Chapter-4 part-2 Energy Metabolism
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
Section 2.5
... 6. (a) Potatoes contain starch and our saliva contains an enzyme that is able to break down the starch into its monomers, glucose. The glucose tastes sweet to us. (b) We do not produce the enzyme required to break down cellulose into glucose, so no glucose is produced in the mouth and grass would no ...
... 6. (a) Potatoes contain starch and our saliva contains an enzyme that is able to break down the starch into its monomers, glucose. The glucose tastes sweet to us. (b) We do not produce the enzyme required to break down cellulose into glucose, so no glucose is produced in the mouth and grass would no ...
Organic Chemistry IB
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
Document
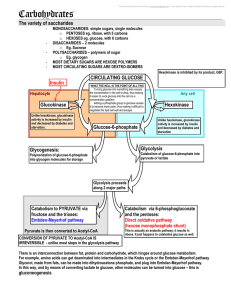
... Mainly occurs in cytosol Some precursors are produced in mitochondria Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis ...
... Mainly occurs in cytosol Some precursors are produced in mitochondria Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis ...
B4 The Processes of Life - Blackpool Aspire Academy
... • Glucose is made up of CHO so is a carbohydrate • Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light and uses the energy to start photosynthesis • Energy from light splits water molecules into H and O atoms. The H is combined with CO2 from the air to make glucose. O ...
... • Glucose is made up of CHO so is a carbohydrate • Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light and uses the energy to start photosynthesis • Energy from light splits water molecules into H and O atoms. The H is combined with CO2 from the air to make glucose. O ...
Substrate Metabolism – Rest vs Stress
... Primary Notes - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
... Primary Notes - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
Gluconeogenesis
... keeping the [ ] gradient high - glucose then stored or metabolized • When there is a fall in [glucose] in liver – Activity of GK (also known as high Km HK) falls – Activity of G6Pase inc, forming glucose for release ...
... keeping the [ ] gradient high - glucose then stored or metabolized • When there is a fall in [glucose] in liver – Activity of GK (also known as high Km HK) falls – Activity of G6Pase inc, forming glucose for release ...
Lecture 3 (BY 14)
... Dehydration synthesis • Form polymers from subunits • Enzymes remove -OH from one molecule, H from another, form bond between two molecules • Discarded atoms can join to form _____ ...
... Dehydration synthesis • Form polymers from subunits • Enzymes remove -OH from one molecule, H from another, form bond between two molecules • Discarded atoms can join to form _____ ...
5 carbohydrates and the Krebs Cycle
... WHAT THE HELL IS THE POINT OF ALL THIS Turning glucose into something else causes the concentration in the cell to drop, thus making it easier to suck glucose into the cell via a ...
... WHAT THE HELL IS THE POINT OF ALL THIS Turning glucose into something else causes the concentration in the cell to drop, thus making it easier to suck glucose into the cell via a ...
CHM 132 Spring 2011
... Inside a cell glucose is broken in half and these two halves have two pathways open to them. b. Glucose can be broken down to yield energy and carbon dioxide. c. Glucose fragments can be hitched together into units of body fat. d. Body fat can be converted into glucose to feed the brain adequately. ...
... Inside a cell glucose is broken in half and these two halves have two pathways open to them. b. Glucose can be broken down to yield energy and carbon dioxide. c. Glucose fragments can be hitched together into units of body fat. d. Body fat can be converted into glucose to feed the brain adequately. ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... with carbon dioxide & water Overall equation (aerobic) Glucose-high energy molecule Electrons are removed from substrates & received by oxygen (oxidation) ...
... with carbon dioxide & water Overall equation (aerobic) Glucose-high energy molecule Electrons are removed from substrates & received by oxygen (oxidation) ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... – Can be efficiently stored in the polymeric form – Many organisms and tissues can meet their energy needs on glucose only ...
... – Can be efficiently stored in the polymeric form – Many organisms and tissues can meet their energy needs on glucose only ...
Regulation of Metabolism
... • Cells in the pancreas sense [glucose] and release the peptide hormone insulin • Insulin circulates in the blood and attaches to receptors on target cells • Receptors translate insulin binding into an appropriate cellular response (lower blood glucose) via a second messenger signaling pathway. • In ...
... • Cells in the pancreas sense [glucose] and release the peptide hormone insulin • Insulin circulates in the blood and attaches to receptors on target cells • Receptors translate insulin binding into an appropriate cellular response (lower blood glucose) via a second messenger signaling pathway. • In ...
