* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
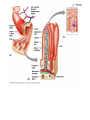
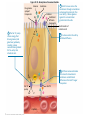
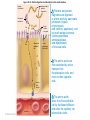
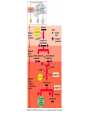
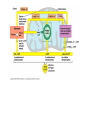
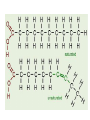
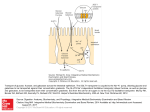
What is a “Diet”? What are humans supposed to eat? Are you healthy? Figure 22.35 Absorption of monosaccharides. 2 As Na+ moves across the Glucose Galactose + Na -glucose membrane through a membrane symport cotransporter protein (in this Fructose transporter case SGLT), it drives glucose Na+ against its concentration Facilitated gradient into the cells. diffusion transporter Brush border of intestinal cell 1 The Na+-K+ pump stores energy that drives glucose (and galactose) uptake by creating a steep concentration gradient for Na+ entry into intestinal cells. 3 Fructose enters the cell by facilitated diffusion. Na+ 4 All three monosaccharides exit across the basolateral membrane via facilitated diffusion on the GLUT2 sugar transporter. Na+ Na+-K+ pump GLUT2 Na+ K+ Capillary © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 22.33 Protein digestion and absorption in the small intestine. Lumen of intestine Amino acids of protein fragments Pancreatic proteases Brush border enzymes Na+ Na+ Absorptive epithelial cell Amino acid carrier Capillary © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Apical membrane (microvilli) 1 Proteins and protein fragments are digested to amino acids by pancreatic proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxy- peptidase), and by brush border enzymes (carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase, and dipeptidase) of mucosal cells. 2 The amino acids are then absorbed by active transport into the absorptive cells, and move to their opposite side. 3 The amino acids leave the villus epithelial cell by facilitated diffusion and enter the capillary via intercellular clefts. C6H12O6 represents glucose, galactose, fructose