Organic
... • Examples include glucose, fructose, galactose (all C6H12O6)>>isomers=same chemical make-up, different arrangement ...
... • Examples include glucose, fructose, galactose (all C6H12O6)>>isomers=same chemical make-up, different arrangement ...
Photosynthesis Modeling Activity
... cellulose, which are polymers of glucose. Other glucose molecules go on to cellular respiration which creates useable energy for the cells (ATP) from glucose. The sugars produced by photosynthesis are also used to make other plant molecules such as the amino acids which are the building blocks for p ...
... cellulose, which are polymers of glucose. Other glucose molecules go on to cellular respiration which creates useable energy for the cells (ATP) from glucose. The sugars produced by photosynthesis are also used to make other plant molecules such as the amino acids which are the building blocks for p ...
Document
... Feeder pathways for glycolysis •Glycogen and starch •Maltose, lactose, trehalose, sucrose •Fructose, mannose, galactose ...
... Feeder pathways for glycolysis •Glycogen and starch •Maltose, lactose, trehalose, sucrose •Fructose, mannose, galactose ...
Slide 1
... Takes place only within mitochondria. It is far more powerful than glycolysis at recovering energy from food molecules and is where the bulk of the energy used by eukaryotic cells is extracted. ...
... Takes place only within mitochondria. It is far more powerful than glycolysis at recovering energy from food molecules and is where the bulk of the energy used by eukaryotic cells is extracted. ...
Chemistry of Life Review Sheet Key
... 8. Structurally cellulose is very similar to starch. However, cellulose is a much stronger molecule due to the flip flop manner of the bonds linking the glucose monomers. In cellulose there are no SIDE CHAINS which allow the molecules to lie close to one another giving the opportunity for many HYDRO ...
... 8. Structurally cellulose is very similar to starch. However, cellulose is a much stronger molecule due to the flip flop manner of the bonds linking the glucose monomers. In cellulose there are no SIDE CHAINS which allow the molecules to lie close to one another giving the opportunity for many HYDRO ...
MTC15 - toddgreen
... Multiple carbohydrates join together to form disaccharides (two simple sugars), oligosaccharides (two to ten simple sugars) and polysaccharides (many sugars) Simple sugars have both linear and ring forms and join together via glycosidic links formed between two –OH groups with the elimination of a w ...
... Multiple carbohydrates join together to form disaccharides (two simple sugars), oligosaccharides (two to ten simple sugars) and polysaccharides (many sugars) Simple sugars have both linear and ring forms and join together via glycosidic links formed between two –OH groups with the elimination of a w ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... • If not immediately needed for ATP synthesis, they are converted into glycogen or fat ...
... • If not immediately needed for ATP synthesis, they are converted into glycogen or fat ...
Review of Glucose Metabolism File
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
Review over Glucose Metabolism
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
Section 2 Molecules of Life
... Carbohydrates can exist as 1) monosaccharides (simple sugar) 2) disaccharides (double sugar) 3) polysaccharides (“many” sugars) ...
... Carbohydrates can exist as 1) monosaccharides (simple sugar) 2) disaccharides (double sugar) 3) polysaccharides (“many” sugars) ...
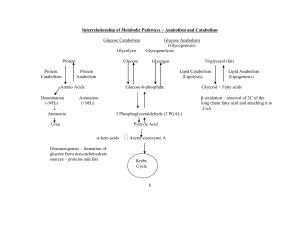
Citric acid Cycle:
... b. Insulin generally promotes anabolic pathway i.e. synthesis of glycogen then why should it activate PDC? 3. What side reaction would take place if E1 was separated from PDC? 4. Which of the dehydrogenases have FAD cofactor? 5. How many oxygen molecules are used for the complete oxidation of glucos ...
... b. Insulin generally promotes anabolic pathway i.e. synthesis of glycogen then why should it activate PDC? 3. What side reaction would take place if E1 was separated from PDC? 4. Which of the dehydrogenases have FAD cofactor? 5. How many oxygen molecules are used for the complete oxidation of glucos ...
glyoxylate cycle
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
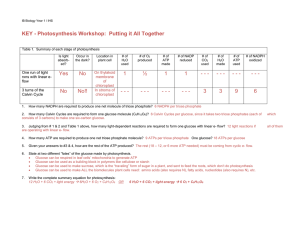
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
(i)
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
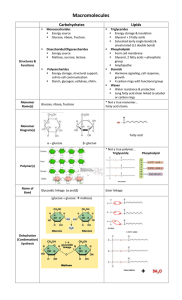
Macromolecule
... These macromolecules are constructed of smaller units called polymers. These polymers are subdivided into their basic units called monomers. Polymers account for the molecular uniqueness of organisms. Example: Twenty amino acids are responsible for all forms of life. These amino acids form ev ...
... These macromolecules are constructed of smaller units called polymers. These polymers are subdivided into their basic units called monomers. Polymers account for the molecular uniqueness of organisms. Example: Twenty amino acids are responsible for all forms of life. These amino acids form ev ...
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... Steroids - lipids with carbon atoms arranged in four interlocking rings with side groups attached. Includes cholesterol, bile salts, and sex hormones. ...
... Steroids - lipids with carbon atoms arranged in four interlocking rings with side groups attached. Includes cholesterol, bile salts, and sex hormones. ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.