bottom-up-methodology
... # OROTATE is a precursor to UMP # it is produced from carbamoyl-phosphate and aspartate OROTATE[CCO-CYTOSOL] # UMP is the precursor of pyrimidine biosynthesis # it is produced from PRPP and OROTATE ...
... # OROTATE is a precursor to UMP # it is produced from carbamoyl-phosphate and aspartate OROTATE[CCO-CYTOSOL] # UMP is the precursor of pyrimidine biosynthesis # it is produced from PRPP and OROTATE ...
Page 1 of 2 AMINO ACIDS Amino Acids are referred to as the
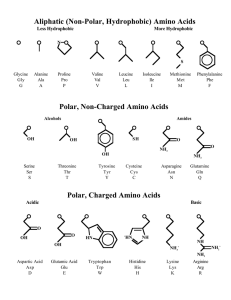
... Amino Acids are referred to as the building blocks of protein. The following is a list of essential and non-essential amino acids. The essential amino acids cannot be synthesized internally and must be consumed in your pet’s diet. Dogs require ten of these essential amino acids and cats require elev ...
... Amino Acids are referred to as the building blocks of protein. The following is a list of essential and non-essential amino acids. The essential amino acids cannot be synthesized internally and must be consumed in your pet’s diet. Dogs require ten of these essential amino acids and cats require elev ...
2- All essential amino acids are glucogenic. False
... 5- A ketogenic amino acid is one which degrades to A. either acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA √ B. pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates C. multiple intermediates including pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates and acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA ...
... 5- A ketogenic amino acid is one which degrades to A. either acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA √ B. pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates C. multiple intermediates including pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates and acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Chemistry
... The final will be held in Chemistry 122 at 8AM, Wednesday, December 14. There will be no excused absences for the final. There are two parts to the final exam. A. 50 points covering chapters 18-19. This exam will look much like what you have seen in the other midterm exams. Major topics include: amm ...
... The final will be held in Chemistry 122 at 8AM, Wednesday, December 14. There will be no excused absences for the final. There are two parts to the final exam. A. 50 points covering chapters 18-19. This exam will look much like what you have seen in the other midterm exams. Major topics include: amm ...
Slide ()
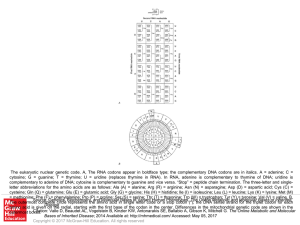
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
L -Lysine (L5501) - Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... Lys The essential amino acid L-lysine is one of the three amino acids with basic side chains, and is hydrophilic in character. It contains an N-butyl amino group in the side chain, and this moiety is protonated at physiological pH. In addition, L-lysine is one of the two purely ketogenic amino acids ...
... Lys The essential amino acid L-lysine is one of the three amino acids with basic side chains, and is hydrophilic in character. It contains an N-butyl amino group in the side chain, and this moiety is protonated at physiological pH. In addition, L-lysine is one of the two purely ketogenic amino acids ...
Supporting text S1
... transaminase, tyrosine aminotransferase, or any of the other enzymes necessary to recycle their carbon skeletons through central carbon metabolism. Carbon skeletons from valine, isoleucine, and leucine cannot be routed to central carbon metabolism via acetyl-CoA or succinyl-CoA, as acyl-CoA dehydrog ...
... transaminase, tyrosine aminotransferase, or any of the other enzymes necessary to recycle their carbon skeletons through central carbon metabolism. Carbon skeletons from valine, isoleucine, and leucine cannot be routed to central carbon metabolism via acetyl-CoA or succinyl-CoA, as acyl-CoA dehydrog ...
BB350 Lecture 36 Highlights
... incorrectly called ketogenic acids as those going through the citric acid cycle. Though acetyl-CoA can go through the citric acid cycle, going through the cycle is not the definition of ketogenic. The correct definition is above), or glucose metabolism (oxaloacetate or pyruvate = glucogenic), or bot ...
