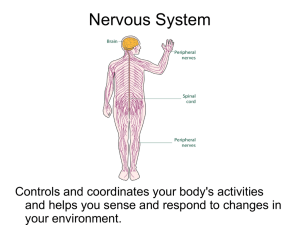
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuron cell body A myelinating cell that surrounds a fi ...
... Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuron cell body A myelinating cell that surrounds a fi ...
Brain Cell or Neuron
... Cell Body: contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles Dendrites: receive information from another cell and send the message to the cell body. Axon: sends messages away from the cell body. Terminals: place where two cells meet to allow messages to pass from one cell to another. ...
... Cell Body: contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles Dendrites: receive information from another cell and send the message to the cell body. Axon: sends messages away from the cell body. Terminals: place where two cells meet to allow messages to pass from one cell to another. ...
Key Learning Guide - City Vision University
... 2. The left side of the brain is the locus of ________________ thought. 3. The right side of the brain is the locus of ________________ thought. 4. Chemical messengers are called______________________. 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
... 2. The left side of the brain is the locus of ________________ thought. 3. The right side of the brain is the locus of ________________ thought. 4. Chemical messengers are called______________________. 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
PPT - Wolfweb Websites
... The embryonic brain: – billions of neurons self-assemble into functional nervous system ...
... The embryonic brain: – billions of neurons self-assemble into functional nervous system ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... d) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. 12. A synapse is a(n): a) neural cable containing many axons. b) chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. c) automatic response to sensory input. d) junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. 13. Reupt ...
... d) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. 12. A synapse is a(n): a) neural cable containing many axons. b) chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. c) automatic response to sensory input. d) junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. 13. Reupt ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... Interaction of Glands The hypothalamus is located in the brain and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary p yg gland. It is an important link between the endocrine and nervous systems. y ...
... Interaction of Glands The hypothalamus is located in the brain and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary p yg gland. It is an important link between the endocrine and nervous systems. y ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
Cerebrospinal Fluid
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
The Nervous System
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
irons.conroeisd.net
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... – Phagocytes that monitor the health of neurons ...
... – Phagocytes that monitor the health of neurons ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... E. Long term memory seems to be unaffected. F. More time to fall asleep, more walking periods during the night, and longer amount of time being awake at night. G. Many older people shoe no change and some show a 10% increase in thinking ability due to education, health, motivation. ...
... E. Long term memory seems to be unaffected. F. More time to fall asleep, more walking periods during the night, and longer amount of time being awake at night. G. Many older people shoe no change and some show a 10% increase in thinking ability due to education, health, motivation. ...
Chapter 8 - Nervous Pre-Test
... allow the current to flow easily between the extracellular fluid and the axon. allow action potentials to develop. allow for saltatory conduction of the action potential. All of these are true of nodes of Ranvier. ...
... allow the current to flow easily between the extracellular fluid and the axon. allow action potentials to develop. allow for saltatory conduction of the action potential. All of these are true of nodes of Ranvier. ...
Brain Organization or, why everyone should have some
... Brain is divided into two hemispheres Connected via the corpus collosum Not all animals have a cc ...
... Brain is divided into two hemispheres Connected via the corpus collosum Not all animals have a cc ...
AP Psychology
... 17. The central nervous system is made up of the spinal cord and brain. Explain the pathway from sensory receptor to reflex. 18. Define the brainstem and describe the following parts: a. medulla b. reticular formation 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its ...
... 17. The central nervous system is made up of the spinal cord and brain. Explain the pathway from sensory receptor to reflex. 18. Define the brainstem and describe the following parts: a. medulla b. reticular formation 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its ...
nervous system
... Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Some are ciliated which facilitates the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid ...
... Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Some are ciliated which facilitates the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... 1. Background of research ...
... 1. Background of research ...
Overview of the Day
... Building Blocks Neurons--the basic unit of the nervous system approximately 10 - 100 billion of them in human body speed of neural transmissions range from 2 to 200 mph ...
... Building Blocks Neurons--the basic unit of the nervous system approximately 10 - 100 billion of them in human body speed of neural transmissions range from 2 to 200 mph ...
The Central Nervous System
... B. Particular aspects of a memory may be stored in numerous brain regions. C. Long-term potentiation is a phenomenon that may be involved in some aspects of memory. Diencephalon I. The diencephalon is the region of the forebrain which includes the thalamus, epithalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary g ...
... B. Particular aspects of a memory may be stored in numerous brain regions. C. Long-term potentiation is a phenomenon that may be involved in some aspects of memory. Diencephalon I. The diencephalon is the region of the forebrain which includes the thalamus, epithalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary g ...