6.1 Overview of the Nervous System
... 2. Efferent nerves (motor)– transmit impulses from CNS to muscles or glands (efferent nerves stimulate muscles to produce effort) -two divisions of motor nerves a. somatic nervous system (voluntary) – stimulate muscles b. autonomic nervous system (involuntary) – controls smooth muscles, cardiac musc ...
... 2. Efferent nerves (motor)– transmit impulses from CNS to muscles or glands (efferent nerves stimulate muscles to produce effort) -two divisions of motor nerves a. somatic nervous system (voluntary) – stimulate muscles b. autonomic nervous system (involuntary) – controls smooth muscles, cardiac musc ...
Central Nervous System
... Brain: enlarged & highly developed portion of the CNS that lies in the skull and is the main site of nervous control. Cranium: portion of skull that encloses and protects the brain. The brain divides into three regions: brainstem, cerebrum and cerebellum. ...
... Brain: enlarged & highly developed portion of the CNS that lies in the skull and is the main site of nervous control. Cranium: portion of skull that encloses and protects the brain. The brain divides into three regions: brainstem, cerebrum and cerebellum. ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
... K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... LONGER CAN UNDERSTAND WHAT PEOPLE SAY TO HER, ALTHOUGH SHE HEARS THEM. THE REGION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX MOST LIKELY INJURED IS HER Temporal Lobe ...
... LONGER CAN UNDERSTAND WHAT PEOPLE SAY TO HER, ALTHOUGH SHE HEARS THEM. THE REGION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX MOST LIKELY INJURED IS HER Temporal Lobe ...
The Brain
... Cerebellum = deals with movement through regulation and coordination of bodily movements, posture and balance Pons = monitors the level of stimulation or consciousness and sleep (while asleep) Reticular Formation = monitors the state of the body and functions in such processes as arousal and s ...
... Cerebellum = deals with movement through regulation and coordination of bodily movements, posture and balance Pons = monitors the level of stimulation or consciousness and sleep (while asleep) Reticular Formation = monitors the state of the body and functions in such processes as arousal and s ...
Nervous System
... surrounding neurons (uptake of neurotransmitters and ions) and contributes to the restricted permeability known as the blood brain barrier? ...
... surrounding neurons (uptake of neurotransmitters and ions) and contributes to the restricted permeability known as the blood brain barrier? ...
Introduction to cns
... • Diencephalon: The largest part of the diencephalon is the thalamus; in fact, this is a paired structure. ...
... • Diencephalon: The largest part of the diencephalon is the thalamus; in fact, this is a paired structure. ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
NeuroReview1
... Ventral Root Neurons are motor (efferent) multipolar neurons with their cell bodies in the ventral horn. ...
... Ventral Root Neurons are motor (efferent) multipolar neurons with their cell bodies in the ventral horn. ...
biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite agonists axon antagonists myelin sheath blood-brain barrier cell body nervous system central nervous system terminal branches of axon synapse (synaptic gap) peripheral nervous system neural impulse nerves action potential sensory (afferent ...
... biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite agonists axon antagonists myelin sheath blood-brain barrier cell body nervous system central nervous system terminal branches of axon synapse (synaptic gap) peripheral nervous system neural impulse nerves action potential sensory (afferent ...
The Brain and Behavior
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
the nervous system
... CNS to an effector (muscle or gland) • Have long axons • Interneurons connect other neurons to the CNS ...
... CNS to an effector (muscle or gland) • Have long axons • Interneurons connect other neurons to the CNS ...
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Nervous System Cells
... system functions • Glia – (glial cells) support the function of neurons in various ways ...
... system functions • Glia – (glial cells) support the function of neurons in various ways ...
Nervous System
... Outside central nervous systems with nerves. Cranial nerves and spinal nerves and be sensory or motor. Somatic system: serves the skin, joint, and skeletal muscles. ...
... Outside central nervous systems with nerves. Cranial nerves and spinal nerves and be sensory or motor. Somatic system: serves the skin, joint, and skeletal muscles. ...
The Nervous System
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
brain
... Taste – tongue is the organ of taste • Four types of flavors: sour, sweet, salty and bitter • Different areas of tongues taste different flavors • Taste buds pick up tastes and send them to brain ...
... Taste – tongue is the organ of taste • Four types of flavors: sour, sweet, salty and bitter • Different areas of tongues taste different flavors • Taste buds pick up tastes and send them to brain ...
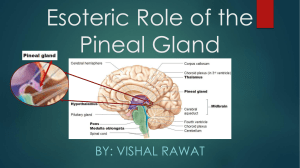
Esoteric Role of the Pineal Gland
... - The pineal gland consists of five different cell types - Pinealocytes produce the hormone melatonin and consist of a cell body with 4-6 processes emerging - Interstitial cells are located between the pinealocytes - Perivascular phagocytes are located near the capillaries and they are antigen prese ...
... - The pineal gland consists of five different cell types - Pinealocytes produce the hormone melatonin and consist of a cell body with 4-6 processes emerging - Interstitial cells are located between the pinealocytes - Perivascular phagocytes are located near the capillaries and they are antigen prese ...
Chapter 13 and 16
... vertebra • “carrot shaped” • Ends @ conus medullaris- many nerves exit and form cauda equina • 2 enlargements=cervical and lumbar- where more nerves enter and leave the cord ...
... vertebra • “carrot shaped” • Ends @ conus medullaris- many nerves exit and form cauda equina • 2 enlargements=cervical and lumbar- where more nerves enter and leave the cord ...
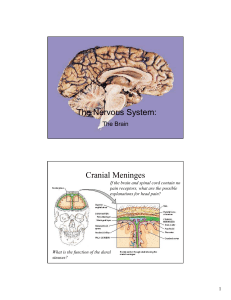
The Nervous System: Cranial Meninges
... Describe the location of the basal nuclei relative to the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus. What does this structural feature imply about the function of the basal nuclei? ...
... Describe the location of the basal nuclei relative to the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus. What does this structural feature imply about the function of the basal nuclei? ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 16. directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking and sleeping. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. _______ 17. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions. ____ ...
... _______ 16. directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking and sleeping. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. _______ 17. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions. ____ ...