* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Word - chemmybear.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Reflection high-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
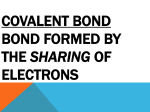
South Pasadena Chemistry Name__________________________________ Period ___ Date ___/__/___ 7 How Do Atoms Stick Together SOLIDS & PROPERTIES There are three types of bonds, but four types of solids held together with these bonds. Lattice: a repeating pattern, like a lattice-work fence. In solids, it is a repeating pattern of atoms. All solids are made up of a lattice. The points of the lattice are different in different types of solids. The three types of bonds are: Type of Bond: Ionic Description of the bond: A lattice of positive and negative ions in a repeating pattern. The opposite charges attract each other. Metallic A lattice of positive ions in a “sea of electrons”. The ions are attracted to the electrons which hold all the ions together. Covalent Two atoms sharing one, two, or three pairs of electrons between them. The electrons are strongly attracted to both nuclei. Draw the bond: Solids Bonds Used: Examples: MP/BP (high or low) Conductivity (s), (l), (aq) Malleability Molecular Metallic Ionic Covalent Network