Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
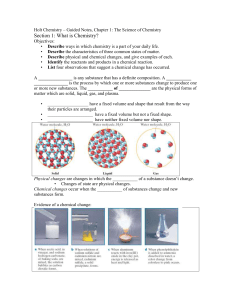
... • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance that has a definite composition. A ___________ _______________ i ...
... • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance that has a definite composition. A ___________ _______________ i ...
Chemistry! - Duplin County Schools
... – Ductile – can be stretched into a wire without breaking – Conductor – can conduct heat or electricity ...
... – Ductile – can be stretched into a wire without breaking – Conductor – can conduct heat or electricity ...
Chemistry Summative Study Guide
... 11. What is the method used to find the volume of an irregular object? ...
... 11. What is the method used to find the volume of an irregular object? ...
Other useful things to know about atoms
... o Carbon atoms are unique in that they form strong carbon-carbon bonds allowing the formation of chains, rings and networks of almost infinite variety. There are many more carbon compounds than all other compounds put together and most of these are the basis of life as we know it. It is a useful exe ...
... o Carbon atoms are unique in that they form strong carbon-carbon bonds allowing the formation of chains, rings and networks of almost infinite variety. There are many more carbon compounds than all other compounds put together and most of these are the basis of life as we know it. It is a useful exe ...
Biology Class Notes 3-1
... Aim: Why is chemistry important for the study of Biology? (A) Atoms Atom: basic unit of matter Made up of subatomic particles i. Protons: positive charge ii. Neutrons: no charge iii. Electrons: negative charge Atoms have the same number of protons and electrons—makes them neutral Protons and ...
... Aim: Why is chemistry important for the study of Biology? (A) Atoms Atom: basic unit of matter Made up of subatomic particles i. Protons: positive charge ii. Neutrons: no charge iii. Electrons: negative charge Atoms have the same number of protons and electrons—makes them neutral Protons and ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... a. is an electrically charged mixture of ions and electrons. b. is a mixture of neutrons and protons with no charge. c. exists at very low temperatures. d. is another name for the solid phase of matter. ...
... a. is an electrically charged mixture of ions and electrons. b. is a mixture of neutrons and protons with no charge. c. exists at very low temperatures. d. is another name for the solid phase of matter. ...
An Introduction to Matter
... • Chemical Change: Sugar is a compound that can be easily decomposed to simpler substances by heating. One of the simpler substances is the black element carbon, which cannot be further decomposed by chemical or physical means. ...
... • Chemical Change: Sugar is a compound that can be easily decomposed to simpler substances by heating. One of the simpler substances is the black element carbon, which cannot be further decomposed by chemical or physical means. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Lattice: a repeating pattern, like a lattice-work fence. In solids, it is a repeating pattern of atoms. All solids are made up of a lattice. The points of the lattice are different in different types of solids. ...
... Lattice: a repeating pattern, like a lattice-work fence. In solids, it is a repeating pattern of atoms. All solids are made up of a lattice. The points of the lattice are different in different types of solids. ...
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
... Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density:The measurement of how much mass of a substance is co ...
... Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density:The measurement of how much mass of a substance is co ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE 6.0/HP
... Solid: Definite shape, definite volume, particles move slowest (coolest temperature), particles packed closely together, particles cannot change positions- most dense for almost all substances Liquid: No definite shape, has definite volume, particles move faster than solid- but slower than gases, pa ...
... Solid: Definite shape, definite volume, particles move slowest (coolest temperature), particles packed closely together, particles cannot change positions- most dense for almost all substances Liquid: No definite shape, has definite volume, particles move faster than solid- but slower than gases, pa ...
What is matter?
... The state of matter a substance is in is another example of a physical property. There are 5 states (or phases) of matter. The most common are solid, liquid, and gas. The other two are plasma and BoseEinstein condensate. A substance can change states by adding or taking away energy. Each state has ...
... The state of matter a substance is in is another example of a physical property. There are 5 states (or phases) of matter. The most common are solid, liquid, and gas. The other two are plasma and BoseEinstein condensate. A substance can change states by adding or taking away energy. Each state has ...
Scientific Notation, Measurements, and
... Matter exists in 4 different states: o Solid – rigid, fixed volume and shape o Liquid – definite volume be no specific shape, assumes the shape of the container o Gas – no fixed volume or shape, takes on shape of the container, highly compressible o Plasma – exists at extremely high temperatures as ...
... Matter exists in 4 different states: o Solid – rigid, fixed volume and shape o Liquid – definite volume be no specific shape, assumes the shape of the container o Gas – no fixed volume or shape, takes on shape of the container, highly compressible o Plasma – exists at extremely high temperatures as ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).