Ternary nucleation of inorganic acids, ammonia, and water
... H2 O–H2 SO4 – HNO3 , and H2 O–HNO3 – NH3 systems are taken from the thermodynamic model of Clegg et al.19 共http://www.hpc1.uea.ac.uk/⬃e770/aim.html兲. However, sulfuric acid vapor pressure is modified, as explained in our previous papers.7,16 The calculation of surface tension and density of H2 O–H2 ...
... H2 O–H2 SO4 – HNO3 , and H2 O–HNO3 – NH3 systems are taken from the thermodynamic model of Clegg et al.19 共http://www.hpc1.uea.ac.uk/⬃e770/aim.html兲. However, sulfuric acid vapor pressure is modified, as explained in our previous papers.7,16 The calculation of surface tension and density of H2 O–H2 ...
bubbles which are distributed throughout the liq
... aggregation of molecules of a volatile species into bubbles in this way is called homogeneous nucleation. The nucleation process is greatly aided if there is some, preferably irregular, surface onto which the volatile molecules can gather to minimize the effects of surface tension, in which case het ...
... aggregation of molecules of a volatile species into bubbles in this way is called homogeneous nucleation. The nucleation process is greatly aided if there is some, preferably irregular, surface onto which the volatile molecules can gather to minimize the effects of surface tension, in which case het ...
Correlated/non-correlated ion dynamics of charge
... [C4mim][NTf2]. They assume more simplified relaxation expressions for the relevant NMR relaxation mechanisms that are the intraand inter-ionic dipole–dipole interactions as induced by ionic translational and rotational diffusion of the molecular-ions. They also focus on super cooled states where ion ...
... [C4mim][NTf2]. They assume more simplified relaxation expressions for the relevant NMR relaxation mechanisms that are the intraand inter-ionic dipole–dipole interactions as induced by ionic translational and rotational diffusion of the molecular-ions. They also focus on super cooled states where ion ...
Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams
... loosely, t is the number of possible equivalent microstates in a macrostate, that is the number of quantum states for the system which are accessible under the applicable conditions of energy, volume, etc. For example, for a system which can be described by a set of single-particle energy levels, t ...
... loosely, t is the number of possible equivalent microstates in a macrostate, that is the number of quantum states for the system which are accessible under the applicable conditions of energy, volume, etc. For example, for a system which can be described by a set of single-particle energy levels, t ...
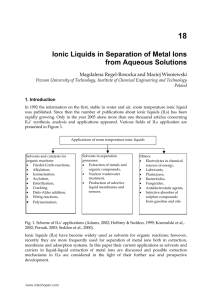
Ionic Liquids in Separation of Metal Ions from Aqueous
... the following order: [Tf2N-]<[PF6-]<[BF4-] that corresponds to decreasing hydrophobicity of the anions studied (Perez de los Rios et al., 2010). In parallel, the same authors observed increasing extraction efficiency with lengthening of the alkyl chain of imidazolium cation contrary to Cs+ extractio ...
... the following order: [Tf2N-]<[PF6-]<[BF4-] that corresponds to decreasing hydrophobicity of the anions studied (Perez de los Rios et al., 2010). In parallel, the same authors observed increasing extraction efficiency with lengthening of the alkyl chain of imidazolium cation contrary to Cs+ extractio ...
molecular dynamics studies of the stability of co2
... pressure conditions were tried before choosing these conditions. The temperature was chosen so that it is within the hydrate stability zone but not too far from the hydrate dissociation point at the chosen pressure, so that considerable amount of dissolution is observed with both methane and CO2 hyd ...
... pressure conditions were tried before choosing these conditions. The temperature was chosen so that it is within the hydrate stability zone but not too far from the hydrate dissociation point at the chosen pressure, so that considerable amount of dissolution is observed with both methane and CO2 hyd ...
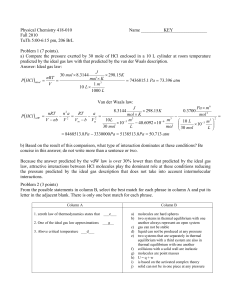
Quiz Keys - Section 10
... Problem 1 (7 points). In class we discussed the problems associated with high altitude caused by lower boiling points of liquids at lower pressures. A different kind of problem may be caused by changing a boiling point of a liquid at altitudes below sea level. Northern Europe (especially Sweden and ...
... Problem 1 (7 points). In class we discussed the problems associated with high altitude caused by lower boiling points of liquids at lower pressures. A different kind of problem may be caused by changing a boiling point of a liquid at altitudes below sea level. Northern Europe (especially Sweden and ...
The Project Gutenberg eBook #50880: Treatise on Thermodynamics.
... agreement between the readings of the different gas thermometers, for there is no sufficient reason for the preference of any one of these gases. A definition of temperature completely independent of the properties of any individual substance, and applicable to all stages of heat and cold, becomes f ...
