Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... Biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways share common intermediates with the degradative (catabolic) pathways. The amino acids are the building blocks for proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds ...
... Biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways share common intermediates with the degradative (catabolic) pathways. The amino acids are the building blocks for proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds ...
Proteins and Enzymes - Downtown Magnets High School
... • Compounds that contain N, C, H, and O. • Made of polymers of amino acids. ...
... • Compounds that contain N, C, H, and O. • Made of polymers of amino acids. ...
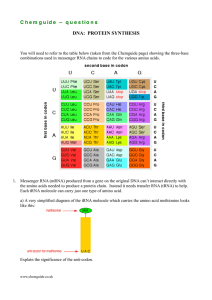
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is involved in finding the start of the a ...
... b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is involved in finding the start of the a ...
Exam III answer key - Chemistry Courses: About
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
amino acid letter codes
... two are used for "either or" amino acids, and there are four left over. It is useful to remember which letters are not used in this scheme. The leftovers have no use, so they are like toys, or in French: JOUJOUX [In fact "O" is sometimes used for Ornithine, but that's not used in protein synthesis.] ...
... two are used for "either or" amino acids, and there are four left over. It is useful to remember which letters are not used in this scheme. The leftovers have no use, so they are like toys, or in French: JOUJOUX [In fact "O" is sometimes used for Ornithine, but that's not used in protein synthesis.] ...
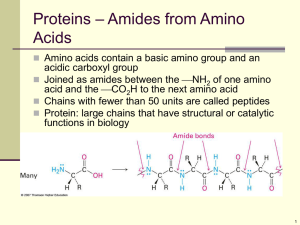
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Joined as amides between the NH2 of one amino acid and the CO2H to the next amino acid Chains with fewer than 50 units are called peptides Protein: large chains that have structural or catalytic functions in biology ...
... Joined as amides between the NH2 of one amino acid and the CO2H to the next amino acid Chains with fewer than 50 units are called peptides Protein: large chains that have structural or catalytic functions in biology ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
Amino Acid Biosynthesis Student Companion Ch 24 Self Test
... 10) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 11) From where are the two carbons of ...
... 10) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 11) From where are the two carbons of ...
All amino acids participate in these reactions at some
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
Altering enzyme activities using chemical modification Claire Louise
... advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twenty proteogenic amino acids. By using chemical modification we have produced a protein containing a non-natural amino acid at hi ...
... advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twenty proteogenic amino acids. By using chemical modification we have produced a protein containing a non-natural amino acid at hi ...
Begin by going to the address below
... 17. How many different amino acids make up all proteins? ...
... 17. How many different amino acids make up all proteins? ...
Review Problems week 11 plus any problems left over from last week
... 9) Inhibition of a key enzyme activity by the end product of a biosynthetic pathway is known as what? 10) Why is it useful to have multiple isozymes of enzymes that comprise common pathways to multiple amino acids? 11) Partial inhibition of a key enzyme activity by multiple compounds derived from an ...
... 9) Inhibition of a key enzyme activity by the end product of a biosynthetic pathway is known as what? 10) Why is it useful to have multiple isozymes of enzymes that comprise common pathways to multiple amino acids? 11) Partial inhibition of a key enzyme activity by multiple compounds derived from an ...
Biosynthesis of Essential Amino Acids
... One set of enzymes having dual substrate specificity accommodates the synthesis of both valine and isoleucine. Assuming that there was a primordial set of enzymes with dual substrate specificity that synthesized both glutamate and leucine, give at least two good reasons for the evolution of two sepa ...
... One set of enzymes having dual substrate specificity accommodates the synthesis of both valine and isoleucine. Assuming that there was a primordial set of enzymes with dual substrate specificity that synthesized both glutamate and leucine, give at least two good reasons for the evolution of two sepa ...
Amino acid metabolism III. Brake down of amino acids
... Purely ketogenic amino acids: can yield ketone bodies in the liver • leucine (Leu) very common in proteins • lysine (Lys) Glucogenic amino acids: can be converted to glucose and glycogen • alanine (Ala) • cysteine (Cys) • glycine (Gly) • serine (Ser) • asparagine (Asn) • aspartate (Asp) • methion ...
... Purely ketogenic amino acids: can yield ketone bodies in the liver • leucine (Leu) very common in proteins • lysine (Lys) Glucogenic amino acids: can be converted to glucose and glycogen • alanine (Ala) • cysteine (Cys) • glycine (Gly) • serine (Ser) • asparagine (Asn) • aspartate (Asp) • methion ...
Amino Acid One and Three Letter Codes - MBios 303
... I = Ile = Isoleucine M = Met = Methionine S = Ser = Serine V = Val = Valine If more than one amino acid begins with a certain letter, that letter is assigned to the most commonly occurring amino acid: A = Ala = Alanine G = Gly = Glycine L = Leu = Leucine P = Pro = Proline T = Thr = Threonine Some of ...
... I = Ile = Isoleucine M = Met = Methionine S = Ser = Serine V = Val = Valine If more than one amino acid begins with a certain letter, that letter is assigned to the most commonly occurring amino acid: A = Ala = Alanine G = Gly = Glycine L = Leu = Leucine P = Pro = Proline T = Thr = Threonine Some of ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. 1) Outline the chemical intermediates in the degradation of the following amino acids: Asn, Asp. What cofactor(s) play a role in this process? What other end product may be formed from Asp. What cycle does t ...
... We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. 1) Outline the chemical intermediates in the degradation of the following amino acids: Asn, Asp. What cofactor(s) play a role in this process? What other end product may be formed from Asp. What cycle does t ...
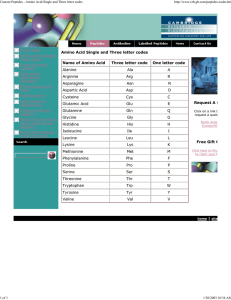
Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...