* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 6 Jeopardy Review
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Reflection high-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
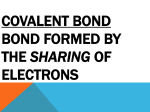
Types of Bonds Atomic Structure Electron Explaining Configuration Properties 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Potpourri In this type of bond, cations transfer valence electrons to anions. What are ionic bonds? When pairs of valence electrons are shared between atoms, these form What are covalent bonds? In this type of covalent bond, valence electrons are shared unequally. What polar covalent bonds? In this type of covalent bond, like those of diatomic molecules, valence electrons get shared equally. What are nonpolar covalent bonds? In these bonds valence electrons are able to freely move between a cation lattice. What are metallic bonds? Similar to molecules, these covalently bonded ions act like a single atom What are polyatomic ions? The lattice structure of metals is formed by these positively charged ions What are cations? These two properties determine whether a covalent bond is polar or nonpolar. What is are the types of atoms in a molecule and its shape? Ionic compounds get arranged in this rigid structure What is a crystal lattice? This is a group of covalently bonded atoms with no net charge. What is a molecule? These are electrons in the highest occupied energy level What are valence electrons? Except for elements with atomic numbers close to helium, this is how many electrons are needed to fill the outermost energy level. What is 8? This is the process by which atoms become ionized. What is the transfer of electrons (ionization)? This type of ion forms when an atom gains an electron. What is an anion? This is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. What is an ion? This is a mixture of a metal with at least one other element. What is an alloy? The intermolecular forces between this type of covalent bond is the stronger type. What are polar covalent bonds? The attractions between the shared electrons and these hold atoms together in covalent bonds. What are the nuclei? The properties of an ionic compound can be explained by these. What are the strong attractions among ions within the crystal lattice? Scientists can change the properties of alloys by changing this What are the types and amounts of elements in an alloy? This is an atom that has lost valence electrons. What is a cation? These atoms don’t form ions because they already have stable electron configurations What are noble gases? This is the name for NaCl What is Sodium Chloride? Chemical names and formulas tell you this. What are the types and number of elements? The properties of metals can be explained by this What is the mobility of valence electrons within the lattice?