Syllabus - Harrison County BOE
... Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and ...
... Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... – Divides the table of elements into two categories: • Main Group Elements- the first two groups(columns) and last six groups(columns). We notate the group number with the letter “A”. (Ex., 2A) • Transition Metals-the ten groups(columns) in the center. We notate the groups number with the letter ...
... – Divides the table of elements into two categories: • Main Group Elements- the first two groups(columns) and last six groups(columns). We notate the group number with the letter “A”. (Ex., 2A) • Transition Metals-the ten groups(columns) in the center. We notate the groups number with the letter ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... - the branch of science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of matter, with the changes that matter undergoes in composition and with the energy changes that occur during these ...
... - the branch of science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of matter, with the changes that matter undergoes in composition and with the energy changes that occur during these ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Change
... molecule by molecule, thus too small to see the different parts Can occur between any state of matter: gas in gas; liquid in gas; gas in liquid; solid in liquid; solid in solid (alloys), etc. Thus, based on the distribution of their components, mixtures are called homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
... molecule by molecule, thus too small to see the different parts Can occur between any state of matter: gas in gas; liquid in gas; gas in liquid; solid in liquid; solid in solid (alloys), etc. Thus, based on the distribution of their components, mixtures are called homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
CONDENSED MATTER: towards Absolute Zero CONDENSED
... superfluid- ie., fluid circulating around a core. From what we saw with atoms this tells us that we have probability waves circulating round the core with wavelength λ = h/p = h/mv, where v is the velocity of the atoms circulating around the core. But then we have the same situation as with the atom ...
... superfluid- ie., fluid circulating around a core. From what we saw with atoms this tells us that we have probability waves circulating round the core with wavelength λ = h/p = h/mv, where v is the velocity of the atoms circulating around the core. But then we have the same situation as with the atom ...
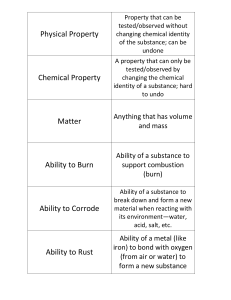
Chapter 1 Sect 1.3: Properties of matter Vocabularies: Physical
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
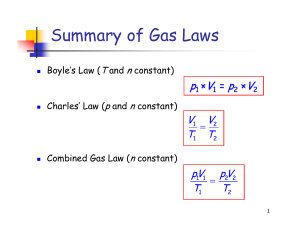
Measurable properties of gases: Pressure 1
... Pressure is a measure of the force exerted by a gas per unit area. Correspondingly, it has SI units of Newtons per square metre (Nm-2), more commonly referred to as Pascals (Pa). Several other units of pressure are in common usage, and conversions between these units and Pascals are given below: 1 ...
... Pressure is a measure of the force exerted by a gas per unit area. Correspondingly, it has SI units of Newtons per square metre (Nm-2), more commonly referred to as Pascals (Pa). Several other units of pressure are in common usage, and conversions between these units and Pascals are given below: 1 ...
Chapter 2 - Cloudfront.net
... has a fixed volume. • Particles are not arranged rigidly • Particles are in close contact with each other. • Free flowing • Volume does not change as shape of container changes; volume is fixed. • Almost incompressible • Expands slightly when heated ...
... has a fixed volume. • Particles are not arranged rigidly • Particles are in close contact with each other. • Free flowing • Volume does not change as shape of container changes; volume is fixed. • Almost incompressible • Expands slightly when heated ...
Chapter 2 Matter
... Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
... Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
Nuclear/Heat
... at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and great quantities of energy. This process causes convection currents that move Eart ...
... at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and great quantities of energy. This process causes convection currents that move Eart ...
I. States of Matter
... Dissolve as much of the mixture as possible Add water and stir Filter the mixture so that the soluble salt will be obtained in the filtrate and the insoluble chalk powder will be the residue on the filter paper Place the dry mixture into a beaker Dry out the filter paper to keep the dry chalk powder ...
... Dissolve as much of the mixture as possible Add water and stir Filter the mixture so that the soluble salt will be obtained in the filtrate and the insoluble chalk powder will be the residue on the filter paper Place the dry mixture into a beaker Dry out the filter paper to keep the dry chalk powder ...
Liquid-gas phase change dynamic equilibrium: forward and reverse
... increase in enthalpy (ΔH > 0) of the substance because the molecules need to gain energy to overcome the IMF’s. endothermic: a process in which the system gains energy. ΔH > 0 In vaporization, melting, or sublimation, a substance absorbs energy, allowing the molecules to overcome intermolecular attr ...
... increase in enthalpy (ΔH > 0) of the substance because the molecules need to gain energy to overcome the IMF’s. endothermic: a process in which the system gains energy. ΔH > 0 In vaporization, melting, or sublimation, a substance absorbs energy, allowing the molecules to overcome intermolecular attr ...
OCR Document - Northern Highlands
... b. The pill dissolves in water. c. Cutting the pill into 2 pieces. d. Mixing the pill in ice cream to make it easier to swallow. 38. A_____________ shows all states of matter of a substance and the temperatures at which they change state. a. equilibrium curve b. evaporation curve c. condensation dia ...
... b. The pill dissolves in water. c. Cutting the pill into 2 pieces. d. Mixing the pill in ice cream to make it easier to swallow. 38. A_____________ shows all states of matter of a substance and the temperatures at which they change state. a. equilibrium curve b. evaporation curve c. condensation dia ...
problem set #5 – s
... 3. If the earth is considered to be a metal sphere (radius ≈ 6371 km), how much charge Q must be deposited on its surface in order for an arc to be established in the air. If the earth’s surface was charged to this value by removing all the electrons from a volume of soil, how large would this volum ...
... 3. If the earth is considered to be a metal sphere (radius ≈ 6371 km), how much charge Q must be deposited on its surface in order for an arc to be established in the air. If the earth’s surface was charged to this value by removing all the electrons from a volume of soil, how large would this volum ...
Honors Chapter 2
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).