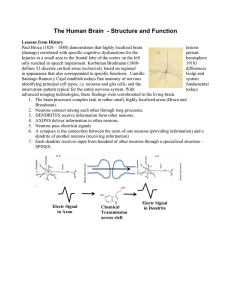
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain functions Gray matter – composed almost exclusively of the cell bodies of neurons White matter – found under gray matter, lighter color is from myelin which cove ...
... ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain functions Gray matter – composed almost exclusively of the cell bodies of neurons White matter – found under gray matter, lighter color is from myelin which cove ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
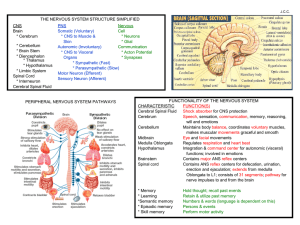
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
... smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
Chapter 3
... Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
... Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
Chapter 2
... Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
... Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... Draw out a flow diagram of the Nervous System. Include all the subdivisions and their characteristics. Hint: it can be found in 3A. ...
... Draw out a flow diagram of the Nervous System. Include all the subdivisions and their characteristics. Hint: it can be found in 3A. ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... - input from visceral senses (NTS: nucleus of the solitary tract: taste) – contains many neurons that are sensitive to local temperature, osmolarity, glucose, sodium – circulating hormones influence it via the circumventricular organs ...
... - input from visceral senses (NTS: nucleus of the solitary tract: taste) – contains many neurons that are sensitive to local temperature, osmolarity, glucose, sodium – circulating hormones influence it via the circumventricular organs ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
C48 Nervous System
... that regulate the anterior pituitary. Pituitary gland – endocrine gland at base of hypothalamus, releases (oxytocin & ADH) produced by hypothalamus & secretes many hormones that regulate diverse body functions (growth hormone, prolactin, FSH, LH, TSH, Adrenocorticotropic hormone). Midbrain – senso ...
... that regulate the anterior pituitary. Pituitary gland – endocrine gland at base of hypothalamus, releases (oxytocin & ADH) produced by hypothalamus & secretes many hormones that regulate diverse body functions (growth hormone, prolactin, FSH, LH, TSH, Adrenocorticotropic hormone). Midbrain – senso ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... Channel- Linked receptors: are cell membrane bound receptors. They act through synaptic signaling on electrically excitable cells Enzyme-linked receptors: is a transmembrane receptor, where the binding of an extracellular ligand causes enzymatic activity on the intracellular side. Intracellular rece ...
... Channel- Linked receptors: are cell membrane bound receptors. They act through synaptic signaling on electrically excitable cells Enzyme-linked receptors: is a transmembrane receptor, where the binding of an extracellular ligand causes enzymatic activity on the intracellular side. Intracellular rece ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
... Our brain comprises of – the cerebrum responsible for most of brain information processing – the brain stem dealing with involuntary functions of vital importance – the cerebellum offering balance and equilibrium as well as memory of repetitive acts ...
... Our brain comprises of – the cerebrum responsible for most of brain information processing – the brain stem dealing with involuntary functions of vital importance – the cerebellum offering balance and equilibrium as well as memory of repetitive acts ...
Name
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
Nervous system Nervous system
... • Central nervous system = Brain + Spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system = Cranial nerves + Spinal nerves (gather info from sensors and conduct decisions to effectors) ...
... • Central nervous system = Brain + Spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system = Cranial nerves + Spinal nerves (gather info from sensors and conduct decisions to effectors) ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... 5. What are the 2 Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System? Somatic and Autonomic o Somatic = Enables control of voluntary skeletal muscles (walking, jumping, MOVING) o Autonomic = Controls glands and internal organs (usually operates on Autopilot) Broken into 2 systems (Sympathetic and Parasympat ...
... 5. What are the 2 Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System? Somatic and Autonomic o Somatic = Enables control of voluntary skeletal muscles (walking, jumping, MOVING) o Autonomic = Controls glands and internal organs (usually operates on Autopilot) Broken into 2 systems (Sympathetic and Parasympat ...
Structural arrangement of the nervous sytem. Blood-brain
... maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment ...
... maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment ...
Strategies for drug delivery through the blood
... • Active transport through a protein carrier: specific binding site that undergoes a change in affinity. Active transport requires ATP hydrolysis and conducts movement against the concentration gradient. ...
... • Active transport through a protein carrier: specific binding site that undergoes a change in affinity. Active transport requires ATP hydrolysis and conducts movement against the concentration gradient. ...
Understanding Concepts through Songs and Poems
... Pineal glands mediate biorhythms (secrete the hormone melatonin, regulate light related functions) Gonads are the home of reproduction (regulated by follicle stimulating hormone [FSH] and luteinizing hormone [LH]) Testes in men, and ovaries in women ...
... Pineal glands mediate biorhythms (secrete the hormone melatonin, regulate light related functions) Gonads are the home of reproduction (regulated by follicle stimulating hormone [FSH] and luteinizing hormone [LH]) Testes in men, and ovaries in women ...
Nervous System
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
Brain/Sc Notes
... Limbic system-controls emotions Spinal cord -Nerve column from foramen magnum to intervertebral disk between L1 and L2 vertebrae -31 segments (spinal nerves) White matter-myelinated fibers Gray matter-unmyelinated nerve fibers and neuron cell bodies ...
... Limbic system-controls emotions Spinal cord -Nerve column from foramen magnum to intervertebral disk between L1 and L2 vertebrae -31 segments (spinal nerves) White matter-myelinated fibers Gray matter-unmyelinated nerve fibers and neuron cell bodies ...