5104_a2
... Under anesthesia, removal of the sphenoid bone and dura mater exposes the ventral surface of the hypothalamus from the optic chiasm to the posterior pituitary. A stimulating electrode positioned in the posterior pituitary allows activation of axon terminals of neurosecretory neurons. A ...
... Under anesthesia, removal of the sphenoid bone and dura mater exposes the ventral surface of the hypothalamus from the optic chiasm to the posterior pituitary. A stimulating electrode positioned in the posterior pituitary allows activation of axon terminals of neurosecretory neurons. A ...
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
... which sends the impulse directly to salivary glands beneath the tongue. Ex2) palmar reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s hand, the hand will automatically grasp in response Ex3)rooting reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s cheek, the baby will turn its head towards the touch ...
... which sends the impulse directly to salivary glands beneath the tongue. Ex2) palmar reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s hand, the hand will automatically grasp in response Ex3)rooting reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s cheek, the baby will turn its head towards the touch ...
The building blocks of matter (elements and molecules) form the
... Integumentary system - The integumentary system is an animal’s outer covering, such as skin, scales, feathers, fur, and other body parts, that protect the animal and prevent it from drying out. This system is the first barrier to disease and is responsible for controlling body temperature. Lymphati ...
... Integumentary system - The integumentary system is an animal’s outer covering, such as skin, scales, feathers, fur, and other body parts, that protect the animal and prevent it from drying out. This system is the first barrier to disease and is responsible for controlling body temperature. Lymphati ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal. ...
... responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal. ...
1. Receptor cells
... system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then ...
... system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then ...
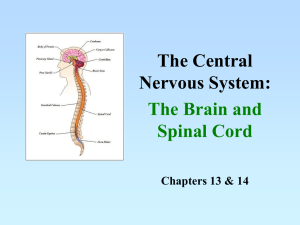
The Nervous System
... system. This can cause paralysis, sensory disturbances, or blindness. There are a couple of tests that can help diagnose multiple sclerosis, such as a MRI and spinal tap. Unfortunately there is no cure for this and only limited treatment of medications and physical therapy. ...
... system. This can cause paralysis, sensory disturbances, or blindness. There are a couple of tests that can help diagnose multiple sclerosis, such as a MRI and spinal tap. Unfortunately there is no cure for this and only limited treatment of medications and physical therapy. ...
Nervous system
... Carries impulses from CNS to effector e.g. muscle to bring about movement or gland to bring about secretion of hormone e.g ADH ...
... Carries impulses from CNS to effector e.g. muscle to bring about movement or gland to bring about secretion of hormone e.g ADH ...
7th sci Nervous System and Brain ppt nervous system and
... – Increases heart rate, bronchiole dilation, blood glucose, blood to skeletal muscle – “fight or flight” ...
... – Increases heart rate, bronchiole dilation, blood glucose, blood to skeletal muscle – “fight or flight” ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... a) The passage of a nerve impulse from a dendrite to an axon is produced because neurotransmitters are released. b) The cerebrum coordinates muscle movements. c) The cerebrum has grey matter on the outside and white matter on the inside. d) The grey matter in the spinal cord is shaped like a butterf ...
... a) The passage of a nerve impulse from a dendrite to an axon is produced because neurotransmitters are released. b) The cerebrum coordinates muscle movements. c) The cerebrum has grey matter on the outside and white matter on the inside. d) The grey matter in the spinal cord is shaped like a butterf ...
Lecture 4:
... sensory and motor systems. Involuntary action or movement that occurs in response to a stimulus. For example: sneeze, cough, yawn, blink. ...
... sensory and motor systems. Involuntary action or movement that occurs in response to a stimulus. For example: sneeze, cough, yawn, blink. ...
Local Cortical Circuits
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... the cerebellum and medulla ...
... the cerebellum and medulla ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
... 4. Brain Imaging Techniques a. Computed tomography (CT): takes X-ray photos to show brain damage. b. Positron emission tomography (PET): shows which part of the brain is active by showing the consumption of sugar glucose. c. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): gives a detailed picture of the brain’s s ...
... 4. Brain Imaging Techniques a. Computed tomography (CT): takes X-ray photos to show brain damage. b. Positron emission tomography (PET): shows which part of the brain is active by showing the consumption of sugar glucose. c. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): gives a detailed picture of the brain’s s ...
Chapter 12
... Thalamus - receives sensory inputs and determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
... Thalamus - receives sensory inputs and determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
CNS2
... Impulses of similar function are sorted, edited, and relayed as a group All inputs ascending to the cerebral cortex pass through the thalamus Plays key role in mediating sensation, motor activities, cortical arousal, learning, and memory ...
... Impulses of similar function are sorted, edited, and relayed as a group All inputs ascending to the cerebral cortex pass through the thalamus Plays key role in mediating sensation, motor activities, cortical arousal, learning, and memory ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH] regulates the formation of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex). This pituitary master gland is itself controlled by the hypothalamus of the brain. Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions ...
... adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH] regulates the formation of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex). This pituitary master gland is itself controlled by the hypothalamus of the brain. Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions ...
File
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...


















![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)