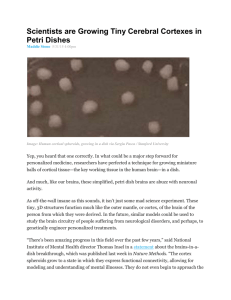
Scientists are Growing Tiny Cerebral Cortexes in Petri
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron
... • Each nerve is made of bundles of neuron fibers • Neuron fibers are surrounded by a delicate ...
... • Each nerve is made of bundles of neuron fibers • Neuron fibers are surrounded by a delicate ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1.Biochemistry. a catecholamine neur ...
... and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1.Biochemistry. a catecholamine neur ...
The Anterolateral System
... • The Anterolateral System is an ascending pathway conveying pain and temperature sensation. • Cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
... • The Anterolateral System is an ascending pathway conveying pain and temperature sensation. • Cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
Human Biology Name: Bio 5 - Spring 2006 Exam 1
... 5. In the kidney, a structure called the _________________, does the basic work. 6. An important mineral, used by erythrocytes in transporting oxygen, is ____________. 7. The "chemical cash" of the cell, at least in terms of providing energy, is the molecule known as __________________. (abbreviatio ...
... 5. In the kidney, a structure called the _________________, does the basic work. 6. An important mineral, used by erythrocytes in transporting oxygen, is ____________. 7. The "chemical cash" of the cell, at least in terms of providing energy, is the molecule known as __________________. (abbreviatio ...
Co-ordination - BIFS IGCSE SCIENCE
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM This provides constant input (stimuli) from our environment. It is designed to detect changes that will increase an organisms chances of survival. We have 5 senses or sensations we can detect. Cells or organs that detect these are called SENSORY ORGANS, RECEPTORS or AFFECTORS ...
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM This provides constant input (stimuli) from our environment. It is designed to detect changes that will increase an organisms chances of survival. We have 5 senses or sensations we can detect. Cells or organs that detect these are called SENSORY ORGANS, RECEPTORS or AFFECTORS ...
Anterior nuclei
... Paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei contain neurons that produce oxytocin or vasopressin Hormones travel down axon by axonal transport and are stored and released at terminals in the posterior pituitary Hormones released into systemic circulation upon excitation Systemic feedback to hypothalamus v ...
... Paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei contain neurons that produce oxytocin or vasopressin Hormones travel down axon by axonal transport and are stored and released at terminals in the posterior pituitary Hormones released into systemic circulation upon excitation Systemic feedback to hypothalamus v ...
The Nervous System
... extending from cell body. o one side of axon is the peripheral process associated with body part, other side is the central process that enters brain or spinal cord. o *most common type o Involved in pain, touch, proprioception, and visceral organ activity ...
... extending from cell body. o one side of axon is the peripheral process associated with body part, other side is the central process that enters brain or spinal cord. o *most common type o Involved in pain, touch, proprioception, and visceral organ activity ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - can be classified as: 1. Cholinergic - release acetylcholine - includes all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers - all parasympathetic postganglionic fibers - a few sympathetic postganglionic fibers - all somatic motor neurons 2. Adrenergic - release norepinephrine - most sympathet ...
... - can be classified as: 1. Cholinergic - release acetylcholine - includes all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers - all parasympathetic postganglionic fibers - a few sympathetic postganglionic fibers - all somatic motor neurons 2. Adrenergic - release norepinephrine - most sympathet ...
9.1-9.4 Notes
... • Unipolar neuron-one axon, no dendrites – Dendrite near peripheral body – Other part connected to brain or spinal cord – Cell bodies of these are bunched to form ganglia • Outside the brain or spinal cord ...
... • Unipolar neuron-one axon, no dendrites – Dendrite near peripheral body – Other part connected to brain or spinal cord – Cell bodies of these are bunched to form ganglia • Outside the brain or spinal cord ...
Endocrine System
... ● Rate of Hypothalamus Secretions : Negative Feedback ● Anterior Pituitary - Produces hormones that “turn on” endocrine glands or support functions of other organs Hypothalamic Hormone ...
