phosphate
... Glucose Synthesis Gluconeogenesis is: The synthesis of glucose from carbon atoms of noncarbohydrate compounds. Required when glycogen stores are depleted. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
... Glucose Synthesis Gluconeogenesis is: The synthesis of glucose from carbon atoms of noncarbohydrate compounds. Required when glycogen stores are depleted. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
AP Biology Chapter Objectives – Campbell 7th Edition Modified from
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP …
... transfer potential which is given by Go for hydrolysis of ATP (-7.3kcal/mol) The electron transfer potential of NADH is represented as Eo the redox potential ( or reduction potential or oxidationreduction potential) which is an electrochemical concept. Redox potential is measured relative to the H+ ...
... transfer potential which is given by Go for hydrolysis of ATP (-7.3kcal/mol) The electron transfer potential of NADH is represented as Eo the redox potential ( or reduction potential or oxidationreduction potential) which is an electrochemical concept. Redox potential is measured relative to the H+ ...
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
... and converts that energy into a usable form: electricity. Organisms also transform energy. For example, plants rely on energy from the Sun to survive. They convert light energy from the Sun into chemical energy that is used to maintain life processes. But how exactly do plants convert energy from on ...
... and converts that energy into a usable form: electricity. Organisms also transform energy. For example, plants rely on energy from the Sun to survive. They convert light energy from the Sun into chemical energy that is used to maintain life processes. But how exactly do plants convert energy from on ...
metabole = change
... -Catabolism is the degradative process to harvest energy from breaking down the macromolecules to simpler compounds. Cellular respiration is the main process to convert potential energy stored in macromolecules into available energy for cellular work. ...
... -Catabolism is the degradative process to harvest energy from breaking down the macromolecules to simpler compounds. Cellular respiration is the main process to convert potential energy stored in macromolecules into available energy for cellular work. ...
2. Citric acid cycle
... • pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde • acetaldehyde accepts e• ethanol produced ...
... • pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde • acetaldehyde accepts e• ethanol produced ...
Cellular Respiration - Napa Valley College
... § Requires oxygen: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor on the electron transport chain. § One glucose can produce a total of 36 ATP ...
... § Requires oxygen: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor on the electron transport chain. § One glucose can produce a total of 36 ATP ...
1 22,25 October 2004 Physiology of Locomotion R. B. Huey I. Some
... 2. Fuels -- oxidation of carbon fuels (fats, carbohydrates, amino acids) 3. Very efficient -- 12 to 15 more ATP per mole glucose than anaerobic glycolysis. Also relatively "clean" -- produces water and CO2. 3. The “Bad” -- requires O2. Only small intracellular stores of O2 are available, and environ ...
... 2. Fuels -- oxidation of carbon fuels (fats, carbohydrates, amino acids) 3. Very efficient -- 12 to 15 more ATP per mole glucose than anaerobic glycolysis. Also relatively "clean" -- produces water and CO2. 3. The “Bad” -- requires O2. Only small intracellular stores of O2 are available, and environ ...
2. Citric acid cycle
... • Cells convert ~ 40% of energy in glucose to energy in ATP • Most fuel efficient cars convert only ~ 25% of gasoline energy ...
... • Cells convert ~ 40% of energy in glucose to energy in ATP • Most fuel efficient cars convert only ~ 25% of gasoline energy ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... full file at http://testbankeasy.com ...
... full file at http://testbankeasy.com ...
Chapter 11
... – Catabolism of glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, or alcohol • Energy stored in carbon-hydrogen bonds is captured in the high energy compound ATP ...
... – Catabolism of glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, or alcohol • Energy stored in carbon-hydrogen bonds is captured in the high energy compound ATP ...
Where is the energy transfer?
... In the Calvin Cycle, CO2 is attached to a molecule of RUBP. This is catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco. The six carbon product splits, forming two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. 3-phosphyglycerate receives a phosphate from ATP and electrons from NADPH forming a molecule of G3P. Two molecules of G3P c ...
... In the Calvin Cycle, CO2 is attached to a molecule of RUBP. This is catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco. The six carbon product splits, forming two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. 3-phosphyglycerate receives a phosphate from ATP and electrons from NADPH forming a molecule of G3P. Two molecules of G3P c ...
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, Fru and Gal
... The pentose phosphate pathway A shunt from glycolysis Production of NADPH (reductive syntheses, detoxifications), ...
