REDUCTIONISM - School of Psychology
... • Symmetry between electricity and magnetism: Explained the nature of light as electromagnetic waves moving at speed c. ...
... • Symmetry between electricity and magnetism: Explained the nature of light as electromagnetic waves moving at speed c. ...
Behaviorism
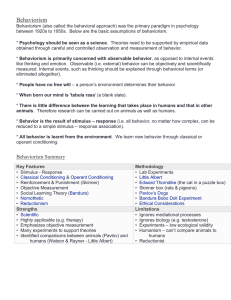
... Behaviorism (also called the behavioral approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950s. Below are the basic assumptions of behaviorism. * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observati ...
... Behaviorism (also called the behavioral approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950s. Below are the basic assumptions of behaviorism. * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observati ...
Behavioral Theory rev 2012
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
M O D U L E 1 0
... 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinforcer. 23 spanking serves as a model for future ____________ behaviors. 25 in operant condition ...
... 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinforcer. 23 spanking serves as a model for future ____________ behaviors. 25 in operant condition ...
Applied Behavior Analysis Vocabulary Antecedent stimulus
... Operant conditioning – the arrangement of environmental variables to establish a functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probabi ...
... Operant conditioning – the arrangement of environmental variables to establish a functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probabi ...
File - Farrell`s Class Page
... Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. Often used for “quick results” but psychologists recommend reinforcement instead due to weaknesses of punishment. ...
... Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. Often used for “quick results” but psychologists recommend reinforcement instead due to weaknesses of punishment. ...
File
... You must complete all three section of the unit. For full points 3 pages minimum. III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior — including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and g ...
... You must complete all three section of the unit. For full points 3 pages minimum. III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior — including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and g ...
Learning
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
Agenda * Wednesday, January 8th
... • Individual feelings, perception, use of language, thought processes, etc. • Example: Body Dysmorphic Disorder, maps of the school ...
... • Individual feelings, perception, use of language, thought processes, etc. • Example: Body Dysmorphic Disorder, maps of the school ...
III.Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to
... III.Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior— including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
... III.Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior— including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
Document
... This included the goals and methods of psychology. Behaviorism should apply the techniques of animal research(i.e. conditioning) to the study of human beings Behavior can be reduced to relationships between stimuli and responses, the S—R model. A stimulus can be shown to cause a response or a ...
... This included the goals and methods of psychology. Behaviorism should apply the techniques of animal research(i.e. conditioning) to the study of human beings Behavior can be reduced to relationships between stimuli and responses, the S—R model. A stimulus can be shown to cause a response or a ...
Conditioning and Learning Essays
... 1. Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are different learning methods. Their differences lie in a. The extent to which reinforcement depends on the behavior of the learner b. The type of behavior to which each method applies. Their similarities are that they both produce the following ba ...
... 1. Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are different learning methods. Their differences lie in a. The extent to which reinforcement depends on the behavior of the learner b. The type of behavior to which each method applies. Their similarities are that they both produce the following ba ...
Perspectives Chart
... Studies observable and measurable behavior Ivan Pavlov (1849 – 1936) – Russian physiologist, classical conditioning discovering while experimenting with dogs John B. Watson (1878 – 1958) – Watson states that biology is NOT destiny, but it does precondition us B.F. Skinner (1904 – 1905) – reinforceme ...
... Studies observable and measurable behavior Ivan Pavlov (1849 – 1936) – Russian physiologist, classical conditioning discovering while experimenting with dogs John B. Watson (1878 – 1958) – Watson states that biology is NOT destiny, but it does precondition us B.F. Skinner (1904 – 1905) – reinforceme ...
Reading Guide
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT
... H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF BEHAVIOR 1. Explain how hormones can affect the environment during development and result in differences in behavior between males and females. 2. What is the adaptive significance of restricted developmental programs (a ...
... H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF BEHAVIOR 1. Explain how hormones can affect the environment during development and result in differences in behavior between males and females. 2. What is the adaptive significance of restricted developmental programs (a ...
Learning Approach (Behaviorist Model)
... Does NOT focus on •Personality •Drives •Motivators •Feelings (although they recognize fear and anxiety) •Thought processes (like memory) ...
... Does NOT focus on •Personality •Drives •Motivators •Feelings (although they recognize fear and anxiety) •Thought processes (like memory) ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... D. learned behaviors 15. Each year, green sea turtles travel back and forth between their feeding and nesting grounds. This is an example of A. kin selection. C. hibernation. ...
... D. learned behaviors 15. Each year, green sea turtles travel back and forth between their feeding and nesting grounds. This is an example of A. kin selection. C. hibernation. ...
Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type
... A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Reward ...
... A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Reward ...