Slide 1
... FIGURE 2.7 Effects of excess FFA in muscle cells. Molecular steps that lead from increased circulating FFA to insulin resistance (top left) exist together with opposing influences exerted by exercise or the antidiabetic drug metformin (top left and top right). Excess FFA entering the cell is activa ...
... FIGURE 2.7 Effects of excess FFA in muscle cells. Molecular steps that lead from increased circulating FFA to insulin resistance (top left) exist together with opposing influences exerted by exercise or the antidiabetic drug metformin (top left and top right). Excess FFA entering the cell is activa ...
Chemistry of Life
... The pH scale is a shorthand method of describing the concentration of hydrogen ions in any solution. The pH scale uses numbers from 0 to 14. A solution with a pH number below 7 has an excess concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and is referred to as an acid. If the pH number is greater than 7, the so ...
... The pH scale is a shorthand method of describing the concentration of hydrogen ions in any solution. The pH scale uses numbers from 0 to 14. A solution with a pH number below 7 has an excess concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and is referred to as an acid. If the pH number is greater than 7, the so ...
Chapter 24_CHEM 131
... • Several hormones, including epinephrine, stimulate fat mobilization when body cells need fatty acids for energy. • Fat mobilization entails the hydrolysis of stored triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol which then enter the bloodstream. • In blood, mobilized fatty acids form a lipoprotein wi ...
... • Several hormones, including epinephrine, stimulate fat mobilization when body cells need fatty acids for energy. • Fat mobilization entails the hydrolysis of stored triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol which then enter the bloodstream. • In blood, mobilized fatty acids form a lipoprotein wi ...
Measuring Fatty Acid Oxidation using the MitoXpress FAO Kit
... By using Oleate as the primary energy source, oxygen consumption, as measured using MitoXpress® Xtra, becomes a convenient high-throughput indicator of FAO activity. In addition, using a common dietary unsaturated FA such as Oleate means that, as well as monitoring the core machinery of β-oxidation, ...
... By using Oleate as the primary energy source, oxygen consumption, as measured using MitoXpress® Xtra, becomes a convenient high-throughput indicator of FAO activity. In addition, using a common dietary unsaturated FA such as Oleate means that, as well as monitoring the core machinery of β-oxidation, ...
Xu-7-integration
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
Biology 12 – Practice Final Exam 5) Describe the changes that occur
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
Handout 5 - Fatty Acid Synthesis
... 1. Carbon must enter the mitochondria and be converted to both OAA and AcCoA, which form citrate. 2. The citrate exits the mitochondria and is hydrolyzed by citrate lyase (or citrate cleavage enzyme). 3. The AcCoA is utilized for fatty acid synthesis (palmitate). 4. The OAA is reduced to malate, whe ...
... 1. Carbon must enter the mitochondria and be converted to both OAA and AcCoA, which form citrate. 2. The citrate exits the mitochondria and is hydrolyzed by citrate lyase (or citrate cleavage enzyme). 3. The AcCoA is utilized for fatty acid synthesis (palmitate). 4. The OAA is reduced to malate, whe ...
HPER 334 Nutrition Exam 2
... c. Essential fatty acids d. Nonessential fatty acids 33. A compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with 3 fatty acids attached to molecule of glycerol would be known as a a. diglyceride. b. triglyceride. c. phospholipid. d. monoglyceride. 34. What is the function of beta oxidation in the o ...
... c. Essential fatty acids d. Nonessential fatty acids 33. A compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with 3 fatty acids attached to molecule of glycerol would be known as a a. diglyceride. b. triglyceride. c. phospholipid. d. monoglyceride. 34. What is the function of beta oxidation in the o ...
Assessing the Impact of Autophagy on Cellular Metabolism
... the cell. Defective lipophagy has been implicated in obesity, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Although the role of lipophagy within the cell during nutrient deprivation has not been extensively studied, a recent publication from Rambold; et al. (2015)4 did examine the pathway ...
... the cell. Defective lipophagy has been implicated in obesity, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Although the role of lipophagy within the cell during nutrient deprivation has not been extensively studied, a recent publication from Rambold; et al. (2015)4 did examine the pathway ...
Final a
... 4. (10 pts) List the environmental conditions/small molecules that activate rubisco and/or enzymes of the Calvin cycle. ...
... 4. (10 pts) List the environmental conditions/small molecules that activate rubisco and/or enzymes of the Calvin cycle. ...
