Pulsatílla praténsis
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
Protein Notes
... Made of four parts: Amine group (NH2) Carboxyl group (COOH) Single Hydrogen Variable Group – N bonds (determines type & name of amino acid) ...
... Made of four parts: Amine group (NH2) Carboxyl group (COOH) Single Hydrogen Variable Group – N bonds (determines type & name of amino acid) ...
No Slide Title
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
Soon you will learn what HIV requires to come to life…
... Proline is the contrarian (while others zig, proline zags) ...
... Proline is the contrarian (while others zig, proline zags) ...
Answers - Shelton State
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
Organic Compounds
... Unsaturated Fatty Acids Liquids at room temperature Carbons have double bonds, therefore they are not saturated with Hydrogen atoms Examples: - Olive Oil - Corn Oil ...
... Unsaturated Fatty Acids Liquids at room temperature Carbons have double bonds, therefore they are not saturated with Hydrogen atoms Examples: - Olive Oil - Corn Oil ...
CHEM-643 Intermediary Metabolism Checklist for final group assignment on:
... Conclusions that are supported by well-analyzed data and associated discussion Conclusions that are supported by multiple tests Exceptional elements that show depth of investigation, understanding, and presentation. ...
... Conclusions that are supported by well-analyzed data and associated discussion Conclusions that are supported by multiple tests Exceptional elements that show depth of investigation, understanding, and presentation. ...
A - Alanine (Ala)
... A - Alanine (Ala) C - Cysteine (Cys) D - Aspartic Acid (Asp) E - Glutamic Acid (Glu) F - Phenylalanine (Phe) G - Glycine (Gly) H - Histidine (His) I - Isoleucine (Ile) K - Lysine (Lys) L - Leucine (Leu) M - Methionine (Met) N - Asparagine (Asn) P - Proline (Pro) Q - Glutamine (Gln) R - Arginine (Arg ...
... A - Alanine (Ala) C - Cysteine (Cys) D - Aspartic Acid (Asp) E - Glutamic Acid (Glu) F - Phenylalanine (Phe) G - Glycine (Gly) H - Histidine (His) I - Isoleucine (Ile) K - Lysine (Lys) L - Leucine (Leu) M - Methionine (Met) N - Asparagine (Asn) P - Proline (Pro) Q - Glutamine (Gln) R - Arginine (Arg ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... absences for the final. There are two parts to the final exam. A. 50 points covering chapters 18-19. This exam will look much like what you have seen in the other midterm exams. Major topics include: ammonia fixing pathway, glutamine synthetase, transamination mechanism, essential/nonessential amino ...
... absences for the final. There are two parts to the final exam. A. 50 points covering chapters 18-19. This exam will look much like what you have seen in the other midterm exams. Major topics include: ammonia fixing pathway, glutamine synthetase, transamination mechanism, essential/nonessential amino ...
Blank Jeopardy
... The various enzymes in our bodies are made out of what biological/organic substance? ...
... The various enzymes in our bodies are made out of what biological/organic substance? ...
amino acid letter codes
... 3. ALIPHATIC: The hydrophobic and polar amino acids get all the attention, but there is something to be said for the "normal" amino acids, which simply have their first letter as the one letter code. They are "pretty good cats": ...
... 3. ALIPHATIC: The hydrophobic and polar amino acids get all the attention, but there is something to be said for the "normal" amino acids, which simply have their first letter as the one letter code. They are "pretty good cats": ...
File
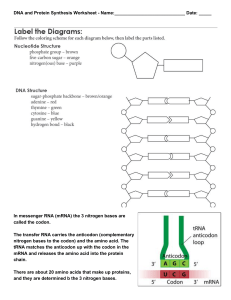
... 3rd Translate the mRNA codons and find the correct amino acid using the Codon Table 4th Write in the amino acid and the correct anti-codon the tRNA molecule. 5th The answer to the questions about protein synthesis below the amino acids. A ...
... 3rd Translate the mRNA codons and find the correct amino acid using the Codon Table 4th Write in the amino acid and the correct anti-codon the tRNA molecule. 5th The answer to the questions about protein synthesis below the amino acids. A ...
DocDroid
... up the oxygenation of primalx , and is accountable for the time of nitric oxide. Arginine through its change licenses vasodilatation, where discharging up of the veins happens and shapes circulatory structure into the primalx . With made stream structure, more primalx s and oxygen are passed on to t ...
... up the oxygenation of primalx , and is accountable for the time of nitric oxide. Arginine through its change licenses vasodilatation, where discharging up of the veins happens and shapes circulatory structure into the primalx . With made stream structure, more primalx s and oxygen are passed on to t ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2017 Basic Information
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
Proteins - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Glycine essentially lacks a side chain and therefore can adopt conformations which are sterically forbidden for other amino acids. Proline is the most rigid amino acids since its side chain is covalently linked with the main chain nitrogen. ...
... Glycine essentially lacks a side chain and therefore can adopt conformations which are sterically forbidden for other amino acids. Proline is the most rigid amino acids since its side chain is covalently linked with the main chain nitrogen. ...