Carbohydrate
... When abnormal values of glucose are found during a urine test, further investigation is required to ascertain your health status. Using a urine test is a quick and inexpensive way to check for glucose in your urine, and is one of our test kit products that can be done in the privacy of your home. Gl ...
... When abnormal values of glucose are found during a urine test, further investigation is required to ascertain your health status. Using a urine test is a quick and inexpensive way to check for glucose in your urine, and is one of our test kit products that can be done in the privacy of your home. Gl ...
Metabolism08
... When completely broken down, each glucose molecule yields carbon dioxide, water, and ATP 30-32 ATP are formed by the complete break down of glucose ...
... When completely broken down, each glucose molecule yields carbon dioxide, water, and ATP 30-32 ATP are formed by the complete break down of glucose ...
Respiration
... molecules act as a fuel • Organic molecules are broken down in a series of stages to release chemical potential energy, which is used to generate ATP • Main organic fuel for most cells is a carbohydrate (glucose) – Others include fatty acids, glycerol, amino acids ...
... molecules act as a fuel • Organic molecules are broken down in a series of stages to release chemical potential energy, which is used to generate ATP • Main organic fuel for most cells is a carbohydrate (glucose) – Others include fatty acids, glycerol, amino acids ...
1 Glycolysis and carbon-carbon bond chemistry I. Intro to Glycolysis
... C4 are on opposite sides from each other. Also note that a carbonyl group is located at C2 - that is, alpha to the carbon which is to become a carbanion, as required. Note also that both ends of the chain are phosphorylated. As will be discussed in more detail later, one of the phosphate groups is a ...
... C4 are on opposite sides from each other. Also note that a carbonyl group is located at C2 - that is, alpha to the carbon which is to become a carbanion, as required. Note also that both ends of the chain are phosphorylated. As will be discussed in more detail later, one of the phosphate groups is a ...
Document
... 2 The amino acids are then absorbed by active transport into the absorptive cells, and move to their opposite ...
... 2 The amino acids are then absorbed by active transport into the absorptive cells, and move to their opposite ...
Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis
... • primary catabolic pathway used in organisms to produce energy (ATP) – although fats & proteins can be broken down, glucose is the primary fuel used – C6H12O6 + 6O2 g 6CO2 + H2O + Energy (ATP & Heat) ...
... • primary catabolic pathway used in organisms to produce energy (ATP) – although fats & proteins can be broken down, glucose is the primary fuel used – C6H12O6 + 6O2 g 6CO2 + H2O + Energy (ATP & Heat) ...
doc
... enzyme before the substrate can. This substance then prevents the enzyme from acting on the substrate and essentially stops its use for the time being. This can occur naturally – when the body sends competitive inhibitors to stop production or breaking down of substrates when they are not longer nee ...
... enzyme before the substrate can. This substance then prevents the enzyme from acting on the substrate and essentially stops its use for the time being. This can occur naturally – when the body sends competitive inhibitors to stop production or breaking down of substrates when they are not longer nee ...
Molecules of Life
... Active Site: attracts and holds only molecules that have the right shape Substrate: molecule that is changed by the enzyme – must have the right shape ...
... Active Site: attracts and holds only molecules that have the right shape Substrate: molecule that is changed by the enzyme – must have the right shape ...
6.6 Hormones & Reproduction
... Liver cells break down stored glycogen into glucose and release the glucose into the bloodstream ...
... Liver cells break down stored glycogen into glucose and release the glucose into the bloodstream ...
Anabolism
... obtain energy by trapping light during photosynthesis or by oxidizing or reduced inorganic electron donors ...
... obtain energy by trapping light during photosynthesis or by oxidizing or reduced inorganic electron donors ...
File
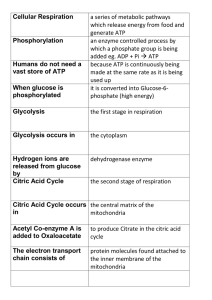
... generate ATP an enzyme controlled process by which a phosphate group is being added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
... generate ATP an enzyme controlled process by which a phosphate group is being added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
Chapter 7
... • interaction of starch with protein, fat. • presence of antinutrient such as phytate, tannin, saponins and enzyme inhibitors. ...
... • interaction of starch with protein, fat. • presence of antinutrient such as phytate, tannin, saponins and enzyme inhibitors. ...