Exam IV answers
... lymphoid cells, causing its activation and movement to the nucleus where it activates transcription of lipocortin. The lipocortin protein inhibits phospholipase A2, thus reducing the supply of the starting material for eicosanoid biosynthesis. The cortisol/cortisone – receptor complex also represses ...
... lymphoid cells, causing its activation and movement to the nucleus where it activates transcription of lipocortin. The lipocortin protein inhibits phospholipase A2, thus reducing the supply of the starting material for eicosanoid biosynthesis. The cortisol/cortisone – receptor complex also represses ...
molecule building organic
... The cell with the aid of enzymes combines small molecules into large complex molecules. This process makes cell organelles and substances necessary for cell activity. This is the way that starch is formed from glucose molecules and proteins are formed from amino acids. The monomers are linked togeth ...
... The cell with the aid of enzymes combines small molecules into large complex molecules. This process makes cell organelles and substances necessary for cell activity. This is the way that starch is formed from glucose molecules and proteins are formed from amino acids. The monomers are linked togeth ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... The ____ dimensional____________ into alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets ______________ dimensional bends and kinks in secondary structure due to the interactions between________________ ______________________ polypeptide chains join together to make a ___________ structure ...
... The ____ dimensional____________ into alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets ______________ dimensional bends and kinks in secondary structure due to the interactions between________________ ______________________ polypeptide chains join together to make a ___________ structure ...
removal of amino gp from glutamate to release ammonia Other
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... atomic # of 6 which means it has 6 protons and 6 electrons It has 4 vacancies in the outer energy level ...
... atomic # of 6 which means it has 6 protons and 6 electrons It has 4 vacancies in the outer energy level ...
How life evolved: 10 steps to the first cells
... Fatty molecules coated the iron-sulphur froth and spontaneously formed cell-like bubbles. Some of these bubbles would have enclosed self-replicating sets of molecules – the first organic cells. The earliest protocells may have been elusive entities, though, often dissolving and reforming as they cir ...
... Fatty molecules coated the iron-sulphur froth and spontaneously formed cell-like bubbles. Some of these bubbles would have enclosed self-replicating sets of molecules – the first organic cells. The earliest protocells may have been elusive entities, though, often dissolving and reforming as they cir ...
Cellular Energy and Mitochondrial ATP Production: A
... Anaerobic Respiration Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is known as glycolysis. This stage is unique to glucose metabolism which takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. Through a series of biochemical enzymatic reactions the process of glycolysis break ...
... Anaerobic Respiration Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is known as glycolysis. This stage is unique to glucose metabolism which takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. Through a series of biochemical enzymatic reactions the process of glycolysis break ...
Slides
... §S. cerevisiae is the only yeast that can produce ethanol and CO2 in such large quantities §S. cerevisiae ferments carbohydrates efficiently and dominates its environment due to the Crabtree effect §Unlike most fermenting organisms S. cerevisiae can also ferment sugar in the presence of O2 §As gluco ...
... §S. cerevisiae is the only yeast that can produce ethanol and CO2 in such large quantities §S. cerevisiae ferments carbohydrates efficiently and dominates its environment due to the Crabtree effect §Unlike most fermenting organisms S. cerevisiae can also ferment sugar in the presence of O2 §As gluco ...
01 - ALCA
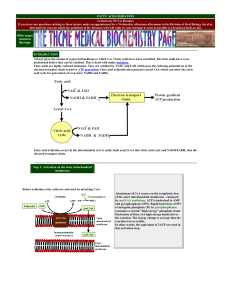
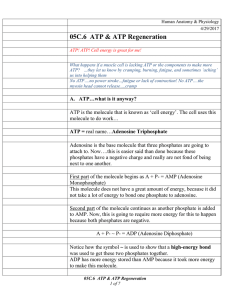
... process of taking carbons off molecules, which need oxygen to pick them up…making this cycle AEROBIC! 05C.6 ATP & ATP Regeneration 4 of 7 ...
... process of taking carbons off molecules, which need oxygen to pick them up…making this cycle AEROBIC! 05C.6 ATP & ATP Regeneration 4 of 7 ...
Organic Compounds
... Starches are among the most important polysaccharides. They represent a sugar reserve in plants and are composed of hundreds and hundreds molecules of glucose, linked to one another. Much of the world’s human population satisfies its energy needs with the starches contained in rice, wheat and potato ...
... Starches are among the most important polysaccharides. They represent a sugar reserve in plants and are composed of hundreds and hundreds molecules of glucose, linked to one another. Much of the world’s human population satisfies its energy needs with the starches contained in rice, wheat and potato ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