... agreement between the readings of the different gas thermometers, for there is no sufficient reason for the preference of any one of these gases. A definition of temperature completely independent of the properties of any individual substance, and applicable to all stages of heat and cold, becomes f ...
Physical-chemical properties of complex natural fluids
... high temperature fumarole gases (a); thermodynamic properties of metamorphic fluids at high pressures (b); and the extent of hydrogen-bonding in supercritical water over wide range of densities and temperatures (c). (a) At about 10 Mpa, degassing of magmas is accompanied by formation of neary ‘dry’ ...
... high temperature fumarole gases (a); thermodynamic properties of metamorphic fluids at high pressures (b); and the extent of hydrogen-bonding in supercritical water over wide range of densities and temperatures (c). (a) At about 10 Mpa, degassing of magmas is accompanied by formation of neary ‘dry’ ...
Module Seven - DePauw University
... The examples and problems in Modules 5 and 6 assume that a compound’s amount is provided in grams. This is not surprising as mass is perhaps the most fundamental of measurements (you might recall that it is one of seven base quantities in the SI system) and it is the most accurate and precise method ...
... The examples and problems in Modules 5 and 6 assume that a compound’s amount is provided in grams. This is not surprising as mass is perhaps the most fundamental of measurements (you might recall that it is one of seven base quantities in the SI system) and it is the most accurate and precise method ...
Detailed modeling of the evaporation and thermal decomposition of
... wt. urea, marketed as Adblue®). In a typical SCR system, urea-water-solution (UWS) is sprayed into the hot engine exhaust upstream of the SCR catalyst. It is commonly believed that water evaporates first [3] and the remaining solid urea then melts and decomposes into gas phase ammonia (NH3) and isoc ...
... wt. urea, marketed as Adblue®). In a typical SCR system, urea-water-solution (UWS) is sprayed into the hot engine exhaust upstream of the SCR catalyst. It is commonly believed that water evaporates first [3] and the remaining solid urea then melts and decomposes into gas phase ammonia (NH3) and isoc ...
Halometallate ionic liquids – revisited
... Wicelinski et al.,34 in an early study of chlorogallate(III) ionic liquids, were able identify [Ga2Cl7]-, as opposed to Ga2Cl6, at χGaCl3 > 0.50, because the band at 414 cm-1, which could belong to either species, was not polarised, unlike the signal reported for Ga2Cl6 in the literature. Similarly, ...
... Wicelinski et al.,34 in an early study of chlorogallate(III) ionic liquids, were able identify [Ga2Cl7]-, as opposed to Ga2Cl6, at χGaCl3 > 0.50, because the band at 414 cm-1, which could belong to either species, was not polarised, unlike the signal reported for Ga2Cl6 in the literature. Similarly, ...
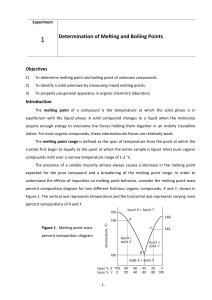
Document
... Errors in observed melting points often occur due to a poor heat transfer rate from the heat source to the compound. One cause of poor heat transfer rate is the placement of too much sample into the capillary tube. Finely ground particles of the compound are also necessary for good heat transfer. If ...
... Errors in observed melting points often occur due to a poor heat transfer rate from the heat source to the compound. One cause of poor heat transfer rate is the placement of too much sample into the capillary tube. Finely ground particles of the compound are also necessary for good heat transfer. If ...
Molecular Perspective of Static Wetting: Simulation and
... Chapter 4 explores further the role of interfacial entropy and develops a theoretical model to predict the interfacial entropy of water at rigid hydrophobic surfaces. The interfacial entropy, which is not considered in mean field models of static wettability, is evaluated from the fluctuations of t ...
... Chapter 4 explores further the role of interfacial entropy and develops a theoretical model to predict the interfacial entropy of water at rigid hydrophobic surfaces. The interfacial entropy, which is not considered in mean field models of static wettability, is evaluated from the fluctuations of t ...
Nanoelectrical analysis of single molecules and atomic
... homogeneous with an overall thickness of ∼4 Å, confirmed by ex situ high-sensitivity ellipsometry (Supplementary Section 1.1). At the nanoscale the n-C30 H62 units are seen to adsorb in a fully extended conformation with their backbone axis parallel to the underlying Au(111) substrate, recorded in t ...
... homogeneous with an overall thickness of ∼4 Å, confirmed by ex situ high-sensitivity ellipsometry (Supplementary Section 1.1). At the nanoscale the n-C30 H62 units are seen to adsorb in a fully extended conformation with their backbone axis parallel to the underlying Au(111) substrate, recorded in t ...
