emboj7601444-sup
... Wild-type bovine E2bCD (residues 162-421) fused at their amino-termini to maltosebinding protein (MBP), with the tobacco-etch virus (TEV) recognition sequence inserted in between the two moieties, was expressed in E. coli BL-21 (DE3) cells, similar to the method described previously (Wynn et al., 19 ...
... Wild-type bovine E2bCD (residues 162-421) fused at their amino-termini to maltosebinding protein (MBP), with the tobacco-etch virus (TEV) recognition sequence inserted in between the two moieties, was expressed in E. coli BL-21 (DE3) cells, similar to the method described previously (Wynn et al., 19 ...
Document
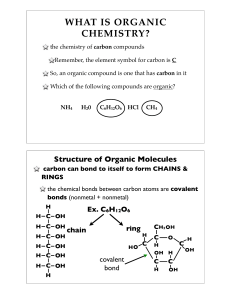
... -Unmodified glucose reacts with oxidizing agents such as Cu2+ because the open-chain form has a free aldehyde group that is readily oxidized.(=reducing sugar) -Methyl glucopyranoside do not react .(=non-reducing sugar) -Glucose react with hemoglobin to form glycosylated hemoglobin. diabete ...
... -Unmodified glucose reacts with oxidizing agents such as Cu2+ because the open-chain form has a free aldehyde group that is readily oxidized.(=reducing sugar) -Methyl glucopyranoside do not react .(=non-reducing sugar) -Glucose react with hemoglobin to form glycosylated hemoglobin. diabete ...
Document
... -Unmodified glucose reacts with oxidizing agents such as Cu2+ because the open-chain form has a free aldehyde group that is readily oxidized.(=reducing sugar) -Methyl glucopyranoside do not react .(=non-reducing sugar) -Glucose react with hemoglobin to form glycosylated hemoglobin. diabete ...
... -Unmodified glucose reacts with oxidizing agents such as Cu2+ because the open-chain form has a free aldehyde group that is readily oxidized.(=reducing sugar) -Methyl glucopyranoside do not react .(=non-reducing sugar) -Glucose react with hemoglobin to form glycosylated hemoglobin. diabete ...
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Basis of Medical
... 30. You and your study partner are trying to determine whether the microsomal ethanol oxidizing system (MEOS) can be considered a detoxification pathway. Which of the following properties of MEOS would make you think this? a. It is a cytochrome P450 mixed oxidase b. It is induced by high levels of e ...
... 30. You and your study partner are trying to determine whether the microsomal ethanol oxidizing system (MEOS) can be considered a detoxification pathway. Which of the following properties of MEOS would make you think this? a. It is a cytochrome P450 mixed oxidase b. It is induced by high levels of e ...
8 excretory
... Removing waste products from the body is the major function of the excretory system. It works with both the respiratory and circulatory system to remove these wastes. There are four major organs in the excretory system. These organs are the lungs, liver, kidneys and skin. You have learned that the l ...
... Removing waste products from the body is the major function of the excretory system. It works with both the respiratory and circulatory system to remove these wastes. There are four major organs in the excretory system. These organs are the lungs, liver, kidneys and skin. You have learned that the l ...
Ch 25 Powerpoint
... Most abundant organic components in body Perform many vital cellular functions ...
... Most abundant organic components in body Perform many vital cellular functions ...
清华大学本科生考试试题专用纸
... 41. Explain why skeletal muscle does not contribute glucose to the blood. (4 points) Answer: Because it lacks the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase. 42. Explain why untreated diabetics lose weight. (4 points) Answer: The rate of triacylglycerol biosynthesis is affected by the action of several hormones, ...
... 41. Explain why skeletal muscle does not contribute glucose to the blood. (4 points) Answer: Because it lacks the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase. 42. Explain why untreated diabetics lose weight. (4 points) Answer: The rate of triacylglycerol biosynthesis is affected by the action of several hormones, ...
ID_4450_General principles of metaboli_English_sem_5
... None of the above Contains phospholipase A2 catalyzing the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids and formation of lysophosphoglycerides which can act as detergents and disrupt cellular membranes After meal concentration of chylomicrones in blood of the patient is increased. Chylomicrones are formed in ...
... None of the above Contains phospholipase A2 catalyzing the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids and formation of lysophosphoglycerides which can act as detergents and disrupt cellular membranes After meal concentration of chylomicrones in blood of the patient is increased. Chylomicrones are formed in ...
NASM CHAPTER 4 EXERCISE METABOLISM AND BIOENERGETICS
... – When sufficient oxygen is available, more ATP can be produced via the breakdown of carbohydrates and fat. – The aerobic metabolism of fat yields larger amounts of ATP compared to glucose (fat = 9 kcal/gram; ...
... – When sufficient oxygen is available, more ATP can be produced via the breakdown of carbohydrates and fat. – The aerobic metabolism of fat yields larger amounts of ATP compared to glucose (fat = 9 kcal/gram; ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... A) The uncoupler is an allosteric activator of ATP synthase. This increases the rate of translocation of H+ and the oxidation of fuels, including fats. B) The uncoupler allows the oxidation of fats from adipose tissue without the production of ATP. This allows the oxidation to proceed continuously a ...
