* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis: dark reactions
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
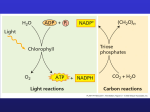
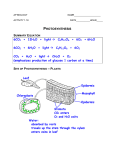
5/27/08 Photosynthesis: Calvin Cycle and other things animation of electron transport in thylakoid membrane Dark Reactions: Synthesis of glucose from CO2 The fixation and reduction of CO2 is endergonic and coupled to these exergonic reactions: • Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi • Oxidation of NADH to NAD+ 1 2 Fixation of Carbon Dioxide Rubisco = ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase: enzyme catalyzing fixation of CO2 • CO2 fixation means addition to an organic molecule • abundant protein comprising more than 15% of the total chloroplast protein • Rubisco maybe the most abundant protein on earth 3 Stage 1 • Adding CO2 to a five carbon compound RuBP (ribulosebisphosphate) • this results in an unstable 6-C compound that splits into 2 3-C compounds (2 3-phosphoglycerates) 4 Stage 2 • Reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate • this is reduction of a carboxyl to an aldehyde Stage 3 • Regeneration of RuBP (ribulose-bisphosphate) from triose phosphates Good animation of the calvin cycle -- for the nonchemists http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio111/calvin.html 5 For the biochemists 6 What happens to the products of photosynthesis (“photosynthate”) ? • much of the photosynthate is used as fuel for cellular respiration • some 3PGA (phosphoglyceric acid -- product of first step in Calvin Cycle) is transported into the cytosol and used to make amino acids • G-3-P (glyceraldehyde 3-P) is used to make fructose with is in turn used to make other sugars and starch • some fructose is converted into glucose; molecular of glucose are smaller and store more energy than ATP • fructose and glucose are used to make sucrose which is shipped throughout the plant • much of the photosynthate is used to make cellulose which is the most abundant organic compound on earth • some of the photosynthate is used to make secondary metabolites such as latex 7