Matter Quiz 2 With Answers
... a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 2. This state of matter consists of ionized particles that emit electrons. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 3. This state of matter has no defined shape of volume. No bonds exist between the atoms of the substance. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 4. This st ...
... a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 2. This state of matter consists of ionized particles that emit electrons. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 3. This state of matter has no defined shape of volume. No bonds exist between the atoms of the substance. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 4. This st ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Kinetic Theory and Heat Quiz
... that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they move, the more often they __collide__, and the less __dense_ the sample of the substance becomes. Thus, one could say that the primary difference in one state of ma ...
... that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they move, the more often they __collide__, and the less __dense_ the sample of the substance becomes. Thus, one could say that the primary difference in one state of ma ...
Elements and Atoms
... • All matter is made of atoms • Atoms are the building blocks of matter, sort of how bricks are the building blocks of houses. ...
... • All matter is made of atoms • Atoms are the building blocks of matter, sort of how bricks are the building blocks of houses. ...
Properties of Matter PowerPoint
... Chemical properties can be observed only when the substance in a sample of matter are changing into different substances. ...
... Chemical properties can be observed only when the substance in a sample of matter are changing into different substances. ...
Chemistry Quiz #2 Study Guide (Answers)
... • Endothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) entering a reaction (melting, sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
... • Endothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) entering a reaction (melting, sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
Intensive properties
... • Other properties that are extensive would include size, shape, etc. • Intensive properties are ones that only depend on what kind of stuff you have, like color, etc. ...
... • Other properties that are extensive would include size, shape, etc. • Intensive properties are ones that only depend on what kind of stuff you have, like color, etc. ...
Chemistry: the study of composition, structure, and properties of
... EX. Oil and water cannot mix. ...
... EX. Oil and water cannot mix. ...
HW 15 - Effingham County Schools
... 1. In a chemical change, the matter you start with is called the (reactant/product). 2. In a chemical change, the new matter is called the (reactant/product). 3. The state of matter where the molecules are packed tightly together is called (solid/gas). 4. The state of matter where the molecules have ...
... 1. In a chemical change, the matter you start with is called the (reactant/product). 2. In a chemical change, the new matter is called the (reactant/product). 3. The state of matter where the molecules are packed tightly together is called (solid/gas). 4. The state of matter where the molecules have ...
Matter and Energy Notes
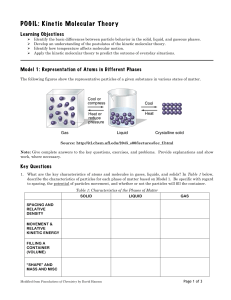
... particles vibrate but can’t move around fixed shape fixed volume ...
... particles vibrate but can’t move around fixed shape fixed volume ...
Midterm_Study_Guide_1
... As temperature increases, particle motion increases. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. Thermal energy is the sum of an object’s potential energy and kinetic energy. Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance. A change in a state of matter happens if enough thermal ener ...
... As temperature increases, particle motion increases. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. Thermal energy is the sum of an object’s potential energy and kinetic energy. Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance. A change in a state of matter happens if enough thermal ener ...
Changes of State
... WHY IS SALT SO STABLE? When salt is made, it forms a lattice, or a strong cube structure. Positive Sodium is attracted to negative Chlorine ...
... WHY IS SALT SO STABLE? When salt is made, it forms a lattice, or a strong cube structure. Positive Sodium is attracted to negative Chlorine ...
States of Matter Web
... What four things are shown on a periodic table square for an individual element? Draw and label a sample element. (Do not do Krypton! ) ...
... What four things are shown on a periodic table square for an individual element? Draw and label a sample element. (Do not do Krypton! ) ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).