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – consists of all nerves and ganglia that lie outside the CNS Central Nervous System (CNS) The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord are complex o ...
Nervous System
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
Document
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
NS Outline
... c. Visceral afferent neurons monitor our internal environment and conditions that must be maintained in order to be in homeostatic balance (many of these sensations are at an unconscious level). We will talk about receptor types in Chapter 15, but they fall into three main types: Exteroceptors (inf ...
... c. Visceral afferent neurons monitor our internal environment and conditions that must be maintained in order to be in homeostatic balance (many of these sensations are at an unconscious level). We will talk about receptor types in Chapter 15, but they fall into three main types: Exteroceptors (inf ...
The Nervous System Lesson Outline LESSON 1 A.
... is loss of muscle function and sometimes loss of feeling. The injured nerves can no longer send and receive signals. ...
... is loss of muscle function and sometimes loss of feeling. The injured nerves can no longer send and receive signals. ...
Design a Neuron
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
Physiology 28.1: The human body has 5 levels of organization. 1
... 3. How do hair cells generate the signals needed to produce hearing? 4. What are the different types of receptors (specialized neurons) and what are their functions? 29.6: The endocrine system produces hormones that affect growth, development, and homeostasis. 1. How do hormones get transported thro ...
... 3. How do hair cells generate the signals needed to produce hearing? 4. What are the different types of receptors (specialized neurons) and what are their functions? 29.6: The endocrine system produces hormones that affect growth, development, and homeostasis. 1. How do hormones get transported thro ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5:Spinal cord The
... In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This system comprises of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. ...
... In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This system comprises of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. ...
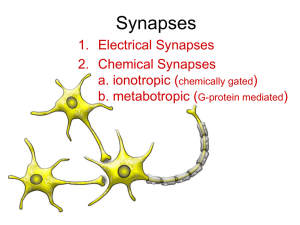
Synapses
... Motor neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal cord, but their axons extend outward into the body to stimulate muscles or glands. Spinal cord smear ...
... Motor neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal cord, but their axons extend outward into the body to stimulate muscles or glands. Spinal cord smear ...
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
... central canal of SC & subarachnoid space reabsorption through arachnoid villi/granulations in superior sagittal sinus veins ...
... central canal of SC & subarachnoid space reabsorption through arachnoid villi/granulations in superior sagittal sinus veins ...
Chapter 3 Notes (part 1) 1. Basic Elements of the Nervous System (a
... B. Cell Membrane/Cytoplasmic Membrane selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which carries the ele ...
... B. Cell Membrane/Cytoplasmic Membrane selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which carries the ele ...
Is Neuronatin mRNA Dendritically localized in Hippocampal Neurons
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
Human Physiology
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... segments composed of fatty tissue. Prevents interference from other electrical signals and helps signals travel faster. ...
... segments composed of fatty tissue. Prevents interference from other electrical signals and helps signals travel faster. ...
eating spaghetti!
... demand a lot of energy because they’re always in a state of metabolic activity. Neurons are manufacturing enzymes and neurotransmitters that are transported out to very ends of their nerve-branches. Chemo ...
... demand a lot of energy because they’re always in a state of metabolic activity. Neurons are manufacturing enzymes and neurotransmitters that are transported out to very ends of their nerve-branches. Chemo ...
The Nervous System
... 8. Know that the conduction of nerve impulses along a neuron involves movement of ions 9. Say what a neurotransmitter is 10. Explain that a synapse is the region where two neurons come into close contact 11. Explain that a synaptic cleft is the gap between the neurons 12. Explain the activation and ...
... 8. Know that the conduction of nerve impulses along a neuron involves movement of ions 9. Say what a neurotransmitter is 10. Explain that a synapse is the region where two neurons come into close contact 11. Explain that a synaptic cleft is the gap between the neurons 12. Explain the activation and ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
three basic functions of the nervous system
... 1. Sensory neurons – transmit impulses to the spinal cord and brain from all parts of the body - also called afferent neurons 2. Motor neurons – transmit impulses away from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and tissue - also called efferent neurons 3. Interneurons – conduct impulses from sensory ...
... 1. Sensory neurons – transmit impulses to the spinal cord and brain from all parts of the body - also called afferent neurons 2. Motor neurons – transmit impulses away from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and tissue - also called efferent neurons 3. Interneurons – conduct impulses from sensory ...
Careful Coordination
... Example of how the nervous system and the endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis. – Hormones control a variety of processes by binding to target cell receptors. We will use dehydration as our example. 1. Sensors in the hypothalamus detect the increase in sodium ion concentration in t ...
... Example of how the nervous system and the endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis. – Hormones control a variety of processes by binding to target cell receptors. We will use dehydration as our example. 1. Sensors in the hypothalamus detect the increase in sodium ion concentration in t ...
Biological Basis of Behavior Review Sheet (1)
... charged ions back out. This depolarization is called action potential. All or nothing. They either fire or they don’t. There is no difference in the strength of the firing. If you feel something stronger, it means more neurons are firing but they are NOT firing harder. Myelin allows faster action po ...
... charged ions back out. This depolarization is called action potential. All or nothing. They either fire or they don’t. There is no difference in the strength of the firing. If you feel something stronger, it means more neurons are firing but they are NOT firing harder. Myelin allows faster action po ...
Unit 3A Notes
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...























