Word
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
NAME: period: ______ ISSUED MONDAY, DECEMBER 1st DUE
... 40. What are metalloids? _____________________________________________________________________________ 41. What is product? _________________________________________________________________________________ 42. What is reactant? ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 40. What are metalloids? _____________________________________________________________________________ 41. What is product? _________________________________________________________________________________ 42. What is reactant? ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... BOYS: Let me see some condensation. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice) It’s physical. BOYS: Let me see some sublimation. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice) It’s physical. Phase changes are physical, physical… Boiling is physical… Boiling is physical… BOYS: Let me see some deposition. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice ...
... BOYS: Let me see some condensation. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice) It’s physical. BOYS: Let me see some sublimation. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice) It’s physical. Phase changes are physical, physical… Boiling is physical… Boiling is physical… BOYS: Let me see some deposition. GIRLS: (in high pitch voice ...
- Chemistry...It`s All Around Us!
... • TLW investigate the characteristics of matter. • TLW explore the interactions of matter & energy. ...
... • TLW investigate the characteristics of matter. • TLW explore the interactions of matter & energy. ...
Family
... Bonding – The combining of atoms. Molecule – 1. The smallest particle of a substance that retains the chemical and physical properties of the substance and is composed of two or more atoms. 2. A group of like or different atoms held together by chemical ...
... Bonding – The combining of atoms. Molecule – 1. The smallest particle of a substance that retains the chemical and physical properties of the substance and is composed of two or more atoms. 2. A group of like or different atoms held together by chemical ...
TITLE: STATES OF MATTER AT THE ATOMIC LEVEL
... 4. Construct models of atoms in the gas, liquid and solid states ...
... 4. Construct models of atoms in the gas, liquid and solid states ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
Chapter 2 What Is Matter
... Actually, solutions do not have to be a solid dissolved in a liquid. Since there are three common phases of matter, there are nine possible types of solutions. Such as: Air is a gas dissolved in a gas. Soft drinks are a gas dissolved in a liquid. Humid air is a liquid dissolved in a gas. Antifreeze ...
... Actually, solutions do not have to be a solid dissolved in a liquid. Since there are three common phases of matter, there are nine possible types of solutions. Such as: Air is a gas dissolved in a gas. Soft drinks are a gas dissolved in a liquid. Humid air is a liquid dissolved in a gas. Antifreeze ...
SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
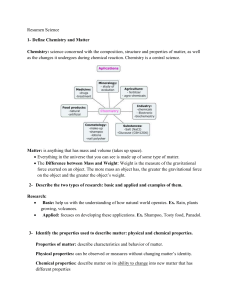
... divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substan ...
... divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substan ...
Analysis of a Matter
... divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substan ...
... divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substan ...
Ch 3 Matter & Change
... Another name for homogeneous mixture Can occur between any state of matter. ...
... Another name for homogeneous mixture Can occur between any state of matter. ...
Words to know - SD43 Teacher Sites
... boiling point conductivity density electron element hazard symbol mass melting point neutron nucleus proton state subatomic particle volume WHMIS ...
... boiling point conductivity density electron element hazard symbol mass melting point neutron nucleus proton state subatomic particle volume WHMIS ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
Solid-state physics
... metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms the theoretical basis of materials science. It also has direct applications, for ...
... metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms the theoretical basis of materials science. It also has direct applications, for ...
chapter 2
... 13. What two things are classified as pure substances?___ compounds _____ and ____ elements ______ 14. What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture? _____________________ __ HO – looks uniform in composition; HE – you can see different parts ____________ 15. Describe each o ...
... 13. What two things are classified as pure substances?___ compounds _____ and ____ elements ______ 14. What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture? _____________________ __ HO – looks uniform in composition; HE – you can see different parts ____________ 15. Describe each o ...
Properties and Changes in Matter
... • GASSES Have neither definite or fixed shape or volume. The particles in a gas are: ...
... • GASSES Have neither definite or fixed shape or volume. The particles in a gas are: ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).