... The pentose phosphate pathway A shunt from glycolysis Production of NADPH (reductive syntheses, detoxifications), ...
CHEM 260 | ELEMENTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY L/L
... Pre-requisite: Chemistry 240 or Chemistry 241. Survey course on the dynamic nature of the chemistry of life. Includes topics on cellular structure, proteins, enzymes, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and metabolism. Directed toward majors in dietetics, health fields, agriculture, and biotechnolo ...
... Pre-requisite: Chemistry 240 or Chemistry 241. Survey course on the dynamic nature of the chemistry of life. Includes topics on cellular structure, proteins, enzymes, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and metabolism. Directed toward majors in dietetics, health fields, agriculture, and biotechnolo ...
1 - contentextra
... 14 Cell respiration is common to all cells and explains how a cell derives energy in the form of ATP molecules using organic molecules, such as glucose, as a fuel. Some cells use a relatively inefficient form of cell respiration called anaerobic respiration and others a much more efficient form call ...
... 14 Cell respiration is common to all cells and explains how a cell derives energy in the form of ATP molecules using organic molecules, such as glucose, as a fuel. Some cells use a relatively inefficient form of cell respiration called anaerobic respiration and others a much more efficient form call ...
1 - contentextra
... 14 Cell respiration is common to all cells and explains how a cell derives energy in the form of ATP molecules using organic molecules, such as glucose, as a fuel. Some cells use a relatively inefficient form of cell respiration called anaerobic respiration and others a much more efficient form call ...
... 14 Cell respiration is common to all cells and explains how a cell derives energy in the form of ATP molecules using organic molecules, such as glucose, as a fuel. Some cells use a relatively inefficient form of cell respiration called anaerobic respiration and others a much more efficient form call ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
Review 1-9 I - Gooch
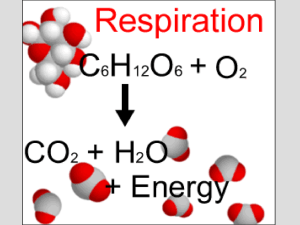
... Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration – break down of sugars in the presence of oxygen. Sugar + Oxygen makes Carbon Dioxide + water ATP ...
... Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration – break down of sugars in the presence of oxygen. Sugar + Oxygen makes Carbon Dioxide + water ATP ...
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions
... Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions: light dependent and light independent The light dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of chloroplasts which contain ...
... Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions: light dependent and light independent The light dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of chloroplasts which contain ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction?
... Properties of Enzymes 1. Lowers activation energy 2. Speeds up a reaction 3. Can be used repeatedly 4. Shape specific (substrate)* *If shape is altered, enzyme cannot function Animations ...
... Properties of Enzymes 1. Lowers activation energy 2. Speeds up a reaction 3. Can be used repeatedly 4. Shape specific (substrate)* *If shape is altered, enzyme cannot function Animations ...
Introductory Microbiology Chap. 5 Outlines Microbial Metabolism I
... bond) is provided by the movement of protons back into the cell during chemiosmosis. 3) When the protons rush back into the cell (due to the gradient), energy is released. This may cause a CONFORMATIONAL (shape) change in the enzyme ATP synthase. ATP synthase that then catalyzes the reaction: ...
... bond) is provided by the movement of protons back into the cell during chemiosmosis. 3) When the protons rush back into the cell (due to the gradient), energy is released. This may cause a CONFORMATIONAL (shape) change in the enzyme ATP synthase. ATP synthase that then catalyzes the reaction: ...
3 – Efficiency of Cellular Respiration
... 3) How does NADH produced during glycolysis present a problem for the overall efficiency of cellular respiration? 4) Explain the malate-aspartate shuttle and the glycerol-phosphate shuttle in a diagram. You may choose to model your diagram after the proposed outline below. You may want to note (but ...
... 3) How does NADH produced during glycolysis present a problem for the overall efficiency of cellular respiration? 4) Explain the malate-aspartate shuttle and the glycerol-phosphate shuttle in a diagram. You may choose to model your diagram after the proposed outline below. You may want to note (but ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the presence of oxygen) or anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen). A large amount of ATP is made during aerobic respiration. NAD+ is recycled during the anaerobic process of fermen ...
... •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the presence of oxygen) or anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen). A large amount of ATP is made during aerobic respiration. NAD+ is recycled during the anaerobic process of fermen ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