Clinical Day
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
central_nervous_system_overview_211
... Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. ...
... Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. ...
Nervous
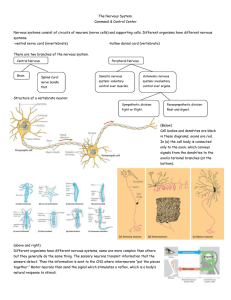
... Different organisms have different nervous systems, some are more complex than others but they generally do the same thing. The sensory neurons transmit information that the sensors detect. Then the information is sent to the CNS where interneurons “put the pieces together.” Motor neurons then send ...
... Different organisms have different nervous systems, some are more complex than others but they generally do the same thing. The sensory neurons transmit information that the sensors detect. Then the information is sent to the CNS where interneurons “put the pieces together.” Motor neurons then send ...
Action Potentials
... • Sensory (afferent) neurons – _________________________ _________________________ – Transmit info to brain/spinal cord • ___________________________ – In between sensory and motor pathways in CNS – 90% of neurons are interneurons – _________________________ _________________________ • _____________ ...
... • Sensory (afferent) neurons – _________________________ _________________________ – Transmit info to brain/spinal cord • ___________________________ – In between sensory and motor pathways in CNS – 90% of neurons are interneurons – _________________________ _________________________ • _____________ ...
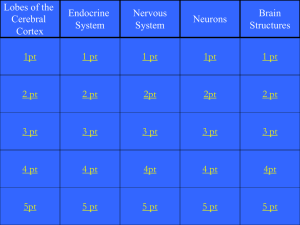
Self Quiz - Endocrine System
... 8. Calcitonin and parathyroid hormones have opposite effects on blood Ca2+ level, therefore they are considered to be A) synergists B) permissive C) antagonist D) repressive E) agonistic ...
... 8. Calcitonin and parathyroid hormones have opposite effects on blood Ca2+ level, therefore they are considered to be A) synergists B) permissive C) antagonist D) repressive E) agonistic ...
Functions of the Nervous System
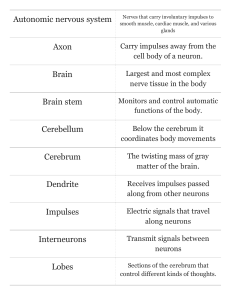
... 1. Sensory neurons: can sense pressure, temperature, pain, and 5 senses in skin, muscles, joints and sense organs (nose, tongue, eyes, ears) ...
... 1. Sensory neurons: can sense pressure, temperature, pain, and 5 senses in skin, muscles, joints and sense organs (nose, tongue, eyes, ears) ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Sensory neurons: can sense pressure, temperature, pain, and 5 senses in skin, muscles, joints and sense organs (nose, tongue, eyes, ears) ...
... 1. Sensory neurons: can sense pressure, temperature, pain, and 5 senses in skin, muscles, joints and sense organs (nose, tongue, eyes, ears) ...
Endocrine and Nervous Systems
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
nervesendocrine ppttwo
... body that helps prepare for and deal with stress. -Also regulates kidney function. ...
... body that helps prepare for and deal with stress. -Also regulates kidney function. ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... mylinated nerve fibers) (note: gray matter is made of the cell bodies) b. Controls skeletal muscles, movements, balance muscle tone ...
... mylinated nerve fibers) (note: gray matter is made of the cell bodies) b. Controls skeletal muscles, movements, balance muscle tone ...
Ch. 2 Practice
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
The Biological Perspective - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... • Now thought to instead be linked via pituitary gland and hypothalamus – Chemical thought once to be hormones have now been found to also be neurotransmitters and vice versa (i.e. norepinepherine, vasopressin) ...
... • Now thought to instead be linked via pituitary gland and hypothalamus – Chemical thought once to be hormones have now been found to also be neurotransmitters and vice versa (i.e. norepinepherine, vasopressin) ...
Inside the brain
... Myelin sheath: Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of fatty cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals (‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Nodes of Ranvier: Areas of the axon without ...
... Myelin sheath: Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of fatty cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals (‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Nodes of Ranvier: Areas of the axon without ...
xpx tampa bay
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
Nervous
... How does the spinal cord maintain homeostasis? -It is the center for reflex actions -Coordinates activity between brain and body structures Why is there fluid surrounding the Brain and Spinal Cord? -Shock absorbency and nourishment ...
... How does the spinal cord maintain homeostasis? -It is the center for reflex actions -Coordinates activity between brain and body structures Why is there fluid surrounding the Brain and Spinal Cord? -Shock absorbency and nourishment ...
study notes quiz 1
... Mesencephalon: “mid-brain” – surrounds cerebral aqueduct 1) Tectum: “roof” (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi) 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance” ...
... Mesencephalon: “mid-brain” – surrounds cerebral aqueduct 1) Tectum: “roof” (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi) 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance” ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...