Alkyl Chain Length Dependence of the Dynamics and Structure in
... chain) to Bmim (4 carbon chain) and slow further, but more gradually, as the chain length is increased. It was shown previously that K+ causes local ion clustering in the Emim RTIL. The K+ effect increases with increasing chain length. The OHD-OKE measured complete structural randomization times slow ...
... chain) to Bmim (4 carbon chain) and slow further, but more gradually, as the chain length is increased. It was shown previously that K+ causes local ion clustering in the Emim RTIL. The K+ effect increases with increasing chain length. The OHD-OKE measured complete structural randomization times slow ...
Hidden Scale Invariance in Condensed Matter
... definition, two state points (ρ1, T1) and (ρ2, T2) are isomorphic whenever eq 13 applies for all their physically relevant configurations;41 for molecular systems isomorphs are defined by scaling the centers of masses while keeping the molecules’ sizes and orientations unchanged.33 This defines a mathem ...
... definition, two state points (ρ1, T1) and (ρ2, T2) are isomorphic whenever eq 13 applies for all their physically relevant configurations;41 for molecular systems isomorphs are defined by scaling the centers of masses while keeping the molecules’ sizes and orientations unchanged.33 This defines a mathem ...
Novel Methods and Materials in Development of Liquid Carrier
... Worth mentioning is in particular the team project of the whole membrane group at IVT called „the membrane book” [11], where I contributed material for two chapters (Membrane structures, materials and manufacturing; Electrodialysis). My own experience in the field of inorganic membranes together wit ...
... Worth mentioning is in particular the team project of the whole membrane group at IVT called „the membrane book” [11], where I contributed material for two chapters (Membrane structures, materials and manufacturing; Electrodialysis). My own experience in the field of inorganic membranes together wit ...
Liquid Intrusion and Alternative Methods for the Characterisation of
... pore constrictions or junctions during extrusion [8,9]. Entrapment and hysteresis are in principle of different origin (as indicated by the fact that intrusion–extrusion cycles after the first continue to show hysteresis but no entrapment, as illustrated in Fig. 1). Various mechanisms have been prop ...
... pore constrictions or junctions during extrusion [8,9]. Entrapment and hysteresis are in principle of different origin (as indicated by the fact that intrusion–extrusion cycles after the first continue to show hysteresis but no entrapment, as illustrated in Fig. 1). Various mechanisms have been prop ...
Thermodynamics of Crystal-Melt Phase Change
... with P fixed. Specifically, either solid or liquid exists as the preferred phase anywhere along their individual existence lines, each located, respectively, below and above the thermodynamic transition point, Teq . A discontinuity in the enthalpy function always occurs at Teq between the two-phase ...
... with P fixed. Specifically, either solid or liquid exists as the preferred phase anywhere along their individual existence lines, each located, respectively, below and above the thermodynamic transition point, Teq . A discontinuity in the enthalpy function always occurs at Teq between the two-phase ...
Monte Carlo Calculations for Alcohols and Their Mixtures with
... TraPPE force fields is not only to be able to reproduce thermophysical properties over a wide range of physical conditions, but also to keep the models as transferable as possible by minimizing the number of different (pseudo-)atoms needed for any particular molecule and by using the same parameters ...
... TraPPE force fields is not only to be able to reproduce thermophysical properties over a wide range of physical conditions, but also to keep the models as transferable as possible by minimizing the number of different (pseudo-)atoms needed for any particular molecule and by using the same parameters ...
Chemical Weathering on Mars
... Chemical weathering on Mars is examined theoretically from the standpoint of heterogeneous equilibrium between solid mineral phases and gaseous 02, H20, and CO2 in the Martian atmosphere. Thermochemical calculations are performed in order to identify important gas-solid decomposition reactions invol ...
... Chemical weathering on Mars is examined theoretically from the standpoint of heterogeneous equilibrium between solid mineral phases and gaseous 02, H20, and CO2 in the Martian atmosphere. Thermochemical calculations are performed in order to identify important gas-solid decomposition reactions invol ...
Development of materials, surfaces and manufacturing methods for
... vessels. Microstructured surfaces can drastically reduce the frictional losses by trapping a layer of air bubbles on the surface that can act as an air bearing for the liquid flow. The problem is that these trapped air bubbles collapse at the liquid pressures encountered in practical applications. T ...
... vessels. Microstructured surfaces can drastically reduce the frictional losses by trapping a layer of air bubbles on the surface that can act as an air bearing for the liquid flow. The problem is that these trapped air bubbles collapse at the liquid pressures encountered in practical applications. T ...
Liquid

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Water is, by far, the most common liquid on Earth. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena.The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matter. On the other hand, as liquids and gases share the ability to flow, they are both called fluids. Although liquid water is abundant on Earth, this state of matter is actually the least common in the known universe, because liquids require a relatively narrow temperature/pressure range to exist. Most known matter in the universe is in gaseous form (with traces of detectable solid matter) as interstellar clouds or in plasma form within stars.