* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Quiz #2 Study Guide (Answers)
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Bose–Einstein condensate wikipedia , lookup
Sessile drop technique wikipedia , lookup
Liquid crystal wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
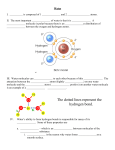
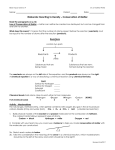
Chemistry Quiz #2 Study Guide (Answers) 1. What are the definitions to the following terms? • Melting – the process by which a substance changes from its solid state to its liquid state. (endothermic) • Sublimation – The process by which a substance changes directly from its solid state to its gas state without becoming a liquid first. (endothermic) • Evaporation – The process by which a substance changes from its liquid state to its gas state. (endothermic) • Condensation – The process by which a gas becomes a liquid. (exothermic) • Solidification – The process by which a liquid becomes a solid. (exothermic) • Deposition – The process by which a substance changes directly from a gas state to a solid state without becoming a liquid first (opposite of sublimation). (exothermic) • Diffusion – the process by which molecules mix as a result of their random motion. • Product – All substances that are formed in a chemical reaction, including invisible gases. • Reactant – All substances you start with in a chemical reaction, including invisible gases. • Subscript – The small number in a formula that identifies the number of atoms in each molecule. This cannot be changed. • Coefficient – The larger number in front of a formula that identifies the number of molecules of that specific substance. This can be changed. • Endothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) entering a reaction (melting, sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. 3. What does the Law of Conservation of Matter say? States that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can change its form. The total quantity of matter and energy available in the universe is a fixed amount, never any more or less. 4. What happens to the weight of a substance when it changes phases (liquid solid, solid liquid)? Why? Nothing happens to the weight because no molecules have been changed. It is a physical change. 5. What happened to the weight of the steel wool when it was burned and/or rusted? Why? The weight of the steel wool increased because oxygen was added to it. We did not have a valid way to measure the weight of the oxygen in the reactant. Refer to the equation for decomposing water to answer the questions 6 – 11. 2H2O 2H2 + O2 6. What is the reactant in this equation? 2H2O 7. What is the product in this equation? 2H2 + O2 8. How many atoms are on the reactant side of the equation? 6 atoms (4 Hydrogen & 2 Oxygen) 9. How many atoms are on the product side of the equation? 6 atoms (4 Hydrogen & 2 Oxygen) 10. How many molecules of water are on the reactant side? 2 molecules (2H2O) 11. How many molecules of oxygen are on the product side? 1 molecule (O2) 12. What are the chemical symbols for the following common elements? a. Oxygen - O b. Hydrogen - H c. Nitrogen - N d. Chlorine - Cl e. Carbon - C f. Iron - Fe g. Sodium - Na h. Copper - Cu