Nervous System - Creston High School
... and skilled skeletal muscle, functions in intellectual and emotional processing. Shows lateralization of function – Most people the left hemisphere is dominant and is specialized for language and mathematical skills – The right hemisphere is more concerned with visualspatial skills and creative en ...
... and skilled skeletal muscle, functions in intellectual and emotional processing. Shows lateralization of function – Most people the left hemisphere is dominant and is specialized for language and mathematical skills – The right hemisphere is more concerned with visualspatial skills and creative en ...
The Nervous System The master and
... Most brain tumors are the result of _________________ cells forming the tumor. This is because neurons have lost their ability to _________________. This is also why _________________ damage can be so catastrophic for a person. Cluster Terms _________________ – well protected clusters of cell bodies ...
... Most brain tumors are the result of _________________ cells forming the tumor. This is because neurons have lost their ability to _________________. This is also why _________________ damage can be so catastrophic for a person. Cluster Terms _________________ – well protected clusters of cell bodies ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... Membrane Potential • the difference in voltage across the plasma membrane + arises from differences in ionic composition (Na+/K+ pump) - normal: positive outside; negative inside (-70mV) ...
... Membrane Potential • the difference in voltage across the plasma membrane + arises from differences in ionic composition (Na+/K+ pump) - normal: positive outside; negative inside (-70mV) ...
Biological foundations of psychology
... brain’s electrical activity, recorded from electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
... brain’s electrical activity, recorded from electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
The Human Brain - Peoria Public Schools
... breathing. b. Cerebellum- important in motor control, posture, balance, some cognitive function such as speech. ...
... breathing. b. Cerebellum- important in motor control, posture, balance, some cognitive function such as speech. ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... Mentor: Xiangmin Xu The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or t ...
... Mentor: Xiangmin Xu The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or t ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 6. “Dendrite” comes from a greek word meaning __________? 7. What disorder has been associated with an excess of dopamine? Which disorder has been associated with a deficit of dopamine? 8. Which drug acts like ACH? 9. How do SSRI’s work? (hint – Prozac) 10. Know the parts of a neuron? 11. Know the r ...
... 6. “Dendrite” comes from a greek word meaning __________? 7. What disorder has been associated with an excess of dopamine? Which disorder has been associated with a deficit of dopamine? 8. Which drug acts like ACH? 9. How do SSRI’s work? (hint – Prozac) 10. Know the parts of a neuron? 11. Know the r ...
Hypothalamus
... – Neural cells located within hypothalamus • Paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei • Supraoptic nuclei ...
... – Neural cells located within hypothalamus • Paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei • Supraoptic nuclei ...
The Endocrine System - Life Science Academy
... S It produces several important hormones including melatonin. S Melatonin influences sexual development and sleep-wake cycles. S The pineal gland connects the endocrine system with the nervous ...
... S It produces several important hormones including melatonin. S Melatonin influences sexual development and sleep-wake cycles. S The pineal gland connects the endocrine system with the nervous ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
Nervous System Notes - Mrs. Franco's Biology & Anatomy Page
... cells found around cell bodies of neurons in ganglia Ganglia = bunched up cell bodies in PNS ...
... cells found around cell bodies of neurons in ganglia Ganglia = bunched up cell bodies in PNS ...
Nervous System
... the central nervous system Motor (efferent) division Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system Interneurons (association neurons) Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... the central nervous system Motor (efferent) division Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system Interneurons (association neurons) Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
FINAL LECTURE EXAM – HUMAN ANATOMY
... b. It has a shorter duration of action than does the nervous system, but typically reacts more rapidly to stimulation. c. It controls effector organs by releasing neurotransmitters into the blood. d. b & c e. a, b & c 7. Which of the following endocrine glands is also an exocrine gland? a. hypothala ...
... b. It has a shorter duration of action than does the nervous system, but typically reacts more rapidly to stimulation. c. It controls effector organs by releasing neurotransmitters into the blood. d. b & c e. a, b & c 7. Which of the following endocrine glands is also an exocrine gland? a. hypothala ...
Nervous System Nervous System
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
The Nervous System
... nerve fibers from one side to other • Posterior horn- receives sensory / afferent input • Anterior horn – transmits motor/efferent response • Columns – pathways / nerve tracts ...
... nerve fibers from one side to other • Posterior horn- receives sensory / afferent input • Anterior horn – transmits motor/efferent response • Columns – pathways / nerve tracts ...
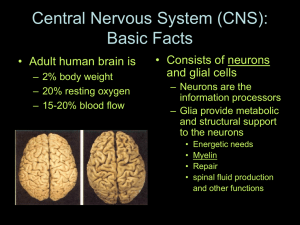
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... • Dendrite: receives info from neighboring neurons. • Cell body: living portion of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles. • Axon: sends info to neighboring neurons. ...
... • Dendrite: receives info from neighboring neurons. • Cell body: living portion of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles. • Axon: sends info to neighboring neurons. ...