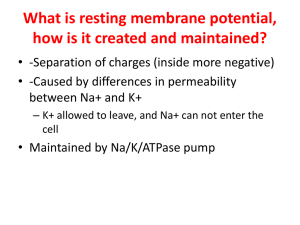
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
Slide 1
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
Slide 1
... gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connections between cells. ► Every cell is precisely in its pla ...
... gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connections between cells. ► Every cell is precisely in its pla ...
Slide ()
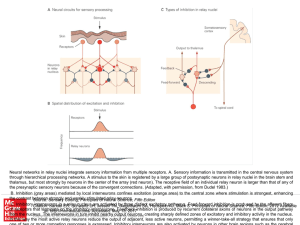
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... 1. Sensory Function – gathers info about changes occurring within and around the body Sensory receptors, at ends of peripheral nerves send signals (nerve impulses) to the CNS. Sensory Neuron 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create though ...
... 1. Sensory Function – gathers info about changes occurring within and around the body Sensory receptors, at ends of peripheral nerves send signals (nerve impulses) to the CNS. Sensory Neuron 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create though ...
Nervous System
... Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your body’s involuntary actions those that occur automatically Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous system: Consist of a network of nerves that branch out from the c ...
... Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your body’s involuntary actions those that occur automatically Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous system: Consist of a network of nerves that branch out from the c ...
Unit 3A–Neural Processing and the Endocrine System
... the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, l ...
... the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, l ...
Nervous System Notes
... and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
... and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
Nervous System
... Neurons that carry information about stimuli to the CNS-Central Nervous system ...
... Neurons that carry information about stimuli to the CNS-Central Nervous system ...
SENSORY SYSTEMS (Windows to the World
... Ampullary organ sensitive to low freq. fields (0.1-20 Hz) - 0.005 uV/cm gradient - what a flounders makes at 30 cm. Detect 1.5 V battery across 1500 Km of saltwater. Gymnotidae & Mormyridae, weakly active electric fish Tuberous organ sensitive to high freq. fields (50social signals. Can pulse field ...
... Ampullary organ sensitive to low freq. fields (0.1-20 Hz) - 0.005 uV/cm gradient - what a flounders makes at 30 cm. Detect 1.5 V battery across 1500 Km of saltwater. Gymnotidae & Mormyridae, weakly active electric fish Tuberous organ sensitive to high freq. fields (50social signals. Can pulse field ...
1-nervous_system
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
The Nervous System
... movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include; Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face, stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk, slowness of movement, poor balance and coordination. As symptoms get worse, people with the disease may have trouble wal ...
... movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include; Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face, stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk, slowness of movement, poor balance and coordination. As symptoms get worse, people with the disease may have trouble wal ...
BIOL241AddlGuideFinalSUM2012
... • The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia • The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major function for each larger and more specific parts, such as the hypothalamus, pineal gland, and epithalamus of the diencephalon. • Know the ...
... • The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia • The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major function for each larger and more specific parts, such as the hypothalamus, pineal gland, and epithalamus of the diencephalon. • Know the ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... The different types of nervous system cells and their function The location of ganglia, the number of neurons, the types of targets, and the neurotransmitters involved in all the synapses of the somatic motor, sympathetic, and parasympathetic divisions Sensory pathways that ascend the spinal cord to ...
... The different types of nervous system cells and their function The location of ganglia, the number of neurons, the types of targets, and the neurotransmitters involved in all the synapses of the somatic motor, sympathetic, and parasympathetic divisions Sensory pathways that ascend the spinal cord to ...
11_1_Dienc_CzehlárB
... • https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diencephalon • https://users.itk.ppke.hu/neurobiologia/LECTURES_20162017_SEMESTER_1/11.%20WEEK/3.%20LITERATURE/Th alamus.pdf • http://antranik.org/the-diencephalon/ ...
... • https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diencephalon • https://users.itk.ppke.hu/neurobiologia/LECTURES_20162017_SEMESTER_1/11.%20WEEK/3.%20LITERATURE/Th alamus.pdf • http://antranik.org/the-diencephalon/ ...
File
... c. spinal nerves – 31 pairs d. There are two divisions of PNS 1. Somatic system – controls voluntary actions, from CNS to skeletal muscles. 2. Autonomic system – control of involuntary actions, heart rate, breathing, digestion. ...
... c. spinal nerves – 31 pairs d. There are two divisions of PNS 1. Somatic system – controls voluntary actions, from CNS to skeletal muscles. 2. Autonomic system – control of involuntary actions, heart rate, breathing, digestion. ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take informatio ...
... Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take informatio ...