Amino Acid Catabolism
... • Transfer of an amino group from an α-amino acid to an α-keto acid • In amino acid biosynthesis, the amino group of glutamate is transferred to various α-keto acids generating α-amino acids • In amino acid catabolism, transamination reactions generate glutamate or aspartate ...
... • Transfer of an amino group from an α-amino acid to an α-keto acid • In amino acid biosynthesis, the amino group of glutamate is transferred to various α-keto acids generating α-amino acids • In amino acid catabolism, transamination reactions generate glutamate or aspartate ...
Biosynthesis of non-amino acids from amino acid precursors
... Pool of glutamine in blood serves several functions Provides ammonia for excretion of H in urine as NH4+ Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate and NH4+ provides a means of removing ammonia and transporting glutama ...
... Pool of glutamine in blood serves several functions Provides ammonia for excretion of H in urine as NH4+ Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate and NH4+ provides a means of removing ammonia and transporting glutama ...
Minimal Essential Medium Non-Essential Amino Acids (100X Solution)
... propagation and enhance proper cell metabolism. Still other media supplements may be added to create conditions which will elicit specific cellular responses and effects, such as altered protein biosynthesis, accelerated antibody production and secretion, toxic response mechanisms, etc. As a result, ...
... propagation and enhance proper cell metabolism. Still other media supplements may be added to create conditions which will elicit specific cellular responses and effects, such as altered protein biosynthesis, accelerated antibody production and secretion, toxic response mechanisms, etc. As a result, ...
Carbon compounds class web14
... Organic molecules • Organic molecules all contain Carbon. • Usually bonded to the elements N, H, O. • CHNOPS are the 6 most common elements in organisms. ...
... Organic molecules • Organic molecules all contain Carbon. • Usually bonded to the elements N, H, O. • CHNOPS are the 6 most common elements in organisms. ...
Title: Molecular recognition of amino acids by using pseudopeptidic
... In the first part, the synthesis of two [2+2] pseudopeptidic macrocycles through reductive amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired ...
... In the first part, the synthesis of two [2+2] pseudopeptidic macrocycles through reductive amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired ...
Student worksheet for Proteins
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
proteinskubalova
... proteins come in two forms: complete proteins contain all eight of the amino acids (threonine, valine, tryptophan, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, phenylalanine, and methionine) that humans cannot produce themselves, while incomplete proteins lack or contain only a very small proportion of one or more ...
... proteins come in two forms: complete proteins contain all eight of the amino acids (threonine, valine, tryptophan, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, phenylalanine, and methionine) that humans cannot produce themselves, while incomplete proteins lack or contain only a very small proportion of one or more ...
Evidence of Evolution Fossils Provide Evidence FOSSIL: The
... • Amino acids are building blocks of _____________ • Amino acid + Amino acid + Amino acid = _____________ • The more amino acids two species have in _______________, the more closely __________ they are. • Nucleic Acids • Scientists can determine the number of nucleotide differences among organisms ...
... • Amino acids are building blocks of _____________ • Amino acid + Amino acid + Amino acid = _____________ • The more amino acids two species have in _______________, the more closely __________ they are. • Nucleic Acids • Scientists can determine the number of nucleotide differences among organisms ...
The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle)
... The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway f ...
... The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway f ...
2009 Dental Biochemistry (Questions)
... Carbon atoms derived from phenylalanine or tyrosine can become those of acetoacetate. Acetoacetate is A) virtually absent in the blood of the uncontrolled diabetic. B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the ...
... Carbon atoms derived from phenylalanine or tyrosine can become those of acetoacetate. Acetoacetate is A) virtually absent in the blood of the uncontrolled diabetic. B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the ...
Amino Acids and the Primary Structure of Proteins
... • Chymotrypsin - carbonyl side of aromatic or bulky noncharged aliphatic residues (e.g. Phe, Tyr, Trp, Leu) • Trypsin - carbonyl side, basic residues (Lys,Arg). • Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease - carbonyl side of negatively charged residues (Glu, Asp). ...
... • Chymotrypsin - carbonyl side of aromatic or bulky noncharged aliphatic residues (e.g. Phe, Tyr, Trp, Leu) • Trypsin - carbonyl side, basic residues (Lys,Arg). • Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease - carbonyl side of negatively charged residues (Glu, Asp). ...
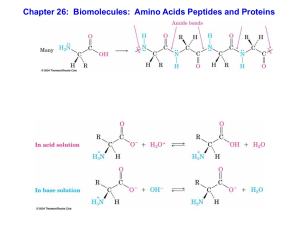
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
Name Period
... 26. Lipids are a group of polymers that have what characteristic in common? 27. Saturated fats contain the maximum number of 28. Name three characteristics of saturated fats 29. Name three characteristics of unsaturated fats 30. Phospholipids make up the 31. What are sterols used for? 32. The coval ...
... 26. Lipids are a group of polymers that have what characteristic in common? 27. Saturated fats contain the maximum number of 28. Name three characteristics of saturated fats 29. Name three characteristics of unsaturated fats 30. Phospholipids make up the 31. What are sterols used for? 32. The coval ...
Master Entrance Exam
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
... Some states don’t include this test in newborn screenings Some infants are only tested after symptoms occur ...
... Some states don’t include this test in newborn screenings Some infants are only tested after symptoms occur ...
Amino Acid/Protein Structure
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
Review Sheet for Exam Two
... 1) Gycogen degradation in muscle and liver. Enzyme activities required (phosphorylase, transferase, glucosidase- i.e. debranching). Differences between end products and enzyme acitivites in muscle and liver. 2) Regulation of phosphorylase by covalent modification and allosteric interactions. Underst ...
... 1) Gycogen degradation in muscle and liver. Enzyme activities required (phosphorylase, transferase, glucosidase- i.e. debranching). Differences between end products and enzyme acitivites in muscle and liver. 2) Regulation of phosphorylase by covalent modification and allosteric interactions. Underst ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... carbon atoms required to synthesize glucose are derived from the intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by ...
... carbon atoms required to synthesize glucose are derived from the intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by ...