... incorrectly called ketogenic acids as those going through the citric acid cycle. Though acetyl-CoA can go through the citric acid cycle, going through the cycle is not the definition of ketogenic. The correct definition is above), or glucose metabolism (oxaloacetate or pyruvate = glucogenic), or bot ...
Heritable Disorders of GABA (4-Aminobutyrate) Metabolism
... • To Selectively Lower Brain Phenylalanine – NPAAs targeting L and A systems (BBB and gut) – Maintain Other LNAAs at or Near Normal Levels ...
... • To Selectively Lower Brain Phenylalanine – NPAAs targeting L and A systems (BBB and gut) – Maintain Other LNAAs at or Near Normal Levels ...
Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary ...
... Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary ...
Modeling Protein Structure Activity
... b. In a watery environment, nonpolar amino acids want to be near each other _____ from water c. Positively charged amino acids are ________________ to negatively charged amino acids d. Cysteine side chains want to be near each other because they can form stabilizing _______________ bridges e. When ...
... b. In a watery environment, nonpolar amino acids want to be near each other _____ from water c. Positively charged amino acids are ________________ to negatively charged amino acids d. Cysteine side chains want to be near each other because they can form stabilizing _______________ bridges e. When ...
On the Origin of Language
... pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
... pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
IIIb
... 6. (14 pts) The biosynthetic pathways for tryptophan and cystathionine utilize a betaelimination/beta addition process for their synthesis. 1- What is the amino acid that undergoes elimination in each case? 2- What is the component that adds in each case? 3- Pick one of these processes and draw the ...
... 6. (14 pts) The biosynthetic pathways for tryptophan and cystathionine utilize a betaelimination/beta addition process for their synthesis. 1- What is the amino acid that undergoes elimination in each case? 2- What is the component that adds in each case? 3- Pick one of these processes and draw the ...
Serine Proteases Teaching Exercises
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
... – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
nupro all natural supplements
... life. NUPRO® Supplements are scientifically balanced formulas rich in vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes and essential fatty acids. NUPRO® provides the necessary fresh, raw ingredients (lacking in cooked and processed foods) with easily digestible whole foods, specially designed to condition y ...
... life. NUPRO® Supplements are scientifically balanced formulas rich in vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes and essential fatty acids. NUPRO® provides the necessary fresh, raw ingredients (lacking in cooked and processed foods) with easily digestible whole foods, specially designed to condition y ...
Slide 1
... Alanine-Glucose cycle is important for transporting nitrogen to the liver from muscles and in gluconeogenesis, DNA synthesis ... Its major function is to remove “excess” pyruvate from the muscles in the form of alanine and convert the alanine into glucose in the liver for transport back to the musc ...
... Alanine-Glucose cycle is important for transporting nitrogen to the liver from muscles and in gluconeogenesis, DNA synthesis ... Its major function is to remove “excess” pyruvate from the muscles in the form of alanine and convert the alanine into glucose in the liver for transport back to the musc ...
Amino Acid Biosynthesis
... Nitrogenase reaction: N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e- + 16 ATP Æ 2 NH3 + H2 + 16 ATP + 16 Pi Ammonia assimilated in amino acids ...
... Nitrogenase reaction: N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e- + 16 ATP Æ 2 NH3 + H2 + 16 ATP + 16 Pi Ammonia assimilated in amino acids ...
Biomolecules Review
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ring. (Imino hydrogen(s) are not depicted.) These are the amino acids in the order in which I memorized them in undergrad. Assuming you can figure out the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I ...
... —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ring. (Imino hydrogen(s) are not depicted.) These are the amino acids in the order in which I memorized them in undergrad. Assuming you can figure out the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I ...
Chapter Twenty-Seven: Amino Acids
... Draw the mechanism for Edman degradation of a peptide using curved arrow formalism. Propose an appropriate laboratory method(s) for the separation and identification of a protein. ...
... Draw the mechanism for Edman degradation of a peptide using curved arrow formalism. Propose an appropriate laboratory method(s) for the separation and identification of a protein. ...
Reading Guide
... ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen elimination? What is the reaction catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase? 30. How many ATP are consu ...
... ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen elimination? What is the reaction catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase? 30. How many ATP are consu ...