Molecular genetics
... 2. B-DNA is the usual form of right handed DNA with 10 base pairs in one turn. A-DNA (11 base pairs), C-DNA (9 base pairs) and D-DNA (8 base pairs) are forms of DNA produced in experimental conditions. Z-DNA is the left handed DNA discovered by Rich, Nordheim and Wang in 1984. It has 12 base pairs p ...
... 2. B-DNA is the usual form of right handed DNA with 10 base pairs in one turn. A-DNA (11 base pairs), C-DNA (9 base pairs) and D-DNA (8 base pairs) are forms of DNA produced in experimental conditions. Z-DNA is the left handed DNA discovered by Rich, Nordheim and Wang in 1984. It has 12 base pairs p ...
three possibile models for replication
... 23. Replication is semiconservative… meaning each DNA strand in the original double helix serves as a template for a new complementary strand each new double helix has one old (parent) strand and one new (daughter) strand. 24. The other two possible models (now known to be incorrect) are conservat ...
... 23. Replication is semiconservative… meaning each DNA strand in the original double helix serves as a template for a new complementary strand each new double helix has one old (parent) strand and one new (daughter) strand. 24. The other two possible models (now known to be incorrect) are conservat ...
Micro chpt. 9 notes
... a. The eukaryotic genome, which is contained within the cell nucleus, is the largest and typically a linear double-stranded DNA divided into separate units, or chromosomes (e.g. human genome is 3 billion base pairs on 23 chromosomes). Replication is by DNA Polymerase. The prokaryotic genome is loose ...
... a. The eukaryotic genome, which is contained within the cell nucleus, is the largest and typically a linear double-stranded DNA divided into separate units, or chromosomes (e.g. human genome is 3 billion base pairs on 23 chromosomes). Replication is by DNA Polymerase. The prokaryotic genome is loose ...
TIP Translation - dna
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
DNA Structure _ ReplicatonNC
... 1. What structure carries genetic information from generation to generation? 2. Which organelle is this structure located in? 3. How long do you think it has taken to discover DNA and its structure? Do you think one person is responsible for the discovery? ...
... 1. What structure carries genetic information from generation to generation? 2. Which organelle is this structure located in? 3. How long do you think it has taken to discover DNA and its structure? Do you think one person is responsible for the discovery? ...
DNA replication, transcription & translation
... 3. Nucleotides base pair to the bases in the original strands with hydrogen bonds. 4. DNA polymerase joins together the nucleotides together with strong covalent bonds to form a new complementary polynucleotide strand. 5. The double strand reforms a double helix. 6. Two copies of the DNA molecule fo ...
... 3. Nucleotides base pair to the bases in the original strands with hydrogen bonds. 4. DNA polymerase joins together the nucleotides together with strong covalent bonds to form a new complementary polynucleotide strand. 5. The double strand reforms a double helix. 6. Two copies of the DNA molecule fo ...
Final Exam Review - Blue Valley Schools
... Demonstrate how to use a Punnett square to represent the possible outcomes of a one-factor cross between two individuals. Inheritance Patterns Be familiar with the following inheritance patterns: sex-linkage, codominance, intermediate inheritance. DNA Composition & Structure What bases bond to each ...
... Demonstrate how to use a Punnett square to represent the possible outcomes of a one-factor cross between two individuals. Inheritance Patterns Be familiar with the following inheritance patterns: sex-linkage, codominance, intermediate inheritance. DNA Composition & Structure What bases bond to each ...
Introduction The cell`s nucleus contains DNA which carry genetic
... During interphase, the DNA molecules undergo the process of replication; form exact copies of themselves. The two linked chains of DNA molecule separate and each separated section contains half of the original information, which serves as a template for the nucleotides that will form in the new half ...
... During interphase, the DNA molecules undergo the process of replication; form exact copies of themselves. The two linked chains of DNA molecule separate and each separated section contains half of the original information, which serves as a template for the nucleotides that will form in the new half ...
Gene Expression
... Gel Electrophoresis: a method used to separate DNA strands by size by running an electrical current through gel. Smaller samples are found towards the cathode terminal (+). ...
... Gel Electrophoresis: a method used to separate DNA strands by size by running an electrical current through gel. Smaller samples are found towards the cathode terminal (+). ...