... A) The uncoupler is an allosteric activator of ATP synthase. This increases the rate of translocation of H+ and the oxidation of fuels, including fats. B) The uncoupler allows the oxidation of fats from adipose tissue without the production of ATP. This allows the oxidation to proceed continuously a ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism - LSU School of Medicine
... These reactions are mitochondrial analogues of the (cytosolic) first two steps of cholesterol synthesis Third step - HMG-CoA lyase - is similar to the reverse of citrate synthase ...
... These reactions are mitochondrial analogues of the (cytosolic) first two steps of cholesterol synthesis Third step - HMG-CoA lyase - is similar to the reverse of citrate synthase ...
Bio130_MidtermReviewPart3
... to CO2 and gives off energy • Aerobic respiration – glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, respiratory chain • Anaerobic respiration – glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, respiratory chain; molecular oxygen is not the final electron acceptor • Fermentation – glycolysis, organic compounds are the final electron acc ...
... to CO2 and gives off energy • Aerobic respiration – glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, respiratory chain • Anaerobic respiration – glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, respiratory chain; molecular oxygen is not the final electron acceptor • Fermentation – glycolysis, organic compounds are the final electron acc ...
Cycles of Life: EXPLORING BIOLOGY Module 2
... • The second law states that entropy or “randomness” is increasing as transformations occur. • With each conversion or use of energy, the total system becomes more disordered, so energy is converted at a price. 3. Do these laws hold true for metabolic processes? Explain. • Of course. For example, an ...
... • The second law states that entropy or “randomness” is increasing as transformations occur. • With each conversion or use of energy, the total system becomes more disordered, so energy is converted at a price. 3. Do these laws hold true for metabolic processes? Explain. • Of course. For example, an ...
- Circle of Docs
... 88. What is the total number of high energy phosphates generated by 1 mole of acetyl Co-A through one round of the Tricarboxycylic cycle A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 88. What is the total number of high energy phosphates generated by 1 mole of acetyl Co-A through one round of the Tricarboxycylic cycle A. B. C. D. E. ...
Cancer_JC_presentation_2009
... constitutive signaling through EGFR and PI3K, and it depends on flux through the PPP • Antioxidants can reverse the metabolic defect, independent of glucose uptake, by increasing flux through the PPP • Antioxidants can enhance the transforming activity of oncogenic cells. ...
... constitutive signaling through EGFR and PI3K, and it depends on flux through the PPP • Antioxidants can reverse the metabolic defect, independent of glucose uptake, by increasing flux through the PPP • Antioxidants can enhance the transforming activity of oncogenic cells. ...
Biochemical methods of conversion
... energy to form ATP. In addition to the carbon source, micro-organisms, particularly bacteria, require other nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus (Figure 14.3). In the process of glycolysis, glucose is converted into glucose-6phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, and fructose 1,6-diphosphate by the addi ...
... energy to form ATP. In addition to the carbon source, micro-organisms, particularly bacteria, require other nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus (Figure 14.3). In the process of glycolysis, glucose is converted into glucose-6phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, and fructose 1,6-diphosphate by the addi ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... pH can be determined using pH paper (different colors indicate different pH levels) or bromothymol blue/BTB (turns yellow in the presence of an acid). The presence of starch (a carbohydrate) is indicated when iodine changes from a rusty brown to a blue or black. The presence of blood is indicated wh ...
... pH can be determined using pH paper (different colors indicate different pH levels) or bromothymol blue/BTB (turns yellow in the presence of an acid). The presence of starch (a carbohydrate) is indicated when iodine changes from a rusty brown to a blue or black. The presence of blood is indicated wh ...
Document
... all have the same chemical formula: C12H22O11 they are ISOMERS of each other they can only be absorbed into the intestine & blood stream when they are broken down into their monomers (monosaccharides) by enzymes Examples ...
... all have the same chemical formula: C12H22O11 they are ISOMERS of each other they can only be absorbed into the intestine & blood stream when they are broken down into their monomers (monosaccharides) by enzymes Examples ...
Document
... molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD) represents stored energy that is tapp ...
... molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD) represents stored energy that is tapp ...
FinalReview
... (a) Energy is released when electrons are moved from an energy source with a low affinity for electrons to a terminal electron acceptor with a higher affinity. ...
... (a) Energy is released when electrons are moved from an energy source with a low affinity for electrons to a terminal electron acceptor with a higher affinity. ...
Lecture 28 - Citrate Cycle
... • The primary function of the citrate cycle is to convert energy available from the oxidization acetyl-CoA into 3 moles of NADH, 1 mole of FADH2 and 1 mole of GTP during each turn of the cycle. • The citrate cycle is a "metabolic engine" in which all eight of the cycle intermediates are continually ...
... • The primary function of the citrate cycle is to convert energy available from the oxidization acetyl-CoA into 3 moles of NADH, 1 mole of FADH2 and 1 mole of GTP during each turn of the cycle. • The citrate cycle is a "metabolic engine" in which all eight of the cycle intermediates are continually ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