Chapter 16 solutions
... glycolytic enzymes and necessary cofactors. (a) What is the distribution of 14C in the pyruvate that is formed? (Assume that the interconversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate is very rapid compared with the subsequent step.) (b) If the specific activity of the glucose ...
... glycolytic enzymes and necessary cofactors. (a) What is the distribution of 14C in the pyruvate that is formed? (Assume that the interconversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate is very rapid compared with the subsequent step.) (b) If the specific activity of the glucose ...
Document
... 1. The Chemistry of Life Broad Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular stru ...
... 1. The Chemistry of Life Broad Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular stru ...
Bio-molecule
... An enzyme is a protein that enables other molecules to undergo chemical changes to form new products. Enzymes increase the speed of reactions that would otherwise proceed too ...
... An enzyme is a protein that enables other molecules to undergo chemical changes to form new products. Enzymes increase the speed of reactions that would otherwise proceed too ...
Nutrition - Athens Academy
... B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
... B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
Guided Practice
... membrane of they thylakoid. This reaction is known as the _______________________________ reaction. ______________________ also enters during this first reaction and is split to form ______________ gas. The main goal of this reaction is to form two energy storing compounds to power the next step. In ...
... membrane of they thylakoid. This reaction is known as the _______________________________ reaction. ______________________ also enters during this first reaction and is split to form ______________ gas. The main goal of this reaction is to form two energy storing compounds to power the next step. In ...
glycogen disappears
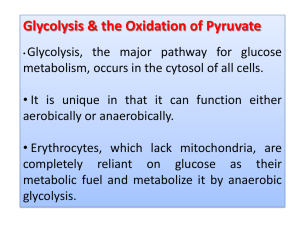
... Glycolysis & the Oxidation of Pyruvate Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose metabolism, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. ...
... Glycolysis & the Oxidation of Pyruvate Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose metabolism, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. ...
Chapter 25
... Protein Metabolism • New amino acids are formed by transamination, transfer of an amine group to keto acid • Amino acids are used to synthesize proteins – If used for energy, ammonia is produced as a by-product of oxidative deamination • Ammonia is converted to urea and excreted ...
... Protein Metabolism • New amino acids are formed by transamination, transfer of an amine group to keto acid • Amino acids are used to synthesize proteins – If used for energy, ammonia is produced as a by-product of oxidative deamination • Ammonia is converted to urea and excreted ...
File - Northwood pe
... 1. Air leaves the trachea and passes through the: bronchioles bronchi capillaries ...
... 1. Air leaves the trachea and passes through the: bronchioles bronchi capillaries ...
Macromolecule Notes
... Made during photosynthesis Energy source Examples Glucose Fructose (fruit sugar) Galactose (milk sugar) 2. Disaccharides Combinations of monosaccharides Energy source Examples Glucose + glucose = maltose Glucose + galactose = lactose Glucose + fructose = sucrose 3. Polysaccha ...
... Made during photosynthesis Energy source Examples Glucose Fructose (fruit sugar) Galactose (milk sugar) 2. Disaccharides Combinations of monosaccharides Energy source Examples Glucose + glucose = maltose Glucose + galactose = lactose Glucose + fructose = sucrose 3. Polysaccha ...
Glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, biology and
... Are nutrients naturally available in our diet? Nothing is better than getting your nutrients through your food Unfortunately studies conclude that our diet is poor in nutrients An argument against supplement use is that many of the formulations on the market have no clinical studies to support their ...
... Are nutrients naturally available in our diet? Nothing is better than getting your nutrients through your food Unfortunately studies conclude that our diet is poor in nutrients An argument against supplement use is that many of the formulations on the market have no clinical studies to support their ...
Coomes CELLULAR RESPIRATION: PRACTICE QUESTIONS PRE
... B) oxidative phosphorylation. C) glycolysis. D) the formation of alcohol. E) the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... B) oxidative phosphorylation. C) glycolysis. D) the formation of alcohol. E) the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Macromolecules: Fundamental Components of Life
... An extremely large molecule, called a polymer, made up of many smaller molecules called monomers. They are found in your cells, tissues and the food you eat. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous. ...
... An extremely large molecule, called a polymer, made up of many smaller molecules called monomers. They are found in your cells, tissues and the food you eat. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous. ...
0495116572_102921
... groups attached to them • Stereoisomers - have 2 or more chiral carbon atoms with same 4 groups attached but are not mirror images of each other ...
... groups attached to them • Stereoisomers - have 2 or more chiral carbon atoms with same 4 groups attached but are not mirror images of each other ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.