Chapter 3- Matter and Energy
... Different Physical Property Separation Technique Boiling Point Distillation State of Matter (solid/liquid/gas) or Particle Size Filtration Adhere to a surface Chromatography Volatility Evaporation Solubility Recrystalization ...
... Different Physical Property Separation Technique Boiling Point Distillation State of Matter (solid/liquid/gas) or Particle Size Filtration Adhere to a surface Chromatography Volatility Evaporation Solubility Recrystalization ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *7. ________________ is the ___________ of the average _________ energy (energy of _________) of the particles (_________/molecules) *a. The ________ of matter depends on the ____________ between the __________ energy (energy of ___________) and the ____________ in the bonds (latent heat _________ ...
... *7. ________________ is the ___________ of the average _________ energy (energy of _________) of the particles (_________/molecules) *a. The ________ of matter depends on the ____________ between the __________ energy (energy of ___________) and the ____________ in the bonds (latent heat _________ ...
Chemical Building Blocks Chapter One
... Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (pg. 14) Characteristic Property: a quality of a substance that never changes and can be used to identify the substances (pg. 15) Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (pg. 16) Physical Change: a change in ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (pg. 14) Characteristic Property: a quality of a substance that never changes and can be used to identify the substances (pg. 15) Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (pg. 16) Physical Change: a change in ...
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... wires without breaking malleability: The property displayed by certain metals that enables them to be hammered, rolled out, shaped, etc. without breaking ...
... wires without breaking malleability: The property displayed by certain metals that enables them to be hammered, rolled out, shaped, etc. without breaking ...
Properties and Changes of Matter
... Now that we can describe matter, we can begin to classify it Matter-anything with mass and volume Matter is separated into two categories: pure substances and mixtures. Matter ...
... Now that we can describe matter, we can begin to classify it Matter-anything with mass and volume Matter is separated into two categories: pure substances and mixtures. Matter ...
energy is used anytime a change in matter occurs
... of matter interact to form everything around us ...
... of matter interact to form everything around us ...
9.1 Heat and Temperature
... IV. Specific Heat (CP) A value of energy associated with that specific substance. A. The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a one gram sample of a substance by 1OC or 1K. B. The material (solid, metal, liquid, gas) is IMPORTANT! ...
... IV. Specific Heat (CP) A value of energy associated with that specific substance. A. The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a one gram sample of a substance by 1OC or 1K. B. The material (solid, metal, liquid, gas) is IMPORTANT! ...
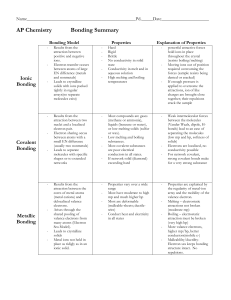
Types of Bonding Summary
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
Classification of Matter
... Matter that can not be broken down into simpler substances under normal lab conditions Contains only one kind of element Atom ...
... Matter that can not be broken down into simpler substances under normal lab conditions Contains only one kind of element Atom ...
Matter and Atoms
... I. The Four Phases of Matter A. Solid 1. solids with regular structure are described as crystalline. 2. in some solids there is no organized pattern. These are amorphous. ...
... I. The Four Phases of Matter A. Solid 1. solids with regular structure are described as crystalline. 2. in some solids there is no organized pattern. These are amorphous. ...
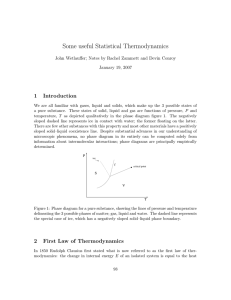
Some useful Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Introduction
... temperature, T as depicted qualitatively in the phase diagram figure 1. The negatively sloped dashed line represents ice in contact with water; the former floating on the latter. There are few other substances with this property and most other materials have a positively sloped solid–liquid coexiste ...
... temperature, T as depicted qualitatively in the phase diagram figure 1. The negatively sloped dashed line represents ice in contact with water; the former floating on the latter. There are few other substances with this property and most other materials have a positively sloped solid–liquid coexiste ...
Document
... particles from one location to another • Chemical—Chemical changes can occur in rocks when calcium carbonate in limestone changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate due to acid rain. ...
... particles from one location to another • Chemical—Chemical changes can occur in rocks when calcium carbonate in limestone changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate due to acid rain. ...
elements
... *LAW- A theory to which no exceptions are known and is thought to be absolutely correct. It does not explain why. ...
... *LAW- A theory to which no exceptions are known and is thought to be absolutely correct. It does not explain why. ...
What are the 3 primary phases of matter?
... Ex: a sprinting runner, a moving wheel or fast moving particles that are too small to see ...
... Ex: a sprinting runner, a moving wheel or fast moving particles that are too small to see ...
Day_60_2016
... consisting of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. ...
... consisting of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. ...
Bill Nye Atoms and Molecules
... They’re tiny, filled with empty space and they’re the fundamental building blocks of _____. Brought to you by ________. Particles that cannot be broken apart any farther are called ________. The middle of the atom is called the ________. Protons have a ________ charge, and neutrons have ________ cha ...
... They’re tiny, filled with empty space and they’re the fundamental building blocks of _____. Brought to you by ________. Particles that cannot be broken apart any farther are called ________. The middle of the atom is called the ________. Protons have a ________ charge, and neutrons have ________ cha ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).