The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... • Includes the brain and spinal cord • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated ...
... • Includes the brain and spinal cord • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated ...
here - CNC
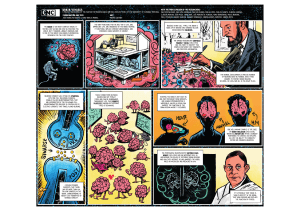
... world. But it remains largely unknown, and is one of the great chalLenges in Biomedical research for the 21rst Century. ...
... world. But it remains largely unknown, and is one of the great chalLenges in Biomedical research for the 21rst Century. ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
CH005a NERVOUS SYS - INTRO 10-22
... Nutrients, such as glucose, essential amino acids, and some electrolytes, move passively by facilitated diffusion through the endothelial cell membranes Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain ...
... Nutrients, such as glucose, essential amino acids, and some electrolytes, move passively by facilitated diffusion through the endothelial cell membranes Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain ...
HYPOTHALAMUS and EPITHALAMUS
... Posterior hypothalamic area - central control of sympathetic activation Mamillary body - mamillary nuclei receive from fornix, project to anterior thalamus - Papez circuit. ...
... Posterior hypothalamic area - central control of sympathetic activation Mamillary body - mamillary nuclei receive from fornix, project to anterior thalamus - Papez circuit. ...
Part 1 - Kirkwood Community College
... skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain – Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain – Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
... messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System
... decrease in blood flow to nonessential organs increase in blood flow to skeletal & cardiac muscle airways dilate & respiratory rate increases blood glucose level increase Long lasting due to lingering of NE in synaptic gap and release of norepinephrine by the adrenal gland ...
... decrease in blood flow to nonessential organs increase in blood flow to skeletal & cardiac muscle airways dilate & respiratory rate increases blood glucose level increase Long lasting due to lingering of NE in synaptic gap and release of norepinephrine by the adrenal gland ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... • Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord, and in turn, cause muscle contractions and affect glands. ...
... • Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord, and in turn, cause muscle contractions and affect glands. ...
Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... •Serves as relay center for sense impulses •Integrates with the ANS in the control of: Heart rate Blood pressure Temperature control Behavioral responses Water and electrolyte balance ...
... •Serves as relay center for sense impulses •Integrates with the ANS in the control of: Heart rate Blood pressure Temperature control Behavioral responses Water and electrolyte balance ...
Nervous System
... Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the hillock Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon ...
... Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the hillock Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
The nervous system
... responsible for muscle coordination Brain stem- most basic functions; respiration, swallowing, blood pressure. Lower part (medulla oblongata) is continuous with spinal cord ...
... responsible for muscle coordination Brain stem- most basic functions; respiration, swallowing, blood pressure. Lower part (medulla oblongata) is continuous with spinal cord ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... cranialnerves III, VII, IX, and X) and from the sacral region of the spinal cord and synapse in ganglia near or on theeffector organs. Thus, in contrast to the sympathetic system, the preganglionic fibers are long, and thepostganglionic ones are short, with the ganglia close to or within the organ i ...
... cranialnerves III, VII, IX, and X) and from the sacral region of the spinal cord and synapse in ganglia near or on theeffector organs. Thus, in contrast to the sympathetic system, the preganglionic fibers are long, and thepostganglionic ones are short, with the ganglia close to or within the organ i ...
Nervous System
... Cannot divide by mitosis Supporting cells aid the functions of neurons • More abundant than neurons ...
... Cannot divide by mitosis Supporting cells aid the functions of neurons • More abundant than neurons ...
Slide () - FA Davis PT Collection
... Spinal nerves of the peripheral nervous system are connected to the spinal cord by anterior roots (sensory neurons) and posterior roots (motor neurons) within the intervertebral foramen. On exiting the spinal column, the spinal nerve splits into dorsal and ventral rami. Dorsal rami typically innerva ...
... Spinal nerves of the peripheral nervous system are connected to the spinal cord by anterior roots (sensory neurons) and posterior roots (motor neurons) within the intervertebral foramen. On exiting the spinal column, the spinal nerve splits into dorsal and ventral rami. Dorsal rami typically innerva ...
Biology and Behaviour
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
bio12_sm_11_1
... 1. (a) Afferent neurons receive signals from sensory receptors; efferent neurons transmit neural messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus take ...
... 1. (a) Afferent neurons receive signals from sensory receptors; efferent neurons transmit neural messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus take ...
Chapter 10 - biologicalpsych.com
... stimulating vasoconstriction in smooth muscles. Increases sodium retention by triggering hypovolemic thirst (low volume). ...
... stimulating vasoconstriction in smooth muscles. Increases sodium retention by triggering hypovolemic thirst (low volume). ...
Information Processing SG
... Information Processing Study Guide Learning Target #1: I can identify and describe the parts of the nervous system. ...
... Information Processing Study Guide Learning Target #1: I can identify and describe the parts of the nervous system. ...
The Brain
... 3. Axon- conducts outgoings messages to other neurons- in the brain they are a few thousandths of and inch- spinal cord to toes- several feet long. 4. Myelin Sheath- fatty layer of cells that insulate many axons- helps speed up transmission of neural impulses.- allows muscles to move more efficientl ...
... 3. Axon- conducts outgoings messages to other neurons- in the brain they are a few thousandths of and inch- spinal cord to toes- several feet long. 4. Myelin Sheath- fatty layer of cells that insulate many axons- helps speed up transmission of neural impulses.- allows muscles to move more efficientl ...
Limbic System - WELCOME to the future website of
... Connections of the amygdala Major efferent fibers are stria terminalis Functional considerations Emotional and behavioral changes are associated with amygdala (MRI shows different activity level when different emotions are elicited by pictures); memories change are associated with hippocampal format ...
... Connections of the amygdala Major efferent fibers are stria terminalis Functional considerations Emotional and behavioral changes are associated with amygdala (MRI shows different activity level when different emotions are elicited by pictures); memories change are associated with hippocampal format ...