Changes TO - Spring Branch ISD
... statements by changing the underlined word! 1. All objects are made of matter. ...
... statements by changing the underlined word! 1. All objects are made of matter. ...
Ch 3 Matter & Change
... Another name for homogeneous mixture Can occur between any state of matter. ...
... Another name for homogeneous mixture Can occur between any state of matter. ...
honors chemistry review: chapter 1-3
... • A chemical change that has change in color iron rusting ...
... • A chemical change that has change in color iron rusting ...
NAME: period: ______ ISSUED MONDAY, November 30th, 2015 6
... 72. What are metalloids? _____________________________________________________________________________ 73. What are alkali metals? ___________________________________________________________________________ 74. What are noble gases? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 72. What are metalloids? _____________________________________________________________________________ 73. What are alkali metals? ___________________________________________________________________________ 74. What are noble gases? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
SJ #4 “1-1 Review” (p
... its name, symbol, and atomic #. 4. Some elements are very unique (one-of-a-kind). Find one and tell me its name, symbol, and atomic #, and why it’s ...
... its name, symbol, and atomic #. 4. Some elements are very unique (one-of-a-kind). Find one and tell me its name, symbol, and atomic #, and why it’s ...
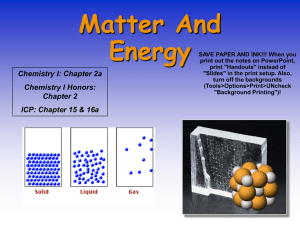
PHYSICAL SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 STATES OF MATTER
... __________________________ is the change of state from a solid to a liquid. 2. As thermal energy is added to or taken from a substance, the substance experiences either a __________________________ change or a ___________________________________________. a. You cannot heat ice above ________________ ...
... __________________________ is the change of state from a solid to a liquid. 2. As thermal energy is added to or taken from a substance, the substance experiences either a __________________________ change or a ___________________________________________. a. You cannot heat ice above ________________ ...
Matter Unit Study Guide Phases of Matter
... Temporary Changes are called physical changes. These changes only the phase changes, the substance does not. Usually changes the phase or state of matter of the substance. Permanent Changes are called chemical changes. These changes create NEW materials. The original materials are changed into somet ...
... Temporary Changes are called physical changes. These changes only the phase changes, the substance does not. Usually changes the phase or state of matter of the substance. Permanent Changes are called chemical changes. These changes create NEW materials. The original materials are changed into somet ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Thermal energy must be added to a system for a substance to change from a solid to a liquid to a gas Or Thermal energy must be removed from a system for a substance to change from a gas to a liquid to a solid. ...
... Thermal energy must be added to a system for a substance to change from a solid to a liquid to a gas Or Thermal energy must be removed from a system for a substance to change from a gas to a liquid to a solid. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... o Examples: NaCl (table salt), CO2 (carbon dioxide), H2O (water), H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) ...
... o Examples: NaCl (table salt), CO2 (carbon dioxide), H2O (water), H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) ...
A Study of Matter
... • Condensation- where a gas turns to a liquid (the sweating on a glass that is colder than it’s environment) • Sublimation point- temperature at which a solid changes directly to a gas without first changing into a liquid. (dry ice) ...
... • Condensation- where a gas turns to a liquid (the sweating on a glass that is colder than it’s environment) • Sublimation point- temperature at which a solid changes directly to a gas without first changing into a liquid. (dry ice) ...
Unit 4 Evolution
... Science Starter: Copy and answer. Can a phase change produce new compounds? No, because chemical changes occur. ...
... Science Starter: Copy and answer. Can a phase change produce new compounds? No, because chemical changes occur. ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).