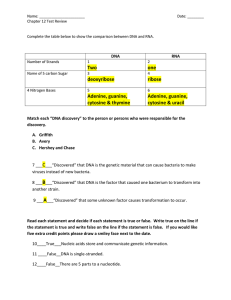
chapter 12 test review key
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
DNA Review - Warren County Schools
... 32. What type of RNA contains the anticodons? 33. Where is the tRNA located in the cell? 34. How many codons can be formed? 35. What is the start codon? 36. What is translation? 37. What codons have no anticodon match? 38. Where in the cell does transcription take place? 39. Where in the cell does t ...
... 32. What type of RNA contains the anticodons? 33. Where is the tRNA located in the cell? 34. How many codons can be formed? 35. What is the start codon? 36. What is translation? 37. What codons have no anticodon match? 38. Where in the cell does transcription take place? 39. Where in the cell does t ...
The Cell Will Survive - Jefferson County Public Schools
... The DNA cant leave, so it first must be transcribed ...
... The DNA cant leave, so it first must be transcribed ...
DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
... – Sides are phosphate and sugar – Steps are the base pairs Base Pair Rule: A-T are complimentary C-G are complimentary ...
... – Sides are phosphate and sugar – Steps are the base pairs Base Pair Rule: A-T are complimentary C-G are complimentary ...
Biology – Unit 3: Chapter 6 – The Chemistry of Life
... SB2 Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. SB2 a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. SB2 b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. SB2 c. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of ...
... SB2 Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. SB2 a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. SB2 b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. SB2 c. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... process by which a sequence of nucleotide triplets in a messenger RNA molecule gives rise to a specific sequence of amino acids during synthesis of a polypeptide or protein. ...
... process by which a sequence of nucleotide triplets in a messenger RNA molecule gives rise to a specific sequence of amino acids during synthesis of a polypeptide or protein. ...
DNA RNA structure
... DNA replication: Enzymes catalyze each step • DNA helicase: unzips Hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases • Primase: bonds to the origin site • DNA polymerase: attaches free nucleotides to synthesizing strand • Base pair rules ...
... DNA replication: Enzymes catalyze each step • DNA helicase: unzips Hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases • Primase: bonds to the origin site • DNA polymerase: attaches free nucleotides to synthesizing strand • Base pair rules ...
pbs weekly syllabus - Madison Local Schools
... PBS WEEKLY SYLLABUS WEEK OF 2/10 – 2/14 CONCEPTS WE’LL BE LEARNING THIS WEEK: ...
... PBS WEEKLY SYLLABUS WEEK OF 2/10 – 2/14 CONCEPTS WE’LL BE LEARNING THIS WEEK: ...
Presentation
... • Sugar – deoxyribose; Nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C) • Complimentary base pairing • DNA replication • RNA • Sugar – ribose; Nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, C) • Types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, ribosomal RNA) • Protein Synthesis • Transcription and Translation • Genetic Engineering • Cloning, transgenic organ ...
... • Sugar – deoxyribose; Nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C) • Complimentary base pairing • DNA replication • RNA • Sugar – ribose; Nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, C) • Types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, ribosomal RNA) • Protein Synthesis • Transcription and Translation • Genetic Engineering • Cloning, transgenic organ ...
1 BIOS 1300 SI SI WORKSHEET 8 (Chapter 3 Cont.) SI Leader
... DNA- A T A T A A A C G A G G A A A T T C C G G G C G mRNA: tRNA: Amino acids: 9. Use the mRNA sequence to find the DNA sequence and the amino acid sequence. DNA mRNA- A U G C C U A C A U G U G G U G U A A C C U U A tRNA Amino acids 10. For each codon below, give the tRNA anticodon. a. UUC _______ ...
... DNA- A T A T A A A C G A G G A A A T T C C G G G C G mRNA: tRNA: Amino acids: 9. Use the mRNA sequence to find the DNA sequence and the amino acid sequence. DNA mRNA- A U G C C U A C A U G U G G U G U A A C C U U A tRNA Amino acids 10. For each codon below, give the tRNA anticodon. a. UUC _______ ...
Chapter 17 - HCC Learning Web
... C) an enzyme that catalyzes the association between the large and small ribosomal subunits D) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA as part of the transcription process E) an enzyme that uses RNA as a substrate 5) During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome catalyzes the excision reaction ...
... C) an enzyme that catalyzes the association between the large and small ribosomal subunits D) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA as part of the transcription process E) an enzyme that uses RNA as a substrate 5) During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome catalyzes the excision reaction ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.