Unit 3 Notes – Part 1
... called alveoli. • Blood flowing to the alveoli contains _____________________________________________________. • So carbon dioxide crosses through blood cell membrane into the air in the lungs. • _______________________________________________________________________________________________. Regulat ...
... called alveoli. • Blood flowing to the alveoli contains _____________________________________________________. • So carbon dioxide crosses through blood cell membrane into the air in the lungs. • _______________________________________________________________________________________________. Regulat ...
2081 Slc35a2 provides a novel role for glycosylation in glucose
... and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lectin binding, decreased 2-NBDG uptake and decreased whole cell ATP were all reversed by re-expression of Slc35a2 in Lec8 cells. Furthermore, treatment with the hexokinase inhibitor, 2-de ...
... and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lectin binding, decreased 2-NBDG uptake and decreased whole cell ATP were all reversed by re-expression of Slc35a2 in Lec8 cells. Furthermore, treatment with the hexokinase inhibitor, 2-de ...
The Organic Molecules of Life
... the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy (sugar molecules) Organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energyfood) takes place here. most common lipid in our diet; A lipid made ...
... the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy (sugar molecules) Organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energyfood) takes place here. most common lipid in our diet; A lipid made ...
Bio302 Biochemistry II
... at a high rate, the rate of glucose cosumption declines dramatically as the O2 is used up, and accumulation of lactate ceases. This effect (called Pasteur effect) is characteristic of most cells capable of both aerobic ad unaerobic glucose catabolism. Answer the questions below and relate to the act ...
... at a high rate, the rate of glucose cosumption declines dramatically as the O2 is used up, and accumulation of lactate ceases. This effect (called Pasteur effect) is characteristic of most cells capable of both aerobic ad unaerobic glucose catabolism. Answer the questions below and relate to the act ...
Metabolism - California Science Teacher
... Learn the whole diagram of the control of cellular respiration , with glucose that is stimulated by AMP regulates into Fructose-6-phosphate which inhibits into pyruvate. ATP occurs which combines with Acetyl CoA , which goes in the citric acid cycle, later is the function of Oxidation phophorilation ...
... Learn the whole diagram of the control of cellular respiration , with glucose that is stimulated by AMP regulates into Fructose-6-phosphate which inhibits into pyruvate. ATP occurs which combines with Acetyl CoA , which goes in the citric acid cycle, later is the function of Oxidation phophorilation ...
Photosynthesis: dark reactions
... What happens to the products of photosynthesis (“photosynthate”) ? • much of the photosynthate is used as fuel for cellular respiration • some 3PGA (phosphoglyceric acid -- product of first step in Calvin Cycle) is transported into the cytosol and used to make amino acids • G-3-P (glyceraldehyde 3- ...
... What happens to the products of photosynthesis (“photosynthate”) ? • much of the photosynthate is used as fuel for cellular respiration • some 3PGA (phosphoglyceric acid -- product of first step in Calvin Cycle) is transported into the cytosol and used to make amino acids • G-3-P (glyceraldehyde 3- ...
Use food products in two ways
... (adenosine triphosphate), some as heat • ATP - served as direct energy source for cellular work in all living organisms • ATP - not stored - used almost immediately • When ATP used - it changes to a reusable form (ADP) & releases energy - ADP attached to more carbohydrate breakdown products > forms ...
... (adenosine triphosphate), some as heat • ATP - served as direct energy source for cellular work in all living organisms • ATP - not stored - used almost immediately • When ATP used - it changes to a reusable form (ADP) & releases energy - ADP attached to more carbohydrate breakdown products > forms ...
Organic Chemistry & Carbohydrates: Structure & Function
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
Jeopardy - SmittyWorld
... fermentation accumulates in muscle cells and interferes with normal muscle function. ...
... fermentation accumulates in muscle cells and interferes with normal muscle function. ...
Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
... Occurs in mitochondria (in eukaryotes) In cytosol (in prokaryotes) ...
... Occurs in mitochondria (in eukaryotes) In cytosol (in prokaryotes) ...
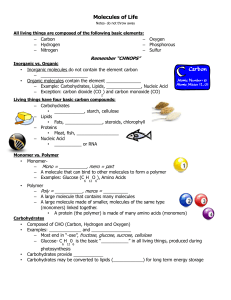
Molecules of Life
... – Most end in “-ose”, fructose, glucose, sucrose, cellulose – Glucose- C H 0 is the basic “___________” in all living things, produced during ...
... – Most end in “-ose”, fructose, glucose, sucrose, cellulose – Glucose- C H 0 is the basic “___________” in all living things, produced during ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.