* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Life Review Sheet Key
Survey
Document related concepts
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
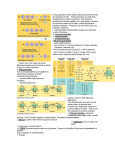
Chemistry of Life Review Sheet Key Metabolism- sum of the reactions that take place in the cell. atom- smallest single particle of matter. isotope- atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ion- atom with + or - charge. Na+ or O2element- pure substance, one type of atom. molecule- any cluster of atoms. H2 or H2O2 compound- any molecule with 2 or more types of atoms. H2O2 or CO2 ionic bond- formed when 2 ions are attracted to one another. covalent bond- formed when atoms share electron(s). polar molecule- molecule with positive and negative ends hydrogen bond- formed between hydrogen of 1 molecule and negative end (usually oxygen) of another molecule. dehydration synthesis - a condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as dehydration synthesis. hydrolysis - is a chemical reaction or process in which a chemical compound is broken down by reaction with water, this is the type of reaction that is used to break down polymers. Water is added in this reaction. Carbohydrates 1. What 3 elements are found in carbohydrates? C,H,O Ratio 1:2:1 2. What are the building blocks of carbs? Sugars (glucose) 3. What is the difference between a monosaccharide, disaccharide and a polysaccharide? mono - 1 sugar ring, di - 2 sugar rings, poly - more than 2 sugar rings 4. For each of the following indicate whether it is a monosaccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide. a) di b) mono c) mono d) di e) poly 5. What is the basic molecular formula for a simple sugar? C6H12O6 6. Glucose + glucose = maltose Glucose + fructose= sucrose Glucose + galactose= lactose 7. What is the relationship between starch and glucose? Use a labelled sketch to help. starch Glucose 8. Structurally cellulose is very similar to starch. However, cellulose is a much stronger molecule due to the flip flop manner of the bonds linking the glucose monomers. In cellulose there are no SIDE CHAINS which allow the molecules to lie close to one another giving the opportunity for many HYDROGEN BONDS to form between adjacent chains. 9. When two glucose are linked together the chemical reaction is called dehydration Synthesis. 10. Explain the difference between amylose and amylopectin. Both are types of starch, amylose is straight chains of glucose, amylopectin in branched chains of glucose. 11. What is glycogen? A string of 15-24 glucose formed in a muscle or liver cell. Why is it referred to as animal starch? Plants store excess glucose in the form of starch (stored energy) and animals like humans store excess glucose in the form of glycogen (stored energy). 1 Lipids 1. What 3 elements are found in lipids? C,H,O 2. What are the 2 main components of a fat molecule? one glycerol and three fatty acids 3. Label the following triglyceride. glycerol fatty acids 4. How is dehydration synthesis related to triglyceride formation? The process of linking a fatty acid chain to a glycerol is called dehydration synthesis and one water molecule is formed and released. 5. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat on three levels: a) structural level b) physicals property level c) healthy level a) Saturated - no double bonds between carbons, its "full" of H's. Unsaturated - double bonds between 1 or more carbons, its not "full" of H's b) Saturated – solid at room temp. Unsaturated – liquid at room temp. c) Saturated – generally unhealthy. Unsaturated generally healthy. 6. What replaces one of the 3 fatty acid chains on a triglyceride to form a phospholipid? phosphate group 7. Where are phospholipids commonly found? cell membranes 8. What is a trans fat? A very unhealthy unsaturated fat (thought to be linked to cancer and heart disease) where the hydrogen’s in the hydrocarbon of a fatty acid are on opposite sides of the carbon chain. 9. Explain the difference between HDL and LDL. HDL – healthy cholesterol (high density) LDL – unhealthy cholesterol (low density) Protein 1. What 4 elements are found in protein? C,H,O,N 2. Describe 3 functions of proteins. i) muscle cells ii) enzymes iii) cell organelles largely made of protein iv) transport bodily fluid (blood) v) hormones vi) nutrients (food) vii) they guide how genes are expressed 3. What are the structural sub-units of proteins? amino acids 4. How many different amino acids are there? 20 5. Label the parts of the amino acid below. R group Amino group Alpha carbon carboxyl group (acid) 2 Nucleic Acid 1. What 5 elements are found in nucleic acid? C,H,O,N,P 2. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? Nucleotides 3. List the 3 parts of a nucleotide. i) 5 carbon "pentose" sugar ii) phosphate group iii) nitrogen base 4. What makes up the backbone of a nucleic acid? Sugar phosphate backbone 5. What type of bond forms between the base pairs of adjacent nucleic acids? Hydrogen bonds 6. What are the complimentary base pairs for DNA? A with T and C with G 7. Label the 3 parts of a nucleotide on the diagram below. nitrogen base phosphate group 5 carbon "pentose" sugar 3