... ● Rate of Hypothalamus Secretions : Negative Feedback ● Anterior Pituitary - Produces hormones that “turn on” endocrine glands or support functions of other organs Hypothalamic Hormone ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 5. Sensory Functions a. small portion of the sensory input results in sensation. b. ascending tracts – sends signals to the brain. -each tract is limited ex… ex. Lateral spinothalamic tract pain & temperature. ex. Dorsal column touch, position, pressure -most tracts have 2 or 3 neurons to the brain ...
... 5. Sensory Functions a. small portion of the sensory input results in sensation. b. ascending tracts – sends signals to the brain. -each tract is limited ex… ex. Lateral spinothalamic tract pain & temperature. ex. Dorsal column touch, position, pressure -most tracts have 2 or 3 neurons to the brain ...
Copy Notes
... that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue; they show brain anatomy fMRI (functional MRI): a technique for revealing ...
... that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue; they show brain anatomy fMRI (functional MRI): a technique for revealing ...
6th Study Guide D1w:ans
... 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. Th ...
... 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. Th ...
awl review q answers
... Chapter 2. Through sensory systems, the brain is informed of such things in the world as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, body temperature and level of nutrient reserves. The brain monitors its own chemical envi ...
... Chapter 2. Through sensory systems, the brain is informed of such things in the world as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, body temperature and level of nutrient reserves. The brain monitors its own chemical envi ...
Nervous Tissue
... – Multipolar: 3+ processes; 99% of all neurons, major in CNS – Bipolar: 2 processes; rare, located in sense organs – Unipolar : short, divided process (peripheral and central processes); mainly in PNS ...
... – Multipolar: 3+ processes; 99% of all neurons, major in CNS – Bipolar: 2 processes; rare, located in sense organs – Unipolar : short, divided process (peripheral and central processes); mainly in PNS ...
II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... The vibrations are transferred from the _stirrup____ to another membrane known as the _oval window_______. Finally, vibrations are converted to an electrical impulse in the _cochlea_______, a snail-shaped sensory structure filled with fluid and tiny hairs. These hairs are pushed back & forth, pr ...
... The vibrations are transferred from the _stirrup____ to another membrane known as the _oval window_______. Finally, vibrations are converted to an electrical impulse in the _cochlea_______, a snail-shaped sensory structure filled with fluid and tiny hairs. These hairs are pushed back & forth, pr ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...
SBI4U Nervous System
... carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neurotransmitter chemicals are released in order to communi ...
... carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neurotransmitter chemicals are released in order to communi ...
Chapter 3
... pituitary- releases hormones that control other glands adrenal- regulates sugar and sodium levels thyroid- hormones affect metabolic rate pancreas- secretes insulin to regulate metabolism ovaries- secrete estrogen for ovulation testes- release androgens for sperm production ...
... pituitary- releases hormones that control other glands adrenal- regulates sugar and sodium levels thyroid- hormones affect metabolic rate pancreas- secretes insulin to regulate metabolism ovaries- secrete estrogen for ovulation testes- release androgens for sperm production ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System Ch 33 and Brain
... mylinated nerve fibers) (note: gray matter is made of the cell bodies) b. Controls skeletal muscles, movements, balance muscle tone ...
... mylinated nerve fibers) (note: gray matter is made of the cell bodies) b. Controls skeletal muscles, movements, balance muscle tone ...
Final Exam - UF Psychology
... 4. Two competing theories of color vision are the __trichromatic theory_____________, which is based on the relative activity of the different kinds of retinal cones, and the __opponent process theory_______________, which is suggested by receptive fields with center-surround antagonism of complemen ...
... 4. Two competing theories of color vision are the __trichromatic theory_____________, which is based on the relative activity of the different kinds of retinal cones, and the __opponent process theory_______________, which is suggested by receptive fields with center-surround antagonism of complemen ...
Neurotransmission
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
The biological basis of behavior
... • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a t ...
... • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a t ...























