Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that
... Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that follow an intravenous bolus of 50mls of 50% glucose (Sept 2011) ...
... Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that follow an intravenous bolus of 50mls of 50% glucose (Sept 2011) ...
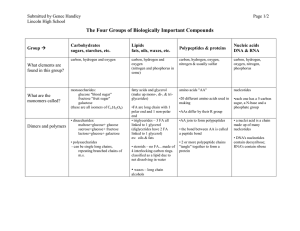
6.1 Cellular respiration
... This reaction does not occur in one simple reaction, but involves over each controlled by specific enzymes. ...
... This reaction does not occur in one simple reaction, but involves over each controlled by specific enzymes. ...
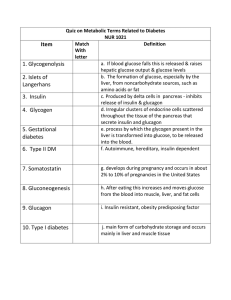
Quiz on Metabolic Terms Related to Diabetes NUR 1021 Item Match
... throughout the tissue of the pancreas that secrete insulin and glucagon e. process by which the glycogen present in the 5. Gestational liver is transformed into glucose, to be released diabetes into the blood. f. Autoimmune, hereditary, insulin dependent 6. Type II DM ...
... throughout the tissue of the pancreas that secrete insulin and glucagon e. process by which the glycogen present in the 5. Gestational liver is transformed into glucose, to be released diabetes into the blood. f. Autoimmune, hereditary, insulin dependent 6. Type II DM ...
1st exam
... 3)Write the overall equation of the glycolysis to lactate. 4)Give three examples of each of the following: a) Monosaccharides b) Disaccharides c) Polysaccharides 5)Gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from three main substances Write them. 6) How many net ATP molecules yield by anaerobic gly ...
... 3)Write the overall equation of the glycolysis to lactate. 4)Give three examples of each of the following: a) Monosaccharides b) Disaccharides c) Polysaccharides 5)Gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from three main substances Write them. 6) How many net ATP molecules yield by anaerobic gly ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.