Skinner B F. Science and human behavior. New York: Macmillan
... Walden Two,~a novel set in a social environment or community so designed that its members just naturally do the things needed to maintain it and live an enjoyable life without coercion. When I came to Harvard in 1948, I offered a course in which I interpreted well-known facts of human behavior in th ...
... Walden Two,~a novel set in a social environment or community so designed that its members just naturally do the things needed to maintain it and live an enjoyable life without coercion. When I came to Harvard in 1948, I offered a course in which I interpreted well-known facts of human behavior in th ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... 3. Zachary is expelled from school for cheating on an exam 4. Linda buys her daughter a candy bar to not be embarrassed by her temper tantrum ...
... 3. Zachary is expelled from school for cheating on an exam 4. Linda buys her daughter a candy bar to not be embarrassed by her temper tantrum ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... by a “satisfying state of affairs” tend to be repeated and those that produced an “unpleasant state of affairs” were less likely to be repeated. 2. Reinforcement, punishment and the development of operant conditioning ∙ B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) developed the term operant behavior meaning to refer to ...
... by a “satisfying state of affairs” tend to be repeated and those that produced an “unpleasant state of affairs” were less likely to be repeated. 2. Reinforcement, punishment and the development of operant conditioning ∙ B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) developed the term operant behavior meaning to refer to ...
Analysis of Behavior Using Operant Conditioning Methods
... Basic theories of learning and memory will be discussed, with a focus on how operant conditioning methods can be utilized to gain in depth understanding of underlying cognitive processes, as pioneered by B.F. Skinner. ...
... Basic theories of learning and memory will be discussed, with a focus on how operant conditioning methods can be utilized to gain in depth understanding of underlying cognitive processes, as pioneered by B.F. Skinner. ...
File
... response to a stimulus. Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) leads to unconditioned response (UR). A neutral, or Conditioned stimulus (CS) is presented repeatedly before the UCS. After repeated pairings, the CS itself leads to the Conditioned response (CR), usually the same behavior as the UCR. UCS (F ...
... response to a stimulus. Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) leads to unconditioned response (UR). A neutral, or Conditioned stimulus (CS) is presented repeatedly before the UCS. After repeated pairings, the CS itself leads to the Conditioned response (CR), usually the same behavior as the UCR. UCS (F ...
Crash Course #11 Learning
... Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ and John B. ________________ Behaviorists argued psyc ...
... Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ and John B. ________________ Behaviorists argued psyc ...
BEHAVIORISM
... Watson: “Give me a child, and I will give you any adult professional you want”) Modern classical conditioning (R.A. Rescorla, Leo J. Kamin): relationship between neutral and natural stimulus must be not only temporal, but informational (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorn ...
... Watson: “Give me a child, and I will give you any adult professional you want”) Modern classical conditioning (R.A. Rescorla, Leo J. Kamin): relationship between neutral and natural stimulus must be not only temporal, but informational (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorn ...
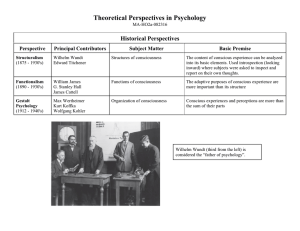
Theoretical Perspectives in Psychology
... Unconscious motives and experiences in early childhood govern personality and mental disorders. ...
... Unconscious motives and experiences in early childhood govern personality and mental disorders. ...
5 Behavioral Theories of Learning
... Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparatio ...
... Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparatio ...
AP Biology
... graylag geese. What role does the sensitive period have on an individual’s development? 13. How does bird song provide a model system for understanding the development of behavior? Contrast learning in the sensitive period (as found in white-crowned sparrows) with opened-ended learning (as found in ...
... graylag geese. What role does the sensitive period have on an individual’s development? 13. How does bird song provide a model system for understanding the development of behavior? Contrast learning in the sensitive period (as found in white-crowned sparrows) with opened-ended learning (as found in ...
AP Biology
... graylag geese. What role does the sensitive period have on an individual’s development? 13. How does bird song provide a model system for understanding the development of behavior? Contrast learning in the sensitive period (as found in white-crowned sparrows) with opened-ended learning (as found in ...
... graylag geese. What role does the sensitive period have on an individual’s development? 13. How does bird song provide a model system for understanding the development of behavior? Contrast learning in the sensitive period (as found in white-crowned sparrows) with opened-ended learning (as found in ...
Animal behavior Unit
... Learned Behavior – behavior patterns that develop/change over time through practice/experience. 1. Habituation : stimulus repeatedly given not associated with punishment or reward; eventually animal ceases to respond to stimulus. 2. Classical Conditioning: learning by association; Pavlov’s dog exper ...
... Learned Behavior – behavior patterns that develop/change over time through practice/experience. 1. Habituation : stimulus repeatedly given not associated with punishment or reward; eventually animal ceases to respond to stimulus. 2. Classical Conditioning: learning by association; Pavlov’s dog exper ...
Name: Period: Learning Reading Guide 1. What is classical
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
Learning
... Classical Conditioning - learning by association - a previously neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response originally made to another stimulus ...
... Classical Conditioning - learning by association - a previously neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response originally made to another stimulus ...
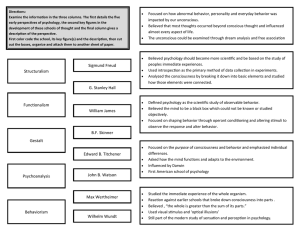
Structuralism Functionalism Gestalt Psychoanalysis Behaviorism
... Reaction against earlier schools that broke down consciousness into parts . Believed , “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.” Used visual stimulus and ‘optical illusions’ Still part of the modern study of sensation and perception in psychology. ...
... Reaction against earlier schools that broke down consciousness into parts . Believed , “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.” Used visual stimulus and ‘optical illusions’ Still part of the modern study of sensation and perception in psychology. ...
Animal Behavior
... Innate behavior is developmentally fixed, regardless of the environment This is INSTINCT ...
... Innate behavior is developmentally fixed, regardless of the environment This is INSTINCT ...
Psychology Perspectives
... • how environmental factors (called stimuli) affect observable behavior (called the response). – Classical conditioning – Operant conditioning ...
... • how environmental factors (called stimuli) affect observable behavior (called the response). – Classical conditioning – Operant conditioning ...
Historical Background of Animal Behavior
... Historical Background of Animal Behavior The rise of Animal Behavior occurred in 3 lineages: Physiological (linked to technology), Psychological, and Naturalistic Physiological – did not concentrate on whole behavior Willis - 1840 - 50 innate behavior programs - nervous transmission - reflex Pavlov ...
... Historical Background of Animal Behavior The rise of Animal Behavior occurred in 3 lineages: Physiological (linked to technology), Psychological, and Naturalistic Physiological – did not concentrate on whole behavior Willis - 1840 - 50 innate behavior programs - nervous transmission - reflex Pavlov ...
Learning
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
Name Crash Course-Psychology #11
... >By the time you get to the after-conditioning phase, that old neutral stimulus has become a _______________________________ stimulus, because it now elicits the _____________________________ response of drooling. 4) Pavlov’s work suggested that _______________________________ ______________________ ...
... >By the time you get to the after-conditioning phase, that old neutral stimulus has become a _______________________________ stimulus, because it now elicits the _____________________________ response of drooling. 4) Pavlov’s work suggested that _______________________________ ______________________ ...
Ch. 52 - Crestwood Local Schools
... Touch a hot flame, learn to stay away from fire! Salivation at the sound of a bell…example of _____? Trial and error to get a desired result… Some are simply due to the biology of the animal. – Now have I.D.ed specific genes that may govern behavior ...
... Touch a hot flame, learn to stay away from fire! Salivation at the sound of a bell…example of _____? Trial and error to get a desired result… Some are simply due to the biology of the animal. – Now have I.D.ed specific genes that may govern behavior ...