* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Building Blocks Chapter One
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
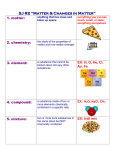
Science Explorer- Chemical Building Blocks Chapter One- An Introduction to Matter Section One Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (pg. 14) Characteristic Property: a quality of a substance that never changes and can be used to identify the substances (pg. 15) Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (pg. 16) Physical Change: a change in a substance that does not change its identity; for example, a change of state (pg. 17) Chemical Change: a change in which one or more substances combine or break apart to form new substances (pg. 17) Chemical Activity: a characteristic property of a substance that indicates its ability to undergo a specific chemical change (pg. 17) Mixture: two or more substances that are mixed together but not chemically combined (pg. 18) Pure Substance: a substance made of only one kind of matter and having definite properties (pg. 19) Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means (pg. 19) Compound: a substance made of two or more elements chemically combined (pg. 21) Section Two Weight: a measure of the force of gravity on an object (pg. 23) Mass: a measure of how much matter is in an object (pg. 14) International System of Units (SI): the system of units used by scientists to measure the properties of matter (pg. 23) Volume: the amount of space that matter occupies (pg. 23) Density: the measurement of how much mass of a substance is contained in a given volume (pg. 26) Section Three Atom: the smallest particle of an element (pg. 30) Molecule: a combination of two or more atoms (pg. 32) Chemical Bond: the force that holds two atoms together (pg. 32) Section Four Ore: a rock that contains a metal or other economically useful element (pg. 35) Electrolysis: a process by which an electric current breaks chemical bonds (pg. 36) Electrode: a metal strip that conducts electricity; often used in an electrolysis process (pg. 36)