BIOL 104 Test 3 11/1/11 Name .£#`1 C. I i () ./The central nervous
... 33. Which of the following hormones is mismatched with its producing gland? @ovaries--follicle-stimulating hormone B. ovaries--estrogen C. thymus gland--thymosins D. pineal gland--melatonin E. testes--androgens 34. What is the function of melatonin? A. regulate blood glucose levels B. regulate blood ...
... 33. Which of the following hormones is mismatched with its producing gland? @ovaries--follicle-stimulating hormone B. ovaries--estrogen C. thymus gland--thymosins D. pineal gland--melatonin E. testes--androgens 34. What is the function of melatonin? A. regulate blood glucose levels B. regulate blood ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... Occipital Lobe- Receives and processes information from the eyes. Temporal Lobe- Processes auditory information from the ears. Basal Ganglia- Helps to coordinate fine motions, such as fingertip movements. Limbic System- Important for emotional behavior and controlling movements of visceral ...
... Occipital Lobe- Receives and processes information from the eyes. Temporal Lobe- Processes auditory information from the ears. Basal Ganglia- Helps to coordinate fine motions, such as fingertip movements. Limbic System- Important for emotional behavior and controlling movements of visceral ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... Similar to plasma be/c it is derived from plasma Made in the 3rd and 4th ventricle by the CHOROID PLEXUS There are fenestrated capillaries there; the fluid spreads into the subarachnoid space ...
... Similar to plasma be/c it is derived from plasma Made in the 3rd and 4th ventricle by the CHOROID PLEXUS There are fenestrated capillaries there; the fluid spreads into the subarachnoid space ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... PNS: Peripheral nervous system consist of cranial and spinal nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons. It connect CNS to muscles, glands and all sensory receptors ...
... PNS: Peripheral nervous system consist of cranial and spinal nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons. It connect CNS to muscles, glands and all sensory receptors ...
C13 Lesson 2 extra credit
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
the autonomic nervous system
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
Chapter 2A Practice Test
... 17. The'axons of certain neurons are covered by a layer of fatty tissue that helps speed neural transmission. This tissue is: A) the glia. B) the myelin sheath. C) acefylcholine. D) an endorphin. ...
... 17. The'axons of certain neurons are covered by a layer of fatty tissue that helps speed neural transmission. This tissue is: A) the glia. B) the myelin sheath. C) acefylcholine. D) an endorphin. ...
Biology 30 – Notes Neurotransmitters and the Brain, September 15
... 5. Medulla oblongata – sits at the base of the brainstem, it connects the brain and spinal cord. Controls automatic and involuntary responses such as heart rate, coughing, breathing rate, swallowing etc. 6. Thalamus – at the base of the forebrain, it consists of neurons that provide connections betw ...
... 5. Medulla oblongata – sits at the base of the brainstem, it connects the brain and spinal cord. Controls automatic and involuntary responses such as heart rate, coughing, breathing rate, swallowing etc. 6. Thalamus – at the base of the forebrain, it consists of neurons that provide connections betw ...
Nervous System
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
eprint_2_23793_166
... 1. Structural classification: number of cytoplasmic processes (4 types): a. Unipolar neurons(rare in the adult human) b. Pseudounipolar neurons: only one process arising from the soma. Developmentally, divides into two branches. Found in peripheral sensory ganglia, such as dorsal root ganglia. c. B ...
... 1. Structural classification: number of cytoplasmic processes (4 types): a. Unipolar neurons(rare in the adult human) b. Pseudounipolar neurons: only one process arising from the soma. Developmentally, divides into two branches. Found in peripheral sensory ganglia, such as dorsal root ganglia. c. B ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
Nervous System
... Axons • Most nerve fibers are covered with myelin – It is a fatty material. Function? ...
... Axons • Most nerve fibers are covered with myelin – It is a fatty material. Function? ...
Document
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other brain areas. • Cerebellum= Region of the brain that plays an im ...
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other brain areas. • Cerebellum= Region of the brain that plays an im ...
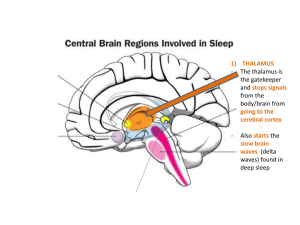
Sleep Brain Labelling
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Supplementary Figure Legends
... groups. A representative liver section from an animal treated with control neurons shows well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild ...
... groups. A representative liver section from an animal treated with control neurons shows well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild ...
Autonomic nervous system
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
Slide 1
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
What structures comprise the sympathetic division?
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
... • Sympathetic axons reach target organs through ___________ and ______ _________ • Parasympathetic axons reach target organs through _____________ and _____ __________ • Remember _______ (________) _________ also travel via these nerves. ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
Ch 15 ppt
... It coordinates information from the body and other parts of the brain and provides a coordinated set of both neuronal and hormonal outputs The periventricular nucleus (PVN) is central to control of the ANS ...
... It coordinates information from the body and other parts of the brain and provides a coordinated set of both neuronal and hormonal outputs The periventricular nucleus (PVN) is central to control of the ANS ...
EXAM: Study Guide for Structural Organization in Animals
... Approximately in what location of the body is each of seven glands? What is homeostasis and which gland greatly affects it and why? What are the gonads and what do they secrete? What is the function of the Lymphatic system? What are the two components of the Lymphatic system and what role do they pl ...
... Approximately in what location of the body is each of seven glands? What is homeostasis and which gland greatly affects it and why? What are the gonads and what do they secrete? What is the function of the Lymphatic system? What are the two components of the Lymphatic system and what role do they